Abstract
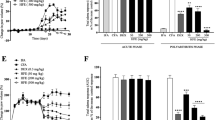
LY221068, 5-[[3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy phenyl]methylene]-3-(dimethylamino)-4-thiazolidinone, and the monomethylamino analog, LY269415, are anti-oxidants and potent inhibitors of iron dependent lipid peroxidation and 5-lipoxygenase enzyme. Since oxygen radical species, lipid peroxides and products of the arachidonic acid cascade have been implicated as important mediators in a variety of inflammatory diseases including arthritis, LY221068 and LY269415 were studied in the Freund's Complete Adjuvant Induced Arthritis (FCA) model in rats. The compounds were administered orally and inhibition of bone damage and paw swelling of both the injected and uninjected paws was assessed. At 50 mg/kg p.o., LY221068 inhibited soft tissue swelling in the uninjected paw by 72% while LY269415 at 25 mg/kg p.o. exhibited 74% inhibition. Bone damage was also significantly inhibited by both compounds. In a dose response study, the minimum effective dose for LY221068 was 10 mg/kg p.o. for LY269415 was 5 mg/kg p.o. In the established FCA model in rats, LY221068 at 50 mg/kg p.o. inhibited the uninjected paw swelling by 71% while LY269415 at 25 mg/kg p.o. inhibited 70%. These results suggest that LY221068 and LY269415 may be useful in the treatment of arthritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Halliwell and J. M. C. Gutteridge,The importance of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human diseases. Mol. Aspects Med.8, 89–193 (1985).
P. P. K. Ho, R. D. Turner and M. A. Esterman,Purification and characterization of fatty acid cyclooxygenase from human platelets. Preparative Biochem.10, 597–613 (1980).
D. E. Griswold, P. J. Marshall, E. F. Webb, R. Godfrey, J. Newton, Jr., M. J. Dimartino, H. M. Sarau, J. G. Gleason, G. Poste and N. Hanna,SK & F 86002: A structurally novel anti-inflammatory agent that inhibits lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase mediated metabolism of arachidonic acid. Biochem. Pharmacol.36, 3463–3470 (1987).
D. N. Benslay and R. Nickander,Radiographic studies of the effect of Benoxaprofen on bone damage in the adjuvant arthritic rat. European J. Rheum. Inflam.5, 175–185 (1982).
S. M. H. Sadrzadeh and J. W. Eaton,Hemoglobin-mediated oxidant damage to the central nervous system requires endogenous ascorbate. J. Clin. Invest.82, 1510–1515 (1988).
D. A. Rowley, J. M. C. Gutteridge, D. R. Blake, M. Farr and B. Halliwell,Lipid peroxidation in rheumatoid arthritis: Thiobarbituric acid reactive material and catalytic iron salts in synovial fluid from rheumatoid patients. Clin. Sci.66, 691–695 (1984).
J. Lunec and D. R. Blake,The determination of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid in the serum and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Free Radical Res. Commun.1, 32–39 (1985).
B. M. Babior,Oxygen dependent microbial killing by phagocytes. N. Eng. J. of Med.298, 721–725 (1978). J. C. Fantone and P. A. Ward,Role of oxygen derived free radicals and metabolites in leukocyte-dependent inflammatory reactions. Am. J. Pathol.107, 397 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panetta, J.A., Benslay, D.N., Shadle, J.K. et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of LY221068 and LY269415. Agents and Actions 34, 100–102 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01993249
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01993249