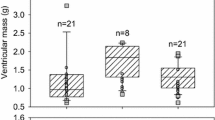
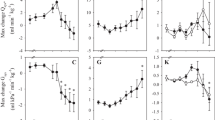
Abstract
This report provides the first direct measurements of the stroke volume and total cardiac output of crustacean hearts, as recorded from a semi-isolated in vitro preparation. The responses to mechanical perturbations, changes in preload and afterload, show that these hearts do not possess automatic compensatory Frank-Starling-like mechanisms. Heart rate, reflecting the burst rate of the cardiac ganglion, is minimally affected by stretch. On the other hand, these hearts are exquisitely responsive to the neurohormones of the pericardial organs. Serotonin, CCAP and proctolin all produce positive chronotropic and inotropic effects, but the responses to each are unique. Two FMRFamide peptides were positively chronotropic, but negatively inotropic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Airiess, C., and McMahon, B. R., Aminergic modulation of circulatory performance in the crabCancer magister, in: Comparative Physiology, vol. 11 Eds R. B. Hill, K. Kuwasawa and B. R. McMahon. Karger, Basel 1992.
Alexandrowicz, J. S., The innervation of the heart of the Crustacea. I. Decapoda. Q. Jl. microsc. Sci.75 (1932) 181–249.
Anderson, M., and Cooke, I. M., Neural activation of the heart of the lobsterHomarus americanus. J. exp. Biol.55 (1971) 449–468.
Anderson, M. E., and Smith, D. S., Electrophysiological and structural studies on the heart muscle of the lobsterHomarus americanus. Tiss. Cell3 (1971) 191–205.
Belman, B. W., Some aspects of the circulatory physiology of the spiny lobsterPanulirus interruptus. Mar. Biol.29 (1975) 295–305.
Belman, B. W., and Childress, J. J., Circulatory adaptations to the oxygen minimum layer in the bathypelagic mysidGnathophausia ingens. Biol. Bull.150 (1976) 15–37.
Benson, J. A., Synaptic and regenerative responses of cardiac muscle fibres in the crab,Portunus sanguinolentus. J. comp. Physiol.143 (1981) 349–356.
Blatchford, J. G., Hemodynamics ofCarcinus meanas (L.) Comp. Biochem. Physiol.39A (1971) 193–202.
Brown, H. F., Electrophysiological investigations of the heart ofSquilla mantis. II. The heart muscle. J. exp. Biol.41 (1964) 701–722.
Bullock, T. H., and Horridge, G. A., Structure and Function in the Nervous Systems of Invertebrates, vol. 2, pp. 988–997. W.H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco 1965.
Burnett, L. E., deFur, P. L., and Jorgensen, D. D., Application of the thermodilution technique for measuring cardiac output and assessing cardiac stroke volume in crabs. J. exp. Zool.218 (1981) 165–173.
Cooke, I. M., Studies on the crustacean cardiac ganglion. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.91C (1988) 205–218.
Cooke, I. M., and Sullivan, R. E., Hormones and neurosecretion, in: The Biology of Crustacea, vol. 2, pp. 205–290. Eds D. E. Bliss, H. L. Atwood and D. C. Sandeman, Academic Press, New York 1982.
Field, L. H., and Larimer, J. L., The cardioregulatory system of cray-fish: Neuroanatomy and physiology. J. exp. Biol.62 (1975) 519–530.
Florey, E., Studies on the nervous regulation of the heart beat in decapod crustacea. J. gen. Physiol.43 (1960) 1061–1081.
Florey, E., and Rathmayer, M., The effects of octopamine and other amines on the heart and on neuromuscular transmission in decapod crustaceans: Further evidence for a role as neurohormone. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.61C (1978) 229–237.
Guyton, A. C., Textbook of Medical Physiology, 8th ed. W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia 1991.
Hawlett, M., Lobster heart: Electrophysiology of single cells including effects of the regulator nerves. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.39A (1971) 643–648.
Kuramoto, T., and Ebara, A., Effects of perfusion pressure on the isolated heart of the lobster,Panulirus japonicus. J. exp. Biol.109 (1984a) 121–140.
Kuramoto, T., and Ebara, A., Neurohormonal modulation of the cardiac outflow through the cardioarterial valve in the lobster. J. exp. Biol.111 (1984b) 123–130.
Kuramoto, T., and Ebara, A., Effects of perfusion pressure on the bursting neurones in the intact or segmented cardiac ganglion of the lobster,Panulirus japonicus. J. Neurosci. Res.13 (1985) 569–580.
Kuramoto, T. and Ebara, A., Combined effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine and filling pressure on the isolated heart of the lobster,Panulirus japonicus. J. comp. Physiol. B158 (1988) 403–412.
Kuramoto, T., and Yamagishi, H., Physiological anatomy, burst formation and burst frequency in the cardiac ganglion of crustaceans. Physiol. Zool.63 (1990) 102–116.
Maynard, D. M., Activity in a crustacean ganglion. I. Cardioinhibition and acceleration inPanulirus argus. Biol. Bull.104 (1953) 156–170.
Maynard, D. M., Activity in a crustacean ganglion. II. Pattern and interaction in burst formation. Biol. Bull.109 (1955) 420–436.
Maynard, D. M., Circulation and heart function, in: Physiology of Crustacea, pp. 161–226. Ed. T. H. Waterman. Academic Press, New York 1960.
Maynard, D. M., Cardiac inhibition in decapod Crustacea, in: Nervous Inhibition, pp. 144–178. Ed. E. Florey. Pergamon Press, Oxford 1961.
McMahon, B. R., and Burnett, L. E., The crustacean open circulatory system: A reexamination. Physiol. Zool.63 (1990) 35–71.
McMahon, B. R., and Wilkens, J. L., Ventilation, perfusion and oxygen uptake, in: Biology of Crustacea, vol. 5, pp. 289–372. Eds D. E. Bilss and L. Mantel. Academic Press, New York 1983.
McMahon, B. R., and Reiber, C., Peptidergic modulation of hemolymph flow in the lobsterHomarus americanus, in: Comparative Physiology. vol. 11. Eds R. B. Hill, K. Kuwasawa and B. R. McMahon. Karger, Basel 1992.
Milnor, W. R., Hemodynamics, 2nd ed. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore 1989.
Pearson, J.,Cancer. Liverpool Marine Biological Committee Memoirs, No. 8. Williams and Nordgate, London 1908.
Peroulta, S. J., The molecular pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes, in: Serotonin Receptor Subtypes: Basic and Clinical Aspects, pp. 65–80. Ed. S. J. Peroutka. Wiley-Liss Inc. New York 1991.
Richardson, B. P., Engel, G., Donatsch, P., and Stakler, P. A., Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature316 (1985) 126–131.
Smith, P. J. S., Cardiac output in the Mollusca: Scope and regulation. Experientia43 (1987) 956–965.
Smith, P. J. S., Integrated cardiovascular control in the Mollusca. Physiol. Zool.63 (1990) 12–34.
Strangier, J., Hilbich, C., Beyreuther, K., and Keller, R., Unusual cardioactive peptide (CCAP) from pericardial organs of the shore crabCarcinus maenas. Proc. natl Acad. Sci. USA84 (1987) 575–579.
Sullivan, R. E., A proctolin-like peptide in crab pericardial organs. J. exp. Biol.210 (1979) 543–552.
Taylor, H. H., Pressure-flow characteristics of crab gills: Implications for regulation of hemolymph pressure. Physiol. Zool.63 (1990) 72–89.
Taylor, H. H., and Greenaway, P., The role of the gills and branchiostegites in gas exchange in a bimodally breathing crab,Holthuisana transversa: Evidence for a facultative change in the distribution of the respiratory circulation. J. exp. Biol.111 (1984) 103–121.
Trimmer, B. A., Kobierski, L. A., and Kravitz, E. A., Purification and characterization of FMRFamide-like immunoreactive substances from the lobster nervous system: Isolation and sequency analysis of two closely related peptides. J. comp. Neurol.266 (1987) 16–26.
Volk, E. L., The role of suspensory ligaments in modifying cardiac output in crustaceans. MSc Thesis, University of Calgary, 1988.
Wilkens, J. L., and Mercier, A. J., Peptidergic modulation of cardiac performance in isolated hearts from the shore crabCarcinus meanas. Submitted.
Wilkens, J. L., Mercier, A. J., and Evans, J., Cardiac and ventilatory responses to stress and to neurohormonal modulators by the shore crab,Carcinus maenas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.82C (1985) 337–343.
Wilkens, J. L., and Walker, R. L., Nervous control of crayfish cardiac hemodynamics, in: Comparative Physiology, vol. 11. Eds R. B. Hill, K. Kuwasawa and B. R. McMahon. Karger, Basel 1992.
Wilkens, J. L., and Young, R. E., Regulation of pulmonary blood flow and of blood pressure in a mangrove crab (Goniopsis cruentata). J. exp. Biol.163 (1992) 297–316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkens, J.L., McMahon, B.R. Intrinsic properties and extrinsic neurohormonal control of crab cardiac hemodynamics. Experientia 48, 827–834 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02118415
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02118415