Abstract
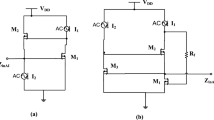
A delay and power model of a CMOS inverter driving aresistive-capacitive load is presented. The model is derivedfrom Sakurai‘s alpha-power law and exhibits good accuracy. Themodel can be used to design and analyze those CMOS invertersthat drive a large RC load when considering bothspeed and power. Expressions are provided for estimating thepropagation delay and transition time which exhibit less than27% discrepancy from SPICE for a wide variety of RCloads. Expressions are also provided for modeling the short-circuitpower dissipation of a CMOS inverter driving a resistive-capacitiveinterconnect line which are accurate to within 15% of SPICEfor most practical loads.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Bothra, B. Rogers, M. Kellam, and C. M. Osburn, “Analysis of the effects of scaling on interconnect delay in ULSI circuits,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices ED-40(3), pp. 591–597, March 1993.
H. B. Bakoglu and J. D. Meindl, “Optimal Interconnection Circuits for VLSI,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices ED-32(5), pp. 903–909, May 1985.
S. Dhar and M. A. Franklin, “Optimum Buffer Circuits for Driving Long Uniform Lines,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits SC-26(1), pp. 32–40, January 1991.
M. Nekili and Y. Savaria, “Optimal Methods of Driving Interconnections in VLSI Circuits,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 21–23, May 1992.
C. Y. Wu and M. Shiau, “Delay Models and Speed Improvement Techniques for RC Tree Interconnections Among Small-Geometry CMOS Inverters,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits SC-25(5), pp. 1247–1256, October 1990.
J. Cong and C.-K. Koh, “Simultaneous Driver and Wire Sizing for Performance and Power Optimization,” IEEE Transactions on VLSI Systems VLSI-2(4), pp. 408–425, December 1994.
R. J. Antinone and G. W. Brown, “The Modeling of Resistive Interconnects for Integrated Circuits,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits SC-18(2), pp. 200–203, April 1983.
L. Bisdounis, S. Nikolaidis, O. Koufopavlou, and C. E. Goutis, “Modeling the CMOS Short-Circuit Power Dissipation,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 4.469, 4.472, May 1996.
A. M. Hill and S.-M. Kang, “Statistical Estimation of Short-Circuit Power in VLSI Circuits,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 4.105–4.108, May 1996.
A. Hirata, H. Onodera, and K. Tamaru, “Estimation of Short-Circuit Power Dissipation and Its Influence on Propagation Delay for Static CMOS Gates,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 4.751–4.754, May 1996.
V. Adler and E. G. Friedman, “Delay and Power Expressions for a CMOS Inverter Driving a Resistive-Capacitive Load,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 4.101–4.104, May 1996.
A. I. Kayssi, K. A. Sakallah, and T. M. Burks, “Analytical Transient Response of CMOS Inverters,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications CAS I-39(1), pp. 42–45, January 1992.
N. Hedenstierna and K. O. Jeppson, “CMOS Circuit Speed and Buffer Optimization,” IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design CAD-6(2), pp. 270–281, March 1987.
T. Sakurai and A. R. Newton, “Alpha-Power Law MOSFET Model and its Applications to CMOS Inverter Delay and Other Formulas,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits SC-25(2), pp. 584–594, April 1990.
H. Shichman and D. A. Hodges, “Modeling and Simulation of Insulated-Gate Field-Effect Transistor Switching Circuits,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits SC-3(3), pp. 285–289, September 1968.
H. J. M. Veendrick, “Short-Circuit Dissipation of Static CMOS Circuitry and Its Impact on the Design of Buffer Circuits,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits SC-19(4), pp. 468–473, August 1984.
S. R. Vemuru and N. Scheinberg, “Short-Circuit Power Dissipation Estimation for CMOS Logic Gates,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications CAS I-41(11), pp. 762–766, November 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adler, V., Friedman, E.G. Delay and Power Expressions for a CMOS Inverter Driving a Resistive-Capacitive Load. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing 14, 29–39 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008282308028
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008282308028