Summary
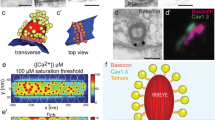
Isolated segments of the newborn mouse organ of Corti were explanted together with the spiral ganglion components. Within the innervation provided by the spiral neurons, we observed presynaptic vesiculated nerve endings that form reciprocal ribbon-afferent/efferent synapses with inner hair cells. These intracochlear presynaptic fibres are characteristically located between adjoining inner hair cells, on the modiolar side, low and close to the supporting cells. The presynaptic fibres display different modes of synaptic connectivity, forming repetitive reciprocal synapses on single inner hair cells or on adjoining hair cells, or connecting adjoining inner hair cells through simultaneous efferent synapses. Many presynaptic fibres exhibit a distinctive ultrastructure: defined clusters of synaptic vesicles, dense core vesicles, coated vesicles, and mitochondria. These organelles occur focally at the synaptic sites; beyond the efferent synaptic specializations, the endings appear quite nondescript and afferent-like.
We believe that the reciprocal synapses, although observed in cultures of the organ of Corti, represent real intracochlear synaptic arrangements providing a feedback mechanism between the primary sensory receptors and a special class of spiral ganglion cells that have yet to be recognized in the organin situ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allerand, C. D. (1971) Patterns of neuronal differentiation in developing cultures of neonatal mouse cerebellum: a living and silver impregnation study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 142, 167–204.
Andres, K. H. (1965) Der Feinbau des bulbus olfactorius der Ratte unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der synaptischen Verbindungen.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 65, 530–61.
Blank, N. K. &Seil, F. J. (1982) Mature Purkinje cells in cerebellar tissue cultures: An ultrastructural study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 208, 169–76.
Borg, E., Densert, O. &Flock, A. (1974) Synaptic vesicles in the cochlea.Acta Otolaryngologica 78, 321–32.
Calvet, M.-C., Calvet, J., Teilhac, J.-R. &Drian, M.-J. (1992) Networks formed by dorsal root ganglion neurites within spinal cord explants: a computer-aided analysis of HRP intracellularly labeled neurons.Brain Research 584, 1–10.
De Robertis, E. &Pellegrino De Iraldi, A. (1961) Plurivesicular secretory processes and nerve endings in the pineal gland of the rat.Journal of Biophysical & Biochemical Cytology 10, 361–72.
Dowling, J. E. (1968) Synaptic organization of the frog retina: an electron microscopic analysis comparing the retinas of frogs and primates.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (B) 170, 205–28.
Dowling, J. E. &Boycott, B. B. (1966) Organization of the primate retina: electron microscopy.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (B) 166, 80–111.
Dunn, R. F. (1976) Reciprocal synapses in the crista ampullaris: a possible mechanism for hair cell interaction.Transactions of the American Academy of Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology 82, 188–9.
Dunn, R. F. (1980) Reciprocal synapses between hair cells and first order afferent dendrites in the crista ampullaris of the bullfrog.Journal of Comparative Neurology 193, 255–64.
Ellis, L. C., Jr. &Rustioni, A. (1981) A correlative HRP, Golgi, and EM study of the intrinsic organization of the feline dorsal column nuclei.Journal of Comparative Neurology 197, 341–67.
Emmerling, M. R., Sobkowicz, H. M., Levenick, C. V., Scott, G. L., Slapnick, S. M. &Rose, J. E. (1990) Biochemical and morphological differentiation of acetyl-cholinesterase-positive efferent fibres in the mouse cochlea.Journal of Electron Microscopy Technique 15, 123–43.
Engström, H., Bergström, B. &Ades, H. W. (1972) Macula utriculi and macula sacculi in the squirrel monkey.Acta Otolaryngologica Supplement 301, 75–126.
Famiglietti, E. V., Jr. (1970) Dendro-dendritic synapses in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat.Brain Research 20, 181–91.
Fex, J. &Altschuler, R. A. (1986) Neurotransmitter related immunocytochemistry of the organ of Corti.Hearing Research 22, 249–63.
Gähwiler, B. H. (1984) Development of the hippocampusin vitro: Cell types, synapses and receptors.Neuroscience 11, 751–60.
Gianessi, F. (1989) On the presence of reciprocal synapses in the paratympanic organ of the chicken.Anatomy and Embryology 180, 175–8.
Gil-Loyzaga, P. &Parés-Herbute, N. (1989) HPLC detection of dopamine and noradrenaline in the cochlea of adult and developing rats.Developmental Brain Research 48, 157–60.
Gobel, S., Falls, W. M., Bennett, G. J., Abdelmoumene, M., Hayashi, H. &Humphrey, E. (1980) An EM analysis of the synaptic connections of horseradish peroxidasefilled stalked cells and islet cells in the substantia gelatinosa of adult cat spinal cord.Journal of Comparative Neurology 194, 781–807.
Guillery, R. W., Sobkowicz, H. M. &Scott, G. L. (1968) Light and electron microscopical observations of the ventral horn and ventral root in long term cultures of the spinal cord of the fetal mouse.Journal of Comparative Neurology 134, 433–76.
Guillery, R. W., Sobkowicz, H. M. &Scott, G. L. (1970) Relationships between glial and neuronal elements in the development of long term cultures of the spinal cord of the fetal mouse.Journal of Comparative Neurology 140, 1–34.
Gummer, A. W. (1991) Postsynaptic inhibition can explain the concentration of short inter-spike-intervals in avian auditory nerve fibers.Hearing Research 55, 231–43.
Hager, H. &Tafuri, W. L. (1959) Elektronenoptischer Nachweis sog. neurosekretorischer Elementargranula in marklosen Nervenfasern des Plexus myentericus (Auerbach) des Meerschweinchens.Die Naturwissenschaften 46, 332–3.
Hámori, J. &Silakov, L. (1980) Plasticity of relay neurons in dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the adult cat: Morphological evidence.Neuroscience 5, 2073–7.
Harding, B. N. (1971) Dendro-dendritic synapses, including reciprocal synapses, in the ventrolateral nucleus of the monkey thalamus.Brain Research 34, 181–5.
Herndon, R. M., Seil, F. J. &Seidman, C. (1981) Synaptogenesis in mouse cerebellum: A comparativein vivo and tissue culture study.Neuroscience 6, 2587–98.
Hild, W. (1954) Das morphologische, kinetische und endocrinologische Verhalten von hypothalamischem und neurohypophysärem Gewebe in vitro.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 40, 257–312.
Hinds, J. W. (1970) Reciprocal and serial dendrodendritic synapses in the glomerular layer of the rat olfactory bulb.Brain Research 17, 530–4.
Hirata, Y. (1964) Some observations on the fine structure of the synapses in the olfactory bulb of the mouse, with particular reference to the atypical synaptic configuration.Archives of Histology Okayama [Saibo Kaku Byorigaku Zasshi]24, 293–302.
Jackowski, A., Parnavelas, J. G. &Lieberman, A. R. (1978) The reciprocal synapse in the external plexiform layer of the mammalian olfactory bulb.Brain Research 159, 17–28.
Jones, N., Fex, J. &Altschuler, R. A. (1987) Tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity identifies possible catecholaminergic fibres in the organ of Corti.Hearing Research 30, 33–8.
Kim, S. U. (1974) Granule cell with somatodendritic synapse in organotypic cultures of mouse cerebellum.Experimental Neurology 45, 659–62.
King, A. S., King, D. Z., Hodges, R. D. &Henry, J. (1975) Synaptic morphology of the carotid body of the domestic fowl.Cell & Tissue Research 162, 459–73.
Landis, D. M. D., Reese, T. S. &Raviola, E. (1974) Differences in membrane structure between excitatory and inhibitory components of the reciprocal synapse in the olfactory bulb.Journal of Comparative Neurology 155, 67–92.
Lavail, M. M. &Hild, W. (1971) Histotypic organization of the rat retinain vitro.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 114, 557–79.
Liberman, M. C. (1980) Morphological differences among radial afferent fibres in the cat cochlea: An electron-microscopic study of serial sections.Hearing Research 3, 45–63.
Lieberman, A. R. (1973) Neurons with presynaptic perikarya and presynaptic dendrites in the rat lateral geniculate nucleus.Brain Research 59, 35–59.
Lieberman, A. R. &Webster, K. E. (1972) Presynaptic dendrites and a distinctive class of synaptic vesicle in the rat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus.Brain Research 42, 196–200.
Massey, S. C., Mills, S. L. &Marc, R. E. (1992) All indoleamine-accumulating cells in the rabbit retina contain GABA.Journal of Comparative Neurology 322, 275–91.
Mcdonald, D. M. (1976) Structure and function of reciprocal synapses interconnecting glomus cells and sensory nerve terminals in the rat carotid body. InChromaffin, Enterochromaffin and Related Cells (edited byCoupland, R. E. &Fujita, T.) pp. 375–94. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Mcdonald, D. M. &Mitchell, R. A. (1975) The innervation of glomus cells, ganglion cells and blood vessels in the rat carotid body: a quantitative ultrastructural analysis.Journal of Neurocytology 4, 177–230.
Nadol, J. B., Jr. (1981) Reciprocal synapses at the base of outer hair cells in the organ of Corti of man.Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology 90, 12–17.
Nadol, J. B., Jr. (1983) Serial section reconstruction of the neural poles of hair cells in the human organ of Corti. II. Outer hair cells.Laryngoscope 93, 780–91.
Nadol, J. B., Jr. (1984) Incidence of reciprocal synapses on outer hair cells of the human organ of Corti.Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology 93, 247–50.
Nadol, J. B., Jr. (1988) Comparative anatomy of the cochlea and auditory nerve in mammals.Hearing Research 34, 253–66.
Nadol, J. B., Jr. (1990) Synaptic morphology of inner and outer hair cells of the human organ of Corti.Journal of Electron Microscopy Technique 15, 187–96.
Pasik, P., Pasik, T. &HÁmori, J. (1986) A newly recognized element in the monkey dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus exhibiting both presynaptic and postsynaptic sites.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 177–86.
Price, J. L. (1968) The termination of centrifugal fibres in the olfactory bulb.Brain Research 7, 483–6.
Pujol, R., Carlier, E. &Lenoir, M. (1980) OntOgenetic approach to inner and outer hair cell function.Hearing Research 2, 423–30.
Pujol, R., Lenoir, M. &Eybalin, M. (1986) Synaptology of the cochlea: Different types of synapse, putative neurotransmitters and physiopathological implications. InBasic and Applied Aspects of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (edited bySalvi, R. J., Henderson, D., Hamernik, R. P. &Colletti, V.) pp. 43–53. New York: Plenum Press.
Rall, W., Shepherd, G. M., Reese, T. S. &Brightman, M. W. (1966) Dendrodendritic synaptic pathway for inhibition in the olfactory bulb.Experimental Neurology 14, 44–56.
Raviola, G. &Raviola, E. (1967) Light and electron microscopic observations on the inner plexiform layer of the rabbit retina.American Journal of Anatomy 120, 403–26.
Rebière, A. &Dainat, J. (1981) Quantitative study of synapse formation in the duck olfactory bulb.Journal of Comparative Neurology 203, 103–20.
Reese, T. S. &Brightman, M. W. (1965) Electron microscopic studies on the rat olfactory bulb.Anatomical Record 151, 492.
Reese, T. S. &Shepherd, G. M. (1972) Dendro-dendritic synapses in the central nervous system. InStructure and Function of Synapses (edited byPappas, G. D. &Purpura, O. P.) pp. 121–36. New York: Raven Press.
Richardson, K. C. (1962) The fine structure of autonomie nerve endings in smooth muscle of the rat vas deferens.Journal of Anatomy 96, 427–42.
Richardson, K. C. (1966) Electron microscopic identification of autonomie nerve endings.Nature 210, 756.
Ross, M. D. (1985) Anatomic evidence for peripheral neural processing in mammalian graviceptors.Aviation, Space and Environmental Medicine 56, 338–43.
Ross, M. D. &Donovan, K. (1984) Gravity receptors: An ultrastructural basis for peripheral sensory processing.The Physiologist (Supplement) 27, S85-S86.
Ross, M. D., Rogers, C. M. &Donovan, K. M. (1986) Innervation patterns in rat saccular macula.Acta Otolaryngologica 102, 75–86.
Ross, M. D., Cutler, L., Meyer, G., Lam, T. &Vaziri, P. (1990) 3-D components of a biological neural network visualized in computer generated imagery.Acta Otolaryngologica 109, 83–92.
Saito, K. (1990) Freeze-fracture organization of hair cell synapses in the sensory epithelium of guinea pig organ of Corti.Journal of Electron Microscopy Technique 15, 173–86.
Seil, F. J. (1979) Cerebellum in tissue culture. InReviews of Neuroscience (edited bySchneider, D. M.) pp. 105–77. New York: Raven Press.
Seil, F. J. (1993) Organotypic neural cultures. InIn Vitro Biological Systems, Methods in Toxicology (edited byTyson, C. A. &Frazier, J. M.) pp. 7–26. Orlando: Academic Press.
Seil, F. J., Drake-Baumann, R., Herndon, R. M. &Leiman, A. L. (1992) Cytosine arabinoside effects in mouse cerebellar cultures in the presence of astrocytes.Neuroscience 51, 149–58.
Smith, C. A. &Sjöstrand, F. S. (1961) Structure of the nerve endings on the external hair cells of the guinea pig cochlea as studied by serial sections.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 5, 523–56.
Sobkowicz, H. M. (1992) The development of innervation in the organ of Corti. InDevelopment of Auditory and Vestibular Systems II (edited byRomand, R.) pp. 59–100. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Sobkowicz, H. M. &Rose, J. E. (1983) Innervation of the organ of Corti of the fetal mouse in culture. InDevelopment of Auditory and Vestibular Systems (edited byRomand, R.) pp. 27–45. New York: Academic Press.
Sobkowicz, H. M. &Slapnick, S. M. (1992) Neuronal sprouting and synapse formation in response to injury in the mouse organ of Corti in culture.International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 10, 545–66.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Guillery, R. W. &Bornstein, M. B. (1968) Neuronal organization in long term cultures of the spinal cord of the fetal mouse.Journal of Comparative Neurology 132, 365–96.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Hartmann, H. A., Monzain, R. &Desnoyers, P. (1973) Growth, differentiation and ribonucleic acid content of the fetal rat spinal ganglion cells in culture.Journal of Comparative Neurology 148, 249–84.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Bleier, R., Bereman, B. &Monzain, R. (1974a) Axonal growth and organization of the mamillary nuclei of the newborn mouse in culture.Journal of Neurocytology 3, 431–47.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Bleier, R. &Monzain, R. (1974b) Cell survival and architectonic differentiation of the hypothalamic mamillary region of the newborn mouse in culture.Journal of Comparative Neurology 155, 355–76.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Bereman, B. &Rose, J. E. (1975) Organotypic development of the organ of Corti in culture.Journal of Neurocytology 4, 543–72.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Scott, G. L., Kuwada, S., Hind, J. E., Oertel, D. &Slapnick, S. M. (1980) Neuronal growth in the organ of Corti in culture. InTissue Culture in Neurobiology (edited byGiacobini, E., Verna-Dakis, A. &Shahar, A.) pp. 253–75. New York: Raven Press.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Scott, G. L. &Slapnick, S. M. (1982) Ribbon synapses in the developing intact and cultured organ of Corti in the mouse.Journal of Neuroscience 2, 942–57.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Scott, G. L. &Holy, J. M. (1984) The ultrastructure of the developing organ of Corti of the mouse in culture. InUltrastructural Atlas of the Inner Ear (edited byFriedmann, I. &Ballantyne, J.)pp. 61–97. London: Butterworths.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Rose, J. E., Scott, G. L. &Levenick, C. V. (1986) Distribution of synaptic ribbons in the developing organ of Corti.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 693–714.
Sobkowicz, H. M., August, B. K. &Slapnick, S. M. (1992) Epithelial repair following mechanical injury of the developing organ of Corti in culture: An electron microscopic and autoradiographic study.Experimental Neurology 115, 44–9.
Sobkowicz, H. M., Loftus, J. M. &Slapnick, S. M. (1993) Tissue culture of the organ of Corti.Acta Otolaryngologica Supplement 502, 3–36.
Sotelo, C. (1977) Formation of presynaptic dendrites in the rat cerebellum following neonatal X-irradiation.Neuroscience 2, 275–83.
Sotello, C. (1982) Synaptic remodeling in agranular cerebella.Experimental Brain Research Supplement 6, 50–68.
ŠpaČek, J., PaŘizek, J. &Lieberman, A. R. (1973) Golgi cells, granule cells and synaptic glomeruli in the molecular layer of the rabbit cerebellar cortex.Journal of Neurocytology 2, 407–28.
Strettoi, E., Dacheux, R. F. &Raviola, E. (1990) Synaptic connections of rod bipolar cells in the inner plexiform layer of the rabbit retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology 295, 449–66.
Tachibana, M. &Kaneko, A. (1988) Retinal bipolar cells receive negative feedback input from GABAergic amacrine cells.Visual Neuroscience 1, 297–305.
Tanaka, K. &Smith, C. A. (1978) Structure of the chicken's inner ear: SEM and TEM study.American Journal of Anatomy 153, 251–72.
Thorn, L., Schinko, I. &Wetzstein, R. (1972) Synaptic bar in the efferent part of a synapse in the organ of Corti.Experientia 28, 835.
Toran-Allerand, C. D. (1978) Culture of hypothalamic neurons: Organotypic culture.Colloques Internationaux du C.N.R.S. 280, 759–76.
Usami, S.-I., Hozawa, J., Tazawa, M., Yoshihara, T., Igarashi, M. &Thompson, G. C. (1988) Immunocytochemical study of catecholaminergic innervation in the guinea pig cochlea.Acta Otolaryngologica 447, 36–45.
Vaughn, J. E., Famiglietti, E. V., Jr., Barber, R. P., Saito, K., Roberts, E. &Ribak, C. E. (1981) GABAergic amacrine cells in rat retina: immunocytochemical identification and synaptic connectivity.Journal of Comparative Neurology 197, 113–27.
Whitlon, D. S. &Sobkowicz, H. M. (1989) GABA-like immunoreactivity in the cochlea of the developing mouse.Journal of Neurocytology 18, 505–18.
Wilson, D. A.&Leon, M. (1988) Noradrenergic modulation of olfactory bulb excitability in the postnatal rat.Developmental Brain Research 42, 69–75.
Wolf, M. K. (1970) Anatomy of cultured mouse cerebellum. II. Organotypic migration of granule cells demonstrated by silver impregnation of normal and mutant cultures.Journal of Comparative Neurology 140, 281–98.
Wolf, M. K. &Dubois-Dalcq, M. (1970) Anatomy of cultured mouse cerebellum. I. Golgi and electron microscopic demonstrations of granule cells, their afferent and efferent synapses.Journal of Comparative Neurology 140, 261–80.
Zimmer, J. &GÄhwiler, B. H. (1984) Cellular and connective organization of slice cultures of the rat hippocampus and fascia dentata.Journal of Comparative Neurology 228, 432–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sobkowicz, H.M., Slapnick, S.M. & August, B.K. Presynaptic fibres of spiral neurons and reciprocal synapses in the organ of Corti in culture. J Neurocytol 22, 979–993 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01218355
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01218355