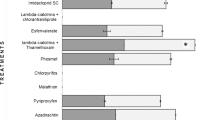
Abstract
Using a continuous exposure technique, the toxicity of 35 compounds to the bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus echinopus (Fumouze and Robin) was examined after 48 h. Sixteen acaricides yielded an LC50 of <1.0 mg cm2. The highest toxicity was exhibited by cyclodiene GABA antagonists (dieldrin, endrin and aldrin), some organophosphate (chlorpyrifos, diazinon and azinphosethyl) and carbamate (carbofuran) anticholinesterases and a thiazolidine flubenzimine. Oxythioquinox, fenazaflor, fenazaquin and amitraz were less toxic than the cyclodienes, organophosphates and carbamates. The sodium channel agonists (DDT and pyrethroids) and several specific acaricides with other modes of action were inactive (LC50 >11.0 mg cm-2).
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abbott, W.S. 1925. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 18: 265–267.
Bai, D., Lummis, S.C.R., Leicht, W., Breer, H. and Sattelle, D.B. 1991. Actions of imidacloprid and a related nitromethylene on cholinergic receptors of an identified insect motor neurone. Pestic. Sci. 33: 197–204.
Bot, J. and Meyer, M.K.P. 1967. An artificial rearing medium for acarid mites. J. Entomol. Soc. S. Africa 29: 199.
Casida, J.E. and Pulman, D.A. 1994. Recent advances on heterocyclic insecticides acting as GABA antagonists. In Advances in the chemistry of insect control III, G.G. Briggs (ed.), pp. 36–51. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge.
Chen, J.-S. 1990a. The biology, insecticide resistance, and control countermeasures of bulb mites. Chinese J. Entomol. 93–106. Spec. Publ. No. 3.
Chen, J.-S. 1990b. An improved method for determining the susceptibility of Rhizoglyphus robini and R. setosus (Acarina: Acaridae) to pesticides. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 8: 175–178.
Chen, J.-S. and Lo, K.-C. 1989. Susceptibility of two bulb mites, Rhizoglyphus robini and R. setosus (Acarina: Acaridae) to some acaricides and insecticides. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 6: 55–66.
Corbett, J.R. and Wright, B.J. 1970. Biochemical mode of action of the acaricide fenazaflor. Pestic. Sci. 1: 120–123.
Corbett, J.R., Wright, K. and Baillie, A.C. 1984. The Biochemical Mode of Action of Pesticides, 2nd edn. Academic, London.
Desaiah, D., Cutkomp, L.K. and Koch, R.B. 1974. Inhibition of spider mite ATPases by Plictran and three organochlorine acaricides. Life. Sci. 13: 1693–1703.
Hackler, R.E., Suhr, R.G., Sheets, J.J., Hatton, C.J., Johnson, P.L., Davis, L.N., Edie, R.G., Kaster, S.V., Jourdan, G.P., Jackson, J.L. and Krumkalns, E.V. 1994. Chemistry and miticidal activity of fused pyrimidine derivatives of fenazaquin. In Advances in the chemistry of insect control III, G.G. Briggs (ed.), pp. 70–84. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge.
Hunt, D.A. 1994. 2-Arylpyrroles: novel uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. In Advances in the chemistry of insect control III, G.G. Briggs (ed.), pp. 127–140. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge.
Kadir, H.A. and Knowles, C.O. 1991a. Toxicological studies of the thiourea diafenthiuron in diamondback moths (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae), twospotted spider mites (Acari: Tetranychidae), and bulb mites (Acari: Acaridae). J. Econ. Entomol. 84: 780–784.
Kadir, H.A. and Knowles, C.O. 1991b. Octopaminergic action of the carbodiimide metabolite of diafenthiuron. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 39: 261–269.
Kadir, H.A. and Knowles, C.O. 1991c. Inhibition of ATP dephosphorylation by acaricides with emphasis on the anti-ATPase activity of the carbodiimide metabolite of diafenthiouron. J. Econ. Entomol. 84: 801–805.
Kadir, H.A. and Knowles, C.O. 1992. Stimulation of diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella) adenylate cyclase activity by a carbodiimide. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 103C: 303–307.
Knowles, C.O. 1990. Exploitation of mite biochemical targets by acaricides. In Pesticides and alternatives, J.E. Casida (ed.), pp. 395–406, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Knowles, C.O., Errampalli, D.D. and El-Sayed, G.N. 1988. Comparative toxicities of selected pesticides to bulb mite (Acari: Acaridae) and twospotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 81: 1586–1591.
Kuwahara, M. 1986. [Resistance of the bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus robini Claparède (Acarina: Acaridae), to insecticides. I. Resistance patterns to organophosphorus insecticides.] Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 30: 290–295 (in Japanese with English summary).
Kuwahara, M., Takai, M. and Fujimoto, K. 1985. [Simple rearing of the bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus robini, and test methods of acaricides.] Syokubutsu-boeki (Plant Protection) 39: 68–70 (in Japanese).
Kuwahara, M., Konno, Y. and Shishido, T. 1991. Mechanism of fenitrothion resistance in the organophosphate-resistant bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus robini Claparède (Acarina: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 26: 205–214.
Liu, M.-Y. and Casida, J.E. 1993. High affinity binding of [3H]imidacloprid in the insect acetylcholine receptor. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 46: 40–46.
Matsumura, F., Tanaka, K. and Ozoe, Y. 1987. GABA-related systems as targets for insecticides. In Sites of action for neurotoxic pesticides, R.M. Hollingworth and M.B. Green (eds), pp. 44–70. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Petroske, E. and Casida, J.E. 1995. Diafenthiuron action: carbodiimide formation and ATPase inhibition. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 53: 60–74.
Rojakovick, A.S. and March, R.B. 1976. Insecticide cyclic nucleotide interactions. I. Quinoxalinedithiol derivatives: a new group of potent phosphorodiesterase inhibitors. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 6: 10–19.
Ruder, F.J., Guyer, W., Benson, J.A. and Kayser, H. 1991. The thiourea insecticide/acaricide diafenthiouron has a novel mode of action: inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by its carbodiimide product. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 41: 207–219.
Ruder, F.J. and Kayser, H. 1992. The carbodiimide product of diafenthiuron reacts covalently with two mitochondrial proteins, the F0-proteolipid and porin, and inhibits mitochondrial ATPase in vitro. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 42: 248–261.
Ruder, F. and Kayser, H. 1993. The carbodiimide product of diafenthiuron inhibits mitochondria in vivo. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 46: 96–106.
SAS Institute 1982. SAS User's Guide: Statistics. SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
Shinkaji, N., Okabe, K. and Amano, H. 1986. [Rhizoglyphine mites (Acari: Acaridae) infesting rakkyo (Allium chinense G. Don) and Chinese chive (A. tuberosum Rottler), and their susceptibility to dimethoate and disulfoton.] Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 30: 285–289 (in Japanese with English summary).
Soderlund, D.M. and Adams, P.M. 1993. Inhibition of octopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in two-spotted mites by dicofol and related diphenylcarbinol acaricides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 46: 228–235.
Soderlund, D.M. and Bloomquist, J.R. 1989. Neurotoxic actions of pyrethroid pesticides. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 34: 77–96.
Takai, M. 1981. [A study on the insecticide resistance of bulb mite.] Kouchichikushiho 13: 45–48 (in Japanese).
Uebayashi, Y., Miyata, T. and Saito, T. 1986. [Insecticide resistance of the bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus robini Claparède (Acarina: Acaridae).] Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. 30: 296–297 (in Japanese with English summary).
Wood, E., Latli, B. and Casida, J.E. 1996. Fenazaquin acaricide specific binding sites in NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase and apparently the ATP synthase stalk. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 54: 135–145.
Zhao, G., Liu, W. and Knowles, C.O. 1996. Clofentezine toxicity and fate in the bulb mite Rhizoglyphus echinopus (Acari: Acaridae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 20: 215–222.
Zoebelein, G., Dorntlein, D. and Hammann, I. 1980. Results of laboratory and field evaluation of Cropotex®, an acaricide of a new chemical group. Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. 33: 169–184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gencsoylu, I., Liu, W., Usmani, K.A. et al. Toxicity of Acaricides to the Bulb Mite Rhizoglyphus Echinopus (Acari: Acaridae). Exp Appl Acarol 22, 343–351 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024513125550
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024513125550