Summary
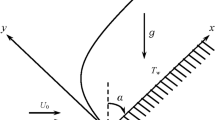
An ignition criterion has been derived for flowing, high velocity, combustible gases with pilot stabilized flames at low pressure.
The behavior of ignition temperatures and induction periods (calculated with the criterion) with ignition compositions and turbulence levels agreed with literature findings.
It was also found that the criterion could be used to fully delineate an ignition limit — velocity curve if only lean ignition limit — velocity data were available.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D :
-
laminar diffusivity, ft2/sec
- ΔH f :
-
heat of formation of water (pilot product), Btu/lb mole
- ΔH c :
-
heat of combustion of combustible, Btu/lb mole
- K :
-
fraction of heat of combustion of combustible mixture delivered during induction period
- R t :
-
correlation function between a particle velocity component at some time and the velocity component of the particle after a time t
- T :
-
\(\int\limits_0^\infty {R_t d_t } \) R t dt
- U :
-
cold stream velocity, ft/sec based on empty combustion chamber
- U p :
-
pilot gas velocity, ft/sec
- C p :
-
mean specific heat of combustible mixture, Btu/lb, mole °F
- C /1 p :
-
mean specific heat of pilot products Btu/lb, mole °F
- f :
-
fraction of turbulence, u′/U
- l 1 :
-
mean eddy diameter, ft (available in references 8 & 9)
- r p :
-
radius of pilot port, feet
- t :
-
induction period, seconds
- u 1 :
-
fluctuating velocity, feet/second
- y :
-
mole fraction combustible in air
- ϕ, ψ, β :
-
functions
- θ i :
-
ignition temperature, °F
- θ 0 :
-
cold stream temperature, °F
- ρ :
-
molar density of combustible-air mixture, lb moles/ft3
- ρ 1 :
-
molar density of pilot products, lb moles/ft3
References
Marble, F. E. and T. C. Adamson, Selected Combustion Problems I, p. 111, Butterworths Scientific Publications, London, 1954.
Cheng, S. I. and A. A. Kovitz, Sixth Symposium on Combustion p. 418, Reinhold, New York, 1957.
Barrere, M., Ibid p. 941.
Wolfhard, H. G. and D. S. Burgess, Combustion and Flame 2 (1958) 3.
Jensen, W. P. and C. W. Shipman, Seventh Symposium on Combustion p. 674, Butterworths Scientific Publications, London, 1959.
Einstein, A., Ann. Phys. 17 (1905) 549.
Karlovitz, B., Selected Combustion Problems I, p. 248, Butterworths Scientific Publications, London, 1954.
Griskey, R. G. and D. H. Archer, A.I.Ch.E. Journal 8 (1962) 498.
Archer, D. H., Ph. D. Thesis, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware, 1953.
Mullins, B. P., Part IV Report Number R96 National Gas Turbine Establishment (1951).
Townend, D. T. A. and M. R. Mandelekar, Proc. Roy. Soc. A 141 (1933) 436.
Mullen, J. W., J. B. Fenn and M. R. Irby, Third Symposium on Combustion p. 317, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland, 1949.
Kumagai, S. and I. Kimura, Sixth Symposium on Combustion p. 554, Reinhold, New York, 1957.
Penner, S. S., Chemistry Problems in Jet Propulsion p. 289, Pergamon Press, New York, 1957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griskey, R.G., Archer, D.H. Ignition criterion for turbulent high velocity, combustible gases with pilot-stabilized flames. Appl. Sci. Res. 14, 309–320 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382254
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382254