Summary
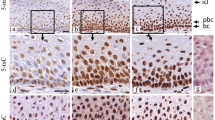
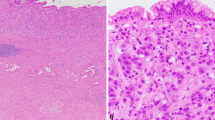
Bromodeoxyuridine (BUDR) is a non-radioactive thymidine analogue which is incorporated into the DNA of proliferating cells. This allows evaluation of the size of the S-phase as the BUDR labelling index (BUDR-LI) not onlyin vitro but alsoin vivo, since BUDR is not toxic at the doses needed to label cells. To ascertain whetherin vivo BUDR incorporation can be detected on routine histological material we tested several different procedures prior to immunoperoxidase staining, on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from five patients with gastric cancer, who received BUDR (250 mg m−2, intravenous) 4 h before surgery. To determine the optimal conditions for detecting BUDR in formalin-fixed tissues, immunohistochemical testing for BUDR was performed simultaneously on duplicate sections fixed with 70% ethanol. It was found that hydrolysis with 3N HCl at 37° C for 30 min and digestion with 0.5% in at 37° C for 30 min were sufficient to detect BUDR immunoreactivity in formalin-fixed sections.
The method presented extends the range of applications of thein vivo BUDR technique for cell kinetics studies in human neoplasms because it can be used on routinely fixed archival material, with the advantage of correlating the kinetic data with histopathological characters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAGSHAW, M. A., DOGGET, R. L. S., SMITH, K. C., KAPLAN, H. S. & NELSEN, T. S. (1967) Intra-arterial 5-bromo-deoxyuridine and x-ray therapy.Amer. J. Roentgenol. 99, 886–94.
BEGG, A. C., MCNALLY, N. J. & SHRIEVE, D. C. (1985) A method to measure the duration of the DNA synthesis and the potential doubling time from a single sample.Cytometry 6, 620–6.
DANOVA, M., WILSON, G., UCCI, G., MAZZINI, G., GIORDANO, P., GIORDANO, M. & RICCARDI, A. (1986) Comparison between bromodeoxyuridine and iododeoxyuridine for cytokinetic studies: a flow cytofluorometric analysis.Basic Appl. Histochem. 30, 63.
DANOVA, M., WILSON, G., RICCARDI, A., MAZZINI, G., UCCI, G., GIORDANO, M., BRUGNATELLI, S., LUONI, R. & ASCARI, E. (1987a)In vivo administration of bromodeoxyuridine and flow cytometry for cell kinetic studies in human malignancies.Haematologica 72, 115–19.
DANOVA, M., RICCARDI, A., MAZZINI, G., UCCI, G., GAETANI, P., SILVANI, V., KNERICH, R., BUTTI, G. & ASCARI, E. (1987b) Ploidy and proliferative activity of human brain tumours: a flow cytofluorometric study.Oncology 44, 102–7.
D'ARDENNE, A. J., BURNS, J., SYKES, B. C. & KIRKPATRIK, P. (1983) Comparative distribution of fibronectin and type III collagen in normal human tissue.J. Pathol. 141, 55–69.
DE FAZIO, A., LEARY, J. L., HEDLEY, D. W. & TATTERSALL, M. H. (1987) Immunohistochemical detection of proliferating cellsin vivo.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 5, 571–7.
DENEKAMP, J. & KALLMANN, R. F. (1973)In vitro andin vivo labelling of animal tumors with tritiated thymidine.Cell Tissue Kinet. 6, 217–27.
FIOCCA, R., VILLANI, P., SOLCIA, E., CORNAGGIA, M., FRIGERIO, B. & CAPELLA, C. (1987) Characterization of four main cell types in gastric cancer: foveolar, mucopeptic, intestinal columnar and goblet cells. An histopathologic, histochemical and ultrastructural study of ‘early’ and ‘advanced’ tumours.Pathol. Res. Pract. 182, 308–25.
FREEMAN, M. V. R., BEISER, S. H., ERLANGER, B. F. & MILLER, O. J. (1971) Reaction of antinucleoside antibodies with human cellsin vitro.Exp. Cell Res. 69, 345–55.
GRATZNER, H. G. (1982) Monoclonal antibody to 5-lodo-deoxyuridine and 5-bromodeoxyuridine: a new reagent for detection of DNA replication.Science 218, 474–5.
GRATZNER, H. G., POLLACK, A., INGRAM, D. J. & LEIF, R. C. (1976) Deoxyribonucleic acid replication in single cell chromosomes by immunologic techniques.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 267–70.
HAMADA, S. (1985) A double labeling technique combining3H-thymidine autoradiography with BrdUrd immunocytochemistry.Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 267–70.
HOSHINO, T., NAGASHIMA, T., CHO, K. G., MUROVIC, J. A., HODES, J. E., WILSON, C. B., EDWARDS, M. S. B. & PITTS, L. H. (1986) S-phase fraction of human brain tumorsin situ measured by uptake of bromodeoxyuridine.Int. J. Cancer 38, 369–74.
HOSHINO, T. & SANO, K. (1969) Radiosensitization of malignant brain tumors with bromouridine (thymidine analog).Acta Radiol. Ther. Phys. Biol. 8, 15–26.
KIRKPATRIK, P. & D'ARDENNE, A. J. (1984) The effect of fixation and enzymatic digestion on the immunohistochemical demonstration of laminin and fibronectin in paraffin-embedded tissue.J. Clin. Pathol. 37, 639–44.
MEPHAM, B. L., FRATER, W. & MITCHELL, B. S. (1979) The use of proteolytic enzymes to improve immunoglobulin staining by the PAP technique.Histochem. J. 11, 345–57.
MORAN, R., DARZYNKIEWICZ, Z., STAIANO-COICO, L. & MELAMED, M. (1985) Detection of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdUrd) incorporation by monoclonal antibodies: role of DNA denaturation step.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33, 821–7.
MORSTYN, G., HSU, S. M., KINSELLA, T., GRATZNER, H., RUSSO, A. & MITCHELL, J. B. (1983) Bromodeoxyuridine in tumors and chromosomes detected with a monoclonal antibody.J. Clin. Invest. 72, 1844–50.
NAGASHIMA, T., MUROVIC, J. A., HOSHINO, T., WILSON, C. B. & DE ARMOND, S. J. (1986) The proliferative potential of human pituitary tumorsin situ.J. Neurosurg. 64, 588–93.
RAZA, A., UCAR, K. & PREISLER, H. D. (1985) Double labeling andin vitro versusin vivo incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine in patients with acute non-lymphocytic leukemia.Cytometry 6, 620–5.
RISIO, M., COVERLIZZA, S., POCCARDI, G., CANDER-LARESI, G. L. & GAIOLA, O. (1986)In vitro immunohistochemical localization of S-phase cells by a monoclonal antibody to bromodeoxyuridine.Basic Appl. Histochem. 30, 469–77.
RUSSO, A., GIANNI, L., KINSELLA, T., KLECKER, R. W., JENKINS, J., ROWLAND, J., GLATSTEIN, E., MITCHELL, J. B., COLLINS, J., MYERS, C. (1984) Pharmacological evaluation of intravenous delivery of 5-bromodeoxyuridine to patients with brain tumours.Cancer Res. 44, 1702–5.
SINCLAIR, R. A., BURNS, J. & DUNNIL, M. S. (1981) Immunoperoxidase staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded, human renal biopsies with a comparison of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) and indirect methods.J. Clin. Pathol. 34, 859–65.
WILSON, G. D., MCNALLY, N. J., DUNPHY, E., PFRAGNER, R., & KARCHER, H. (1985) The labelling index of human and mouse tumours assessed by bromodeoxyuridine stainingin vivo andin vitro and flow cytometry.Cytometry 6, 641–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danova, M., Riccardi, A., Brugnatelli, S. et al. In vivo bromodeoxyuridine incorporation in human gastric cancer: A study on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded sections. Histochem J 20, 125–130 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01746675
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01746675