Abstract
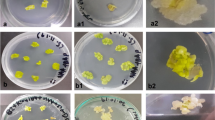
Growth and yield characteristics of two different clones of banana plants (Musa AAA cv. Grande naine) originating from four months old embryogenic cell suspensions were studied. These characteristics were compared with those plants produced by the conventional in vitro budding multiplication method. Two types of variants were observed during the acclimatization phase among 500 embryogenic cell suspension derived plants. The first type related to banana plants with `variegated or deformed leaves' were also observed in in vitro budding derived plants. The second type concerned `fasciated-leafed' plants. During the field growth, these two variant types produced plants morphologically similar to the other plants. Thus, none of the cell suspension derived plants exhibited off-type traits in the field. A Fisher block model was used to compare the field performances of the two clones produced through the two in vitro propagation techniques. The analysis of variance showed that there were no significant differences between the plants produced by either micropropagation techniques for the plant height and circumference, the length of the reference leaf, the number of nodal clusters of the inflorescence and of fruits, the bunch weight, the period of time between planting and flowering, and between planting and harvesting. This study showed that banana plants with an agronomical behaviour similar to those produced by the conventional in vitro budding method could be regenerated from embryogenic cell suspension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous, 1989. SAS Institute Inc., SAS/STA7 User's guide, Version 6, Fourth Edition, Volume 2, Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc., 846 pp.
Baillie, A.M.R., B.G. Rossnagel &; K.K. Kartha, 1992. Field evaluation of barley ( Hordeum vulgare L) genotypes derived from tissue-culture. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 72: 725–733.
Carron, M.P., B.G. Dea, J. Tison, A. Leconte &; J. Keli, 1997. Field growth of Hevea brasiliensis clones produced by in vitro culture. Plantation Recherche Développement 4: 271–273.
Champion, J., 1963. Le bananier. In: Mainsonneuve &; Larose (Eds.), Paris.
Côte, F.X., J.A. Sandoval, P. Marie &; E. Auboiron, 1993. Variations in micropropagated bananas and plantains. Literature survey. Fruits 48: 15–22.
Côte, F.X., R. Domergue, S. Monmarson, J. Schwendiman, C. Teisson &; J.V. Escalant, 1996. Embryogenic cell suspensions from the male flower of Musa AAA cv. Grand nain. Physiol Plant 97: 285–290.
Cronauer, S.S. &; A.D. Krikorian, 1988. Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in the seeded diploid Musa ornata Roxb. Plant Cell Rep 7: 23–25.
Dhed'a, D., F. Dumortier, B. Panis, D. Vuylsteke, &; E. De Langhe, 1991. Plant regeneration in cell suspension cultures of cooking banana cv. 'Bluggoe' (Musa spp. ABB group). Fruits 46: 125–135.
Drew, R. &; M. Smith, 1990. Field evaluation of tissue cultured bananas in south-eastern Queensland. Aust J Exp Agr 30: 569–574.
Duval, Y., F. Engelmann &; T. Durand-Gasselin, 1995. Somatic embryogenesis in oil palm (Elaeis guineesis Jacq.). In: Y.P.S. Bajaj (Ed.), Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol 30 Somatic Embryogenesis and Synthetic Seed I, pp. 335–352. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg.
Escalant, J.V. &; C. Teisson, 1989. Somatic embryogeneis from immature zygotic embryos of the species Musa acuminata and Musa balbisiana. Plant Cell Rep 7: 665–668.
Escalant, J.V., C. Teisson &; F.X. Côte, 1994. Amplified somatic embryogenesis from male flowers of triploid banana and plantain cultivars (Musa sp.). In vitro Cell Dev Biol 30: 181–186.
Grapin, A., J. Schwendiman &; C. Teisson, 1996. Somatic embryogenesis in plantain banana. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 32: 66–71.
Gupta, P.K., R. Timmis &; W.C. Carlson, 1993. Somatic embryogenesis: a possible tool for large-scale propagation of forestry species. In:W.Y. Soh, J.R. Liu &; A. Komamine (Eds.), Advances in Developmental Biology and Biotechnology of Higher Plants, pp. 18-37.
Hanson, K., P. Hucl &; R.J. Baker, 1994. Comparative fiel performance of tissue culture-derived lines and breeder lines of HY320 spring wheat. Plant Breed 112: 183–191.
Hwang, S.C., C.L. Chen, J.C. Lin &; H.L. Lin, 1984. Cultivation of banana using plantlets from meristem culture. HortScience 19: 231–233.
Israeli, Y., O. Reuveni &; E. Lahav, 1991. Qualitative aspects of somaclonal variations in banana propagated by in vitro techniques. Scientia Horticulturae 48: 71–88.
Ma, S.S., 1991. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cell suspension culture of banana. In: National Taiwan University Horticulture Departement, Proceedings of symposium on tissue culture of horticultural crops, pp. 181-188. Taiepei, Taiwan 8-9 March 1988.
Marroquin, C.G., C. Paduscheck, J.V. Escalant &; C. Teisson, 1993. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration through cell suspensions in Musa acuminata. In vitro Cell Dev Biol 29: 43–46.
Novak, F.J., R. Afza, M. Van Duren, M. Perea-Dallos, B.V. Conger &; T. Xiolang, 1989. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in suspension cultures of dessert (AA, AAA) and cooking (AAB) bananas. Bio/Tech 46: 125–135.
Reuveni, O. &; Y. Israeli, 1990. Measures to reduce somaclonal variation in in vitro propagated bananas. Acta Horticulturae 275: 307–313.
Robinson, J.C., C. Fraser &; K. Eckstein, 1993. A field comparison of conventional suckers with tissue culture banana planting material over three crop cycles. J Hortic Sci 68: 831–836.
Roylance, J.T., N.S. Hill &; W.A. Parrot, 1994. Detection of somaclonal variation in tissue culture regenerants of tall fescue. Crop Science 34: 1369–1372.
Stover, R.H. &; N.W. Simmonds, 1987. In: Longman Scientific &; Technical (Eds.), Bananas, 468 pp., New York.
Stover, R.H., 1988. Variation and cultivar nomenclature in Musa AAA group, Cavendish subgroup. Fruits 43: 353–357.
Vuylsteke, D.R., 1989. Shoot-tip culture for the propagation, conservation and exchange of Musa germplasm. In: International Board for Plant Genetics Ressources (Ed.), pp. 1-56, Rome.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cô;te, F., Folliot, M., Domergue, R. et al. Field performance of embryogenic cell suspension-derived banana plants (Musa AAA, cv. Grande naine). Euphytica 112, 245–251 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003960724547
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003960724547