Abstract
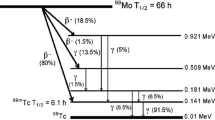
Chondritic meteorite samples were analyzed nondestructively by photon activation analysis. Powdered samples weighing about 50 mg each were irradiated with photons (γ-rays) converted from electrons accelerated by a linear electron accelerator at 20 and 30 MeV. With 30-minute and 6-hour irradiations, 11 and 12 elements with duplication of 6 elements could be determined, respectively. Considering that several major elements including Mg, Si and Fe can be determined in addition to Ti, Rb, Sr, Y and Zr, which cannot or hardly be determined by instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA) with rather high sensitivity, instrumental photon activation analysis is as effective as INAA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Segebade, H.-P. Weise, G. J. Lutz, Photon Activation Analysis, de Gruyter.
E. Jarosewich, R. S. Clarke, Jr., J. N. Barrowa, Smithson. Contrib. Earth Sci., 27 (1977) 1.
A. Ando, H. Kamioka, S. Terashima, S. Itoh, Geochem. J., 23 (1989) 143.
G. Kallemeyn, A. Rubin, J. T. Wasson, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 55 (1991) 881.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebihara, M., Oura, Y., Ishii, T. et al. How Effectively is the Photon Activation Analysis Applied to Meteorite Samples?. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry 244, 491–496 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006766411304
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006766411304