Abstract
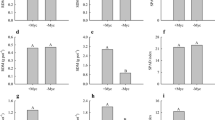
The effect of the fungicide, chlorothalonil, on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) symbiosis was studied in a greenhouse using Leucaena leucocephala as test plant. Chlorothalonil was applied to soil at 0, 50, 100 and 200 μg g−1. The initial soil solution P levels were 0.003 μg mL−1 (sub-optimal) and 0.026 μg mL−1 (optimal). After 4 weeks, the sub-optimal P level was raised to 0.6 μg mL−1 (high). The soil was either uninoculated or inoculated with the VAM fungus, Glomus aggregatum. The fungicide reduced mycorrhizal colonization of roots, development of mycorrhizal effectiveness, shoot P concentration and uptake and dry matter yields at all concentrations tested, although the highest inhibitory effect was noted as the concentration of the fungicide was increased from 50 to 100 μg g−1. Phosphorus applied after four weeks tended to partially offset the deleterious effects of chlorothalonil in plants grown in the inoculated and uninoculated soil which suggests that the fungicide was interfering with plant P uptake. The results suggest that the use of chlorothalonil should be restricted to levels below 50 μg g−1 if the benefits of mycorrhizal symbiosis are to be expected.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Aziz, T and Habte, M 1989a The sensitivity of three vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal species to simulated erosion. J. Plant Nutr. 12, 859–869.
Aziz, T and Habte, M 1989b Influence of inorganic N on mycorrhizal activity, nodulation, and growth of Leucaena leucocephala in an oxisol subjected to simulated erosion. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 20, 239–251.
Aziz, T and Habte, M 1987 Determining vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal effectiveness by monitoring P status of leaf disks. Can. J. Microbiol. 33, 1097–1101.
Fox, R L and Kamprath, E J 1970 Phosphate sorption isotherms for evaluating the phosphate requirements of soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 34, 902–907.
Gbur, E E, Thomas, G L and Miller, F R 1979 Use of segmented regression in the determination of the base temperature in heat accumulation models. Agron. J. 71, 949–953.
Habte, M, Fox, R L, Aziz, T and El-Swaify, S A 1988 Interaction of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi with erosion in an oxisol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 945–950.
Habte, M, Fox, R L and Huang, R S 1987 Determining vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal effectiveness by monitoring P status of subleaflets of an indicator plant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 18, 1403–1420.
Habte, M and Manjunath, A 1987 Soil solution phosphorus status and mycorrhizal dependency in Leucaena leucocephala. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 797–801.
Hepper, C M 1983 Effect of phosphate on germination and growth of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 80, 487–490.
Kreutzer, W A 1960 Soil Treatment. In Plant Pathology: An Advanced Treatise. (Vol. III) Eds. J GHorsfall and A EDimond. pp 431–476. Academic Press, New York and London.
Manjunath, A and Habte, M 1988 Development of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection and the uptake of immobile nutrients in Leucaena leucocephala. Plant and Soil 106, 97–103.
Menge, J A 1982 Effect of soil fumigants and fungicides on vesicular-arbuscular fungi. Phytopathology 72, 1125–1132.
Nemec, S 1980 Effects of 11 fungicides on endomycorrhizal development in sour orange. Can. J. Bot. 58, 522–526.
Nemec, S 1985 Influence of selected pesticides on Glomus species and their infection in citrus. Plant and Soil 84, 133–137.
Phillips, J M and Hayman, D S 1970 Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 55, 158–161.
Rajapakse, S, Zuberer, D A and MillerJr., J C 1989 Influence of phosphorus level on VA mycorrhizal colonization and growth of cowpea cultivars. Plant and Soil 114, 45–52.
SAS Institute, Inc. 1985 SAS User's guide: Statistics. SAS Inst. Inc., Cary, North Carolina, USA.
Schubert, A and Hayman, D S 1986 Plant growth responses to vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza. XVI. Effectiveness of different endophytes at different levels of soil phosphate. New Phytol. 103, 79–90.
Spokes, J R, David, R M M and Hayman, D S 1981 Effects of plant protection chemicals on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas. Pestic. Sci. 12, 346–350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution from Hawaii Institute of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources Journal Series No. 3464.
Contribution from Hawaii Institute of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources Journal Series No. 3464.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aziz, T., Habte, M. & Yuen, J.E. Inhibition of mycorrhizal symbiosis in Leucaena leucocephala by chlorothalonil. Plant Soil 131, 47–52 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010418
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010418