Abstract
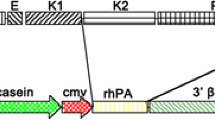
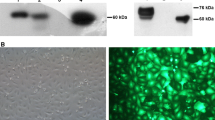
Vitamin K-dependent plasma protein, human Protein C (HPC) has been expressed in transgenic mice, using a 4.2kb mouse whey acidic protein (WAP) promoter, 9.0 kb HPC gene and 0.4 kb 3′flanking sequences. Expression was mammary gland-specific and the recombinant human Protein C (rHPC) was detected in milk at concentrations of 0.1 to 0.7mg ml−1. SDS-PAGE revealed that the single, heavy and light chains of rHPC migrated with increased electrophoretic mobility, as compared to HPC. Enzymatic deglycosylation showed that these molecular weight disparities are in part due to differential glycosylation. The substantial increase observed in the amount of single chain protein, as well as the presence of the propeptide attached to 20–30% of rHPC, suggest that mouse mammary epithelial cells are not capable of efficient proteolytic processing of rHPC. TheK m of purified rHPC for the S-2366 synthetic substrate was similar to that of plasma-derived HPC, while the specific activity was about 42–77%. Amino acid sequence analyses and low anticoagulant activity of purified rHPC suggest that γ-carboxylation of rHPC is insufficient. These results show that proteolytic processing and γ-carboxylation can be limiting events in the overexpression of fully biologically active rHPC in the mouse mammary gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr, P.J. (1991) Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases.Cell 66, 1–3.
Bayna, E.M. and Rosen, J.M. (1990) Tissue-specific, high level expression of the rat whey acidic protein gene in transgenic mice.Nucl. Acids Res. 18, 2977–85.
Brinster, R.L., Allen, J.M., Behringer, R.R., Gelinas, R.E. and Palmiter, R.D. (1988) Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 85, 836–40.
Burdon, T., Sankaran, L., Wall, R.J., Spencer, M. and Hennighausen, L. (1991) Expression of a whey acidic protein transgene during mammary development: evidence for different mechanisms of regulation during pregnancy and lactation.J. Biol. Chem. 266, 6909–14.
Clark, A.J., Bessos, H., Bishop, J.O., Brown, P., Harris, S., Lathe, R., McClenaghan, M., Prowse, C., Simons, J.P., Whitelaw, C.B.A. and Wilmut, I. (1989) Expression of human anti-hemophilic factor IX in the milk of transgenic sheep.Bio Technology 7, 487–92.
Clark, A.J., Cowper, A., Wallace, R., Wright, G. and Simons, J.P. (1992) Rescuing transgene expression by co-integration.Bio Technology 10, 1450–4.
Dale, T.C., Kranacik, M.J., Schmidhauser, C., Yang, C.L.Q., Bissell, M.J. and Rosen, J.M. (1992) High-level expression of the rat whey acidic protein gene is mediated by elements in the promoter and 3′ untranslated region.Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 905–14.
De Stefano, V., Mastrangelo, S., Schwarz, H.P., Pola, P., Flore, R., Bizzi, B. and Leone, G. (1993) Replacement therapy with a purified protein C concentrate during initiation of oral anticoagulation in severe protein C congenital deficiency.Thromb. Haemostas. 70, 247–9.
Dreyfus, M., Magny, J.F., Bridey, F., Schwarz, H.P., Planche, C., Dehan, M. and Tchernia, G. (1991) Treatment of homozygous protein C deficiency and neonatal purpura fulminans with a purified protein C concentrate.N. Engl. J. Med. 325, 1565–8.
Emerick, S.C., Murayama, H., Yan, S.B., Longmon, G.L., Harms, C.S., Marks, C.A., Matter, L.E., Huss, C.A., Comp, P.C., Esmon, N.L., Esmon, C.T. and Bang, N.U. (1987) Preclinical pharmacology of activated protein C. In Holcenberg, J.S. and Winkelhake, J.L. eds.The Pharmacology and Toxicology of Proteins, UCLA Symposia on Molecular and Cellular Biology 65, 351–67. New York: Alan R. Liss, Inc.
Esmon, C.T. (1989) The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 4743–6.
Esmon, C.T. (1990) Regulation of coagulation: the nature of the problem. InProtein C and Related Anticoagulants, Advances in Applied Biotechnology Series 2, 3–10.
Fink, P.S. (1991) Using sodium chloride step gradients to fractionate DNA fragments.Bio Techniques 10, 447–9.
Foster, D.C., Yoshitake, S. and Davie, E.W. (1985) The nucleotide sequence of the gene for human protein C.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 82, 4673–7.
Foster, D.C., Holly, R.D., Sprecher, C.A., Walker, K.M. and Kumar, A.A. (1991) Endoproteolytic processing of the human protein C precursor by the yeast Kex2 endopeptidase coexpressed in mammalian cells.Biochemistry 30, 367–72.
Grinnell, B.W., Berg, D.T., Walls, J. and Yan, S.B. (1987)Trans-activated expression of fully gamma-carboxylated recombinant human protein C, an antithrombotic factor.Bio/Technology 5, 1189–92.
Grinnell, B.W., Walls, J.D., Berg, D.T., Boston, J., McClure, D.B. and Yan, S.B. (1989) Expression, characterization, and processing of recombinant human protein C from Adenovirus-transformed cell lines. In Hershberger, C.L., Queener, S.W. and Hegeman, G. edsGenetics and Molecular Biology of Industrial Microorganisms, pp. 226–37, Washington D.C.: American Society of Microbiologists.
Grinell, B.W., Walls, J.D., Gerlitz, B., Berg, D.T., McClure, D.B., Ehrlich, H., Bang, N.U. and Yan, S.B. (1990) Native and modified recombinant human protein C: function, secretion and posttranslational modifications. In Bruley, D.F. and Drohan, W.N. edsProtein C and Related Anticoagulants, pp. 29–63 Houston, Texas: Gulf Publishing Company.
Grinnell, B.W., Walls, J.D. and Gerlitz, B. (1991) Glycosylation of human protein C affects its secretion, processing, functional activities and activation by thrombin.J. Biol. Chem. 226, 9778–85.
Gruber, A., Griffin, J.H., Harker, L.A. and Hanson, R. (1989) Inhibition of platelet-dependent thrombus formation by activated protein C in a primate model.Blood 73, 639–42.
Hennighausen, L. (1990) The mammary gland as a bioreactor: production of foreign proteins in milk.Protein Expr. and Purif. 1, 3–8.
Hochstrasser, D.F., Harrington, M.G., Hochstrasser, A.C., Miller, M.J. and Merril, C.R. (1988) Methods for increasing the resolution of two-dimensional protein gel electrophoresis.Anal. Biochem. 173, 424–35.
Hogan, B., Constantini, F. and Lacy, E. (1986)Manipulating the Mouse Embryo: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Kang, K., Ryu, D., Drohan, W.N. and Orthner, C.L. (1992) Effect of matrices on affinity purification of protein C.Biotech. Bioeng. 39, 1086–96.
Kessler, C.M. and Strickland, D.K. (1987) Protein C and protein S clinical perspectives.Clin. Chim. Acta 170, 25–36.
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature 227, 680–5.
Maniatis, T., Fitsch, E.F. and Sambrook, J. (1982)Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Martinoli, J.L. and Stocker, K. (1986) Fast functional protein C assay using Protac, a novel protein C activator.Thromb. Res. 43, 253–64.
Odegaard, O.R., Try, K. and Andersson, T.R. (1987) Protein C: an automated activity assay.Hemostasis 17, 109–13.
Orthner, C.L., Battacharya, P. and Strickland, D.F. (1988) Characterization of a protein C activator from the venom of Agkistrodon contortix.Biochemistry 27, 2258–64.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A.R. (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 74, 5463–7.
Schramm, W., Spannagl, M., Bauer, K.A., Rosenberg, R.D., Birkner, B., Linnau, Y. and Schwarz, H.P. (1993) Treatment of coumarin-induced skin necrosis with a monoclonal antibody purified protein C concentrate.Arch. Dermatol. 129, 766–8.
Suttie, J.W. (1986) Report of workshop on expression of vitamin K-dependent proteins in bacterial and mammalian cells.Thromb. Res. 44, 129–34.
Tans, G., Janssen-Claessen, T. and Rosing, J. (1989) Amidolytic detection of prothrombin activation products after SDS-gel electrophoresis.Thromb. Haemost. 61, 386–91.
Taylor, F.B., Jr., Chang, A., Esmon, C.T., D'Angelo, A., Vigano-D'Angelo, S. and Blick, K.E. (1987) Protein C prevents the coagulopathic and lethal effects ofEscherichia coli infusion in the baboon.J. Clin. Invest. 79, 918–26.
Velander, W.H., Page, R.L., Morcol, T., Russell, C.G., Canseco, R., Young, J.M., Drohan, W.N., Gwazdauskas, F.C., Wilkins, T.D. and Johnson, J.L. (1992a) Production of biologically active protein C in the milk of transgenic mice.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 665, 391–403.
Velander, W.H., Johnson, J.L., Page, R.L., Russell, C.G., Subramanian, A., Wilkins, T.D., Gwazdauskas, F.C., Pittius, C. and Drohan, W.N. (1992b) High-level expression of a heterologous protein in the milk of transgenic swine using the cDNA encoding human protein C.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 12003–7.
Walls, J.D., Berg, D.T., Yan, S.B. and Grinnell, B.W. (1989) Amplification of multicistronic plasmids in the human 293 cell line and secretion of correctly processed recombinant human protein C.Gene 81, 139–49.
Yan, B.S., Grinnell, B.W. and Wold, F. (1989) Post-translational modification of protein: some problems left to solve.Trends in Biochemical Sci. 14, 264–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drohan, W.N., Zhang, DW., Paleyanda, R. et al. Inefficient processing of human protein C in the mouse mammary gland. Transgenic Research 3, 355–364 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976767
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976767