Summary
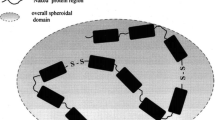
Mucus is the viscoelastic secretion that lines, most epithelial surfaces forming a protective, lubricating barrier. The viscoelastic properties of mucus arise from mucin, a glycoprotein of molecular weight ranging from 2–10 million. In this paper we address two problems where the aggregation and interactions of mucin with colloidal particles is of physiological relevance. The first deals with gastric mucin and the question of the mechanisms that prevent the stomach from digesting itself. Using dynamic light scattering techniques we show that solutions of gastric mucin aggregate below pH 4. Very large aggregates with 100-fold slower diffusion constants than the mucin monomer are observed at pH 2. Viscosity measurements indicate that mucin will eventually gel at low pH, thus acting as a diffusional, barrier and protecting the stomach. The second problem is concerned with the role of mucin in the nucleation of cholesterol crystals which lead to gallstone formation. Using dynamic light scattering we have shown that mucin at relatively low concentrations (4 mg/ml) promotes the fusion of phospholipid + cholesterol vesicles. The time evolution of the fusion process was measured. No changes in the aggregation state of the gallbladder mucin were observed during the fusion process, suggesting that this phenomenon is related to physico-chemical interactions between the polymer (mucin) and the colloidal particle (vesicle).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. W. Toribara, J. R. Gum, P. J. Culhane, R. E. Legace, J. W. Hickset al.J. Clin. Invest., 88, 1005 (1991).
G. J. Strous and J. Dekker: Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 27, 57 (1992).
J. R. Gum: Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol., 7, 557 (1992).
J. K. Sheehan, K. Oates and I. Carlstedt: Biochem. J., 239, 147 (1986).
R. Shogren, T. A. Gerken and N. Jentoft: Biochemistry, 28, 5525 (1989).
I. Carlstedt, H. Lindgren and J. K. Sheehan: Biochem. J., 213, 427 (1983).
K. V. Chace, B. Naziruddin, V. C. Desai, M. Flux and G. P. Sachdev: Exp. Lung Res., 15, 721 (1989).
R. Gupta, N. Jentoft, A. M. Jamieson and J. Blackwell: Biopolymers, 29, 347 (1990).
N. Jentoft: Trends Biochem. Sci., 15, 291 (1990).
M. E. McDonnel and A. M. Jamieson: Biopolymers, 15, 1283 (1976).
K. R. Bhaskar, D. Gong, R. Bansil, S. Pajevic, J. A. Hamilton, B. S. Turner and J. T. LaMont: Am. J. Physiol., 261 (Gastrointes. Liver Physiol., 24), G827 (1991).
S. W. Provencher, J. Hendrix, L. DeMaeyer and N. Laulsen: J. Chem. Phys., 69, 4273 (1978).
A. Allen: Structure and function of gastrointestinal mucus, in Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, edited by L. R. Johnsonet al., Vol. 1 (Raven, New York, N.Y., 1981), p. 617.
H. W. Davenport: Sci. Am., 226, 86 (1972).
K. R. Bhaskar, P. Garik, B. S. Turner, J. D. Bradley, R. Bansil, H. E. Stanley and J. T. LaMont: Nature, 360, 458 (1992).
N. H. Afdhal and B. F. Smith: Views Dig. Dis., 22, 13 (1990).
Z. Halpern, M. A. Dudley, A. Kibe, M. P. Lin, A. C. Brewer and R. T. Holzbach: Gastroenterology, 90, 875 (1986).
N. Duzgunes: Hepatol., 12, 675 (1990).
B. F. Smith: J. Lipid Res., 28, 1088 (1987).
B. F. Smith and J. T. LaMont: J. Biol. Chem., 259, 12170 (1984).
N. H. Afdhal, Niu Niu, N. N. David, R. Bansil, X. Cao, D. Gantz, D. M. Small and G. D. Offner: Validation of a resonance, energy transfer assay to examine vesicle fusion and cholesterol crystal nucleation from model bile, Hepatology (in press) (1995).
S. M. Ilett, A. Orrock, W. C. K. Poon and P. N. Pusey: Phys. Rev. E, 51, 1344 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansil, R., Cao, X., Afdhal, N.H. et al. Mucin: Aggregation and colloidal interactions of relevance to some biomedical problems. Nouv Cim D 16, 1411–1418 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02462025
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02462025