Abstract
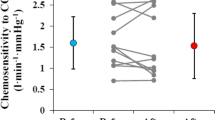
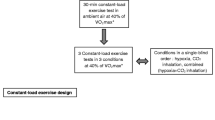
A method of assessing the respiratory response to a hypercapnic stimulus after an increase in alveolar pCO2 in accordance with an assigned program is suggested. The results are independent of the metabolic level, resistance to respiration, and other factors. Unlike the widely used rebreathing method, this new method enables the ventilatory sensitivity to CO2 to be compared at rest, during muscular work, when the resistance to respiration is changed, and so on. It can also be used for both clinical and experimental investigations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
D. J. C. Read, Aust. Ann. Med.,16, 20 (1966).
A. S. Rebuck, Chest,70, 118 (1976).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breslav, I.S., Volkov, B.N., Kalacheva, E.L. et al. Respiratory response to CO2 by controlled alveolar hypercapnia. Bull Exp Biol Med 89, 5–6 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00835484
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00835484