Abstract
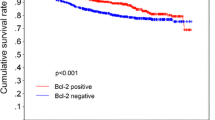
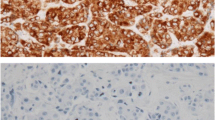
Experimental laboratory data suggest that tumour growth is a balance between apoptosis and proliferation and that suppression of drug-induced apoptosis by oncogenes such as bcl-2 may be an important cause of intrinsic chemoresistance. The aims of this study were to assess the in vivo relationship of apoptosis to proliferation and Bcl-2 protein in human breast tumours both prior to chemotherapy and in the residual resistant cell population at the completion of treatment. We examined apoptotic index (AI), Ki67 and Bcl-2 protein expression in the tissue of 40 patients with operable breast cancer immediately before ECF preoperative chemotherapy, and in 20 of these patients with residual tumour, at the completion of treatment. There was a significant positive association between AI and Ki67 both before and after chemotherapy, and in their percentage change with treatment. In the residual specimens AI and Ki67 were significantly reduced compared with pre-treatment biopsies, while Bcl-2 expression showed a significant increase. No differences were seen in the pre-treatment levels of any of the variables measured between patients obtaining pathological complete response and those who did not, although numbers were small. These data suggest that apoptosis and proliferation are closely related in vivo. It is possible that the phenotype of reduced apoptosis and proliferation, and increased Bcl-2 may be associated with breast cancer cells resistant to cytotoxic chemotherapy, although this can only be proven by assessing larger numbers of patients in relation to pathological response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR: Cell death: The significance of apoptosis. Internat Rev Cytol 68: 251-304, 1980
Hickman JA: Apoptosis induced by anticancer drugs. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11: 121-139, 1992
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nat 348: 334-336, 1990
Miyashita T, Reed JC: Bcl-2 oncoprotein blocks chemotherapy induced apoptosis in a human leukaemia cell line. Blood 81: 151-157, 1993
Kamesaki S, Kamesaki H, Jorgensen J, Tanizawa A, Pommier Y, Cossman J: Bcl-2 protein inhibits etoposide-induced apoptosis through its effects on events subsequent to topoisomerase 2-induced DNA strand breaks and their repair. Cancer Res 53: 4251-4256, 1993
Boise LH, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Postema CE, Ding L, Nunez G, Thompson CB: Bcl-x, a bcl-2 related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell 74: 597-608, 1993
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivowith a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74: 609-619, 1993
Reed JC: Bcl-2: Prevention of apoptosis as a mechanism of drug resistance. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 9: 451-474, 1995
Sumantran VN, Ealovega MW, Nunez G, Clarke MF, Wicha MS: Overexpression of bcl-x sensitizes MCF-7 cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 55: 2507-2510, 1995
Powles TJ, Hickish TF, Makris A, Ashley SE, O'Brien ME, Tidy VA, Casey S, Nash AG, Sacks N, Cosgrove D et al.: Randomized trial of chemoendocrine therapy started before or after surgery for treatment of primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 13: 547-552, 1995
Smith IE, Walsh G, Prendiville J, Johnston SRD, Ramage F, Robertshaw H, Sacks N, Ebbs S, McKinna JA, Baum M: High complete remissions with primary infusional chemotherapy for large early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 13: 424-429, 1995
Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Zucali R, Salvadori B: Primary chemotherapy in surgically resectable breast cancer. Ca Cancer J Clin 45: 227-243, 1995
Clarke RB, Laidlaw IJ, Jones LJ, Howell A, Anderson E: Effect of tamoxifen on Ki67 labelling index in human breast tumours and its relationship to oestrogen and progesterone receptor status. Brit J Cancer 67: 606-611, 1993
DeFriend DJ, Howell A, Nicholson RI, Anderson E, Dowsett M, Mansel RE, Blamey RW, Bundred NJ, Robertson JF, Saunders C, Baun M, Walton P, Sutcliffe E, Wakeling AE: Investigation of a new pure antioestrogen (ICI 182780) in women with primary breast cancer. Cancer Res 54: 408-414, 1994
Daidone MG, Silvestrini R, Luisi A, Mastore M, Benini E, Veneroni S, Brambilla C, Ferrari L, Greco M, Andreola S, Veronesi U: Changes in biological markers after primary chemotherapy for breast cancers. Int J Cancer 61: 301-305, 1995
Rasbridge SA, Gillett CE, Seymour AM, Patel K, Richards MA, Rubens RD, Millis RR: The effects of chemotherapy on morphology, cellular proliferation, apoptosis and oncoprotein expression in primary breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer 70: 335-341, 1994
Wijsman JH, Jonker R, Keijzer R, Van De Velde CJH, Cornelisse CJ, Van Dierendonck JH: A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: In situend-labelling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem 41: 7-12, 1993
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H: Use of the avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) and unlabelled antibody (PAP) procedure. J Histochem Cytochem 29: 577-580, 1981
Lipponen P, Aaltomaa S, Kosma VM, Syrjanen K: Apoptosis in breast cancer as related to histopathological characteristics and prognosis. Eur J Cancer 30A: 2068-2073, 1994
McClelland RA, Finlay P, Walker KJ, Nicholson D, Robertson JFR, Blamey RW: Automated quantitation of immunocytochemically localised oestrogen receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 50: 3545-3550, 1990
Bland JM, Altman DG: Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1: 307-310, 1986
Evan GI, Wyllie AH, Gilbert CS et al.: Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell 69: 119-129, 1992
Harris AL: What does BCL-2 mean in solid tumours - friend or foe? Ann Oncol 5: 388-390, 1994
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kosaka H, Kamiike W, Matsuda H, Tsujimoto Y: Prevention of hypoxia-induced cell death by Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. Nature 374: 811-814, 1995
Hockenbery DM, Oltvai ZN, Yin X-M, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell 75: 241-251, 1993
Reed JC: Regulation of apoptosis by bcl-2 family proteins and its role in cancer and chemoresistance. Curr Opinion Oncol 7: 541-546, 1995
Leek RD, Kaklamanis L, Pezzella F, Gatter KC, Harris AL: bcl-2 in normal human breast and carcinoma: association with oestrogen receptor-positive, epidermal growth factor receptor-negative tumours and in situcancer. Br J Cancer 69: 135-139, 1994
Gee JM, Robertson JF, Ellis IO, Willsher P, McClelland RA, Hoyle HB, Kyme SR, Finlay P, Blamey RW, Nicholson RI: Immunocytochemical localization of BCL-2 protein in human breast cancers and its relationship to a series of prognostic markers and response to endocrine therapy. Int J Cancer 59: 619-628, 1994
Gasparini G, Barbareschi M, Doglioni C, Dalla Palma P, Mauri FA, Boracchi P, Bevilacqua P, Caffo O, Morelli L, Verderio P, Pezella F, Harris AL: Expression of bcl-2 protein predicts efficacy of adjuvant treatments in operable node positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1: 189-198, 1995
Castle VP, Heidelberger KP, Bromberg J: Expression of the apoptosis suppressing protein BCL-2 in neuroblastoma is associated with unfavourable histology and n-myc amplification. Am J Pathol 143: 1543-1550, 1993
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM, Logothetis C, Chung LWK, Hsieh J, Tu S, Campbell ML: Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res 52: 6940-6944, 1992
Pezella F, Turley H, Kazu I, Tungekar MF, Dunnill MS, Pierce CB, Harris A, Gatter KC, Mason DY: bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. New Engl J Med 329: 690-694, 1993
Teixeira C, Reed JC, Pratt MAC: Estrogen promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance by a mechanism involving Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 55: 3902-3907, 1995
Krajewski SBC, Franssila K, Krajewska M, Veli-Matti W, Nlskanen E, Nordling S, Reed JC: Reduced expression of pro-apoptotic gene Bax is associated with poor response rates to combination chemotherapy and shorter survival in women with metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 4471-4478, 1995
Howell A, Harland RNL, Barnes DM, Baildam AD, Wilkinson MJS, Hayward E, Swindell R, Sellwood RA: Endocrine therapy for advanced carcinoma of the breast: relationship between the effect of tamoxifen upon concentrations of progesterone receptor and subsequent response to treatment. Cancer Res 47: 300-304, 1987
Johnston SRD, Saccani-Jotti G, Smith IE, Salter J, Newby J, Coppen M, Ebbs SR, Dowsett M: Changes in estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and pS2 expression in tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer. Cancer Res 55: 3331-3338, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellis, P., Smith, I., Detre, S. et al. Reduced apoptosis and proliferation and increased Bcl-2 in residual breast cancer following preoperative chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 48, 107–116 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005933815809
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005933815809