Abstract
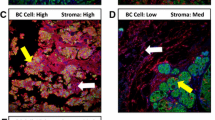
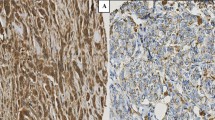
This study was aimed at investigating the influence of cathepsin D (CD) expression by cancer cells and stromal cells on breast cancer prognosis. This is a study of 1348 node‐positive (NPBC) and node‐negative (NNBC) breast cancers diagnosed between 1980 and 1986 and with a minimum follow‐up of 5.2 years. CD expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry on archival material using a polyclonal antibody. The expression by cancer and stromal cells was assessed separately and correlated with distant metastasis free (DMFS) and overall survival (OS). Cancer cells expressed CD (more than 10% cells expressing CD) in 38.9% of cases and reactive stromal cells in 43.6%. CD expression by reactive stromal cells, and not cancer cells, correlated with several factors of poor prognosis by cancer cells. A strong association was also found with expression of other proteases (stromelysin‐3, gelatinase A, and urokinase Plasminogen Activator) by these same reactive stromal cells. CD expression by cancer cells did not predict DMFS or OS but, by univariate analysis, CD expression by reactive stromal cells was associated with earlier recurrence and shorter survival in NNBC (p = 0.0425) and NPBC patients submitted to adjuvant chemotherapy (p = 0.0234). However, CD expression by reactive stromal cells remained a significant predictor of recurrence by multivariate analyses only in a subgroup of NPBC submitted to adjuvant chemotherapy. Overall, those data support the concept that proteases produced by reactive stromal cells are under cancer cell stimulation and that CD by stromal cells, and not cancer cells, influences the prognosis, but only in a subgroup of patients with breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrandina G, Scambia G, Bardelli F, Benedetti Panici P, Mancuso S, Messori A: Relationship between cathepsin-D content and disease-free survival in node-negative breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 76: 661–666, 1997
Isola J, Weitz S, Visakorpi T, Holli K, Shea R, Khabbaz N, Kallioniemi OP: Cathepsin D expression detected by immunohistochemistry has independent prognostic value in axillary node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 11: 36–43, 1993
Lösch A, Tempfer C, Kohlberger P, Joura EA, Denk M, Zajic B, Breitenecker G, Kainz C: Prognostic value of cathepsin D expression and association with histomorphological subtypes in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 78: 205–209, 1998
Domagala W, Striker G, Szadowska A, Dukowicz A, Weber K, Osborn M: Cathepsin D in invasive ductal NOS breast carcinoma as defined by immunohistochemistry. No correlation with survival at 5 years. Am J Pathol 141: 1003–1012, 1992
Kandalaft PL, Chang KL, Ahn CW, Traweek ST, Mehta P, Battifora H: Prognostic significance of immunohistochemical analysis of cathepsin D in low-stage breast cancer. Cancer 71: 2756–2763, 1993
Henry JA, McCarthy AL, Angus B, Westley BR, May FEB, Nicholson S, Cairns J, Harris AL, Home CHW: Prognostic significance of the estrogen-regulated protein, cathepsin D, in breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Cancer 65: 265–271, 1990
Têtu B, Brisson J, Côté C, Brisson S, Potvin D, Roberge N: Prognostic significance of cathepsin D expression in nodepositive breast carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study. Int J Cancer 55: 429–435, 1993
Joensuu H, Toikkanen S, Isola J: Stromal cell cathepsin D expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 71: 156–159, 1995
Nadji M, Fresno M, Nassiri M, Conner G, Herrero A, Morales AR: Cathepsin D in host stromal cells, but not in tumor cells, is associated with aggressive behavior in node-negative breast cancer. Hum Pathol 27: 890–895, 1996
O'Donoghue AEMA, Poller DN, Bell JA, Galea MH, Elston CW, Blamey RW, Ellis IO: Cathepsin D in primary breast carcinoma: adverse prognosis is associated with expression of cathepsin D in stromal cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 33: 137–145, 1995
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H: Use of avidin–biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29: 577–580, 1981
Dressler LG, Bartow SA: DNA flow cytometry in solid tumors: practical aspects and clinical applications. Sem Diagn Pathol 6: 55–82, 1989
Erdos T, Best-Belpomme M, Bessada R: A rapid assay for binding estradiol to uterine receptor(s). Anal Biochem 37: 244–252, 1970
Wolf C, Rouyer N, Lutz Y, Adida C, Loriot M, Bellocq JP, Chambon P, Basset P: Stromelysin-3 belongs to a subgroup of proteinases expressed in breast carcinoma fibroblastic cells and possibly implicated in tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 1843–1847, 1993
Kaplan EL, Meier P: Non-parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Amer Statist Assoc 53: 453–481, 1958
Armitage P: Statistical Methods in Medical Research. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1991
Cox DR: Regression models and lifetables (with discussion). JR Statist Soc 34: 187–220, 1972
Ravdin PM, Tandon AK, Allred DC, Clark GM, Fuqua SA, Hilsenbeck SH, Chamness GC, Osborne CK: Cathepsin D by western blotting and immunohistochemistry: failure to confirm correlations with prognosis in node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 12: 467–474, 1994
Winstanley JH, Leinster SJ, Cooke TG, Westley BR, Platt HA, Rudland PS: Prognostic significance of cathepsin-D in patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer 67: 767–772, 1993
Johnson MD, Tori JA, Lippman ME, Dickson RB: The role of cathepsin D in the invasiveness of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 53: 873–877, 1993
Tandon AK, Clark GM, Chamness GC, Chirgwin JM, McGuire WL: Cathepsin D and prognosis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 322: 297–302, 1990
Duffy MJ, Brouillet JP, Reilly D, McDermott E, O'Higgins N, Fennelly JJ, Maudelonde T, Rochefort H: Cathepsin D concentration in breast cancer cytosols: correlation with biochemical, histological, and clinical findings. Clin Chem 37: 101–104, 1991
Romain S, Muracciole X, Varette I, Bressac C, Brandone H, Martin PM: La cathepsine D: un facteur pronostique indépendant dans le cancer du sein. Bull Cancer Paris 77: 439–447, 1990
Spyratos F, Maudelonde T, Brouillet JP, Brunet M, Defrenne A, Andrieu C, Hacene K, Desplaces A, Rouesse J, Rochefort H: Cathepsin D: an independent prognostic factor for metastasis of breast cancer. Lancet 2: 1115–1118, 1989
Razumovic JJ, Stojkovic RR, Petrovecki M, Gamulin S: Correlation of two methods for determination of cathepsin D in breast carcinoma (immunohistochemistry and ELISA in cytosol). Breast Cancer Res Treat 43: 117–122, 1997
Roger P, Montcourrier P, Maudelonde T, Brouillet JP, Pages A, Laffargue F, Rochefort H: Cathepsin D immunostaining in paraffin-embedded breast cancer cells and macrophages: correlation with cytosolic assay. Hum Pathol 25: 863–871, 1994
Charpin C, Devictor B, Bonnier P, Andrac L, Lavaut MN, Allasia C, Piana L: Cathepsin D immunocytochemical assays in breast carcinomas: image analysis and correlation to prognostic factors. J Pathol 170: 463–470, 1993
Ravdin PM, Chamness GC: The c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene as a prognostic and predictive marker in breast cancer: a paradigm for the development of other macromolecular markers – a review. Gene 159: 19–27, 1995
Têtu B, Brisson J: Prognostic significance of HER-2/neu oncoprotein expression in node-positive breast cancer. The influence of the pattern of immunostaining and adjuvant therapy.Cancer 73: 2359–2365, 1994
Pupa SM, Bufalino R, Invernizzi AM, Andreola S, Rilke F, Lombardi L, Colnaghi MI, Menard S: Macrophage infiltrate and prognosis in c-erbB-2-overexpressing breast carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 14: 85–94, 1996
Leek RD, Lewis CE, Whitehouse R, Greenall M, Clarke J, Harris AL: Association of macrophage infiltration with angiogenesis and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 56: 4625–4629, 1996
Noël AC, Polette M, Lewalle JM, Munaut C, Emonard HP, Birembaut P, Foidart JM: Coordinate enhancement of gelatinase A mRNA and activity levels in human fibroblasts in response to breast-adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 56: 331–336, 1994
Ito A, Nakajima S, Sasaguri Y, Nagase H, Mori Y: Co-culture of human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells and human dermal fibroblasts enhances the production of matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2 and 3 in fibroblasts. Br J Cancer 71: 1039–1045, 1995
Biswas C, Zhang Y, DeCastro R, Guo H, Nakamura T, Kataoka H, Nabeshima K: The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res 55: 434–439, 1995
Gasparini G, Harris L: Clinical importance of the determination of tumor angiogenesis in breast carcinoma: much more than a new prognostic tool. J Clin Oncol 13: 765–782, 1995
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis – correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324: 1–8, 1991
Hildenbrand R, Dilger I, Horlin A, Stutte HJ: Urokinase plasminogen activator induces angiogenesis and tumor vessel invasion in breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract 191: 403–409, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Têtu, B., Brisson, J., Lapointe, H. et al. Cathepsin D expression by cancer and stromal cells in breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study of 1348 cases. Breast Cancer Res Treat 55, 135–145 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006140213493
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006140213493