Abstract
Objective: The association of known prognostic factors with immune cell counts and β2-microglobulin and soluble IL-2 receptor (sIL-2r) serum levels as markers of activation of the immune system was investigated in breastcancer.
Methods: Two hundred thirty five operated stage I and II breast cancer patients to receive adjuvant treatment in IBSCG trials were assessed in a cross-sectional study immediately before the first treatment. Leukocytes, lymphocytes and lymphocyte subset counts, β2-microglobulin and sIL-2r serum levels were assessed as immunological parameters. Prognostic factors were tumor load, receptor status, patient characteristics, and contextual factors of the immune assessment (such as time of the day, time since surgery, type of surgery, concomitant medication, co-morbidity).
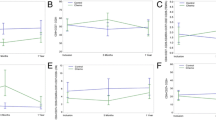
Results: In an operated early stage breast cancer patient population, tumor load was not associated with immune cell counts, β2-microglobulin, or sIL-2r before adjuvant treatment. There was a pattern of association of prognostically favorable factors such as estrogen receptor (ER) positive tumor and older age with higher NK cell counts or with β2-microglobulin or sIL-2r. In addition, immune cell counts and the markers of activation of the immune system were affected by several contextual factors, such as diurnal variability, time since surgery, type of surgery, and the intake of concomitant medication.
Conclusions: The association of NK cell counts and β2-microglobulin or sIL-2r serum levels with prognostically favorable factors such as ER positive tumor and older age supports the assumption that the immune system plays a role in the course of early breast cancer. The exact nature of this role requires furtherstudy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pober JS: Cellular and Molecular Immunology. 2nd Edn. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1994
Mitchel RJ: The delayed hypersensitivity response in primary breast carcinoma as an index of host resistance. Br J Surg 59: 505–508, 1972
Roberts MM, Jones Williams W: The delayed hypersensitivity reaction in breast cancer. Br J Surg 61: 549–522, 1974
Nemoto T, Han T, Minowada J, Angkur V, Chamberlain A, Dao TL: Cell-mediated immune status of breast cancer patients: Evaluation by skin tests lymphocyte stimulation, and counts of rosette-forming cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 53: 641–671, 1974
Catalona WJ, Sample WF, Chretien PB: Lymphocyte reactivity in cancer patients: Correlation with tumor histology and clinical stage. Cancer 31: 65–71, 1973
Head JF, Elliot RL, McCoy JL: Evaluation of lymphocyte immunity in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 26: 77–88, 1993
Garner WL, Minton JP, James AG, Hoffmann CC: Human breast cancer and impaired NK cell function. J Surg Oncol 24(1): 64–66, 1983
Klein B, Levin I, Kfir B, Mishaeli M, Shapira J, Klein T: The significance of soluble interleukin-2, soluble interleukin-2 receptor, soluble ICAM-1 and β2-microglobulin in breast cancer. Tumor Biol 16: 290–296, 1995
Thomas L (Hrsg): Labor und Diagnose. 4. Auflage. Medizinische Verlagsgesellschaft, Marburg, 1995
Abbate I, Correale M, Gargano G, Tedone T, Izzi G, Catino A: Musci MD, Dragone D, Cramarossa A. Tumor necrosis factor and soluble interleukin-2 receptor: two immunological biomarkers in female neoplasm. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 13 (1 Suppl): 92–96, 1992
Sarandakou A, Phocas I, Sikiotis K, Rizos D, Botsis D, Kalambokis K, Trakakis E, Chryssikopoulos A: Cytokines in gynecological cancer. Anticancer Res 17 (5B): 3835–3839, 1997
Kimber CL, Stomski FC, Blunden RW: Cancer of the breast and beta 2 microglobulin. Pathology 19 (1): 67–70, 1987
Mulder H, Euser R, Winckers P, Schop C: Is serum beta 2 microglobulin a useful marker in patients with breast cancer? Anticancer Res 5(3): 321–322, 1985
Focan C: Circadian rhythms and cancer chemotherapy. Pharmac Ther 67 (1): 1–52, 1995
McCulloch PG, Maclntyre A: Effects of surgery on the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells in patients witth breast cancer. Br J Surg 80(8): 1005–1007, 1993
Shephard RJ, Shek PN: Interactions between sleep, other body rhythms, immune responses and exercise. Can J Appl Physiol 22 (2): 95–116, 1997
International Breast Cancer Study Group: Duration and reintroduction of adjuvant chemotherapy for nodes-positive premenopausal breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 14: 1885–1894, 1996
International Breast Cancer Study Group: Effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy in combination with tamoxifen for node-positive postmenopausal breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 15: 1385–1394, 1997
Cuzick J: A Wilcoxon-type test for trend. Stat Med 4: 87–90, 1985
Brunson KW, Goldfarb RH: Immunosuppression by metastatic tumors. In: Herberman RB (ed.) Influence of the host on tumor development. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989, pp 133–138
Levy SM, Herberman RB, Lee J, Whitside T, Kirkwood J, McFeely S: Estrogen receptor concentration and social factors as predictors of natural killer cell activity in early-stage breast cancer patients. Confirmation of a model. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul 9(5) 313–324, 1990
Zielinski CC, Tichatschek E, Muller C, Kalinowski W, Sevelda P, Czerwenka K, Kubista E Spona: Association of increased lytic effector cell function with high estrogen receptor levels in tumor-bearing patients with breast cancer. J Cancer 63(10): 1985–1989, 1989
Wiltschke C, Tyl E, Speiser P, Steininger A, Zeillinger R, Kury F, Czerwenka K Kubista E, Preis P, Krainer M, Zielinski CC: Increased natural killer cell activity correlates with low or negative expression of Her-2/neu oncogene in patients with breast cancer. Cancer 73: 135–139, 1994
Garner WL, Minton JP, James AG, Hoffmann CC: Human breast cancer and impaired NK cell function. J Surg Oncol 24(1): 64–66, 1983
Goodwin JS: Decreased immunity and increased morbidity in the elderly. Nutrition Rev 53 (4): (II) S41–S46, 1995
Riesco A: Five year cancer cure: relation to total amount of peripheral lymphocytes and neutrophils. Cancer 37: 135–140, 1970
Papetestas AE, Lesnick GJ, Genkins G Aufses AHJ: The prognostic significance of peripheral lymphocyte counts in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 37: 164, 1976
Bruckner HW, Lavin PT, Plaxe SC, Stroch JA, Livstione EM: Absolute granulocyte, lymphocyte and monocyte counts. Useful determinants of prognosis for patients with metastatic cancer of the stomach. JAMA 247: 1004–1006, 1982
Mills PJ, Ziegler MG, Dimsdale JE, Parry BL: Enumerative immune changes following acute stress: effect of the menstrual cycle. Brain Behavior Immunity 9: 190–195, 1995
Grossman CJ. Regulation of the immune system by sex steroids. Endocr Rev 5: 435–455, 1984
Schuurs AHWM, Verheul HAM: Effect of gender and sex steroids on the immune response. J Steroid Biochem 35: 157–172, 1990
Kronfol Z, Nair M, Zhang Q, Hill EE, Brown MB: Circadian immune measures in healthy volunteers: Relationship to hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hormones and sympathetic neurotransmitters Psychosomatic Medicine 59: 42–50, 1997
Nieman DC, Cook VD, Henson DA, Suttles J, Rejeski WJ, Ribisl PM, Fagoaga OR, Nehlsen-Cannarella SL: Moderate exercise training and natural killer cell cytotoxic activity in breast cancer patients. Int J Sports Med 16(5): 334–337, 1995
Fuchs J, Matzinger P: Is cancer dangerous to the immune system? Semin Immunol 8: 271–280, 1998
Wei W-Z, Heppner GH: Breast cancer immunology. Cancer Treat Res 83: 395–410, 1996
Stewart THM, Tsai S-CJ: The possible role of stromal cell stimulation in worsening the prognosis of a subset of patients with breast cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 11: 295–305, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbioni, M.E., Siegrist, H.P., Bacchi, M. et al. Association between immunity and prognostic factors in early stage breast cancer patients before adjuvant treatment. Breast Cancer Res Treat 59, 279–287 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006379925343
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006379925343