Abstract
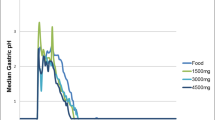
We compared the bioavailability and the efficacy of omeprazole provided either as encapsulated enteric-coated granules or as enteric-coated granules delivered via a nasogastric tube in 10 healthy subjects. Omeprazole reduced mean pentagastrin-stimulated peak gastric acid secretion by 85.5%±23.7% when delivered orally and by 79.6%±32.1% when delivered by nasogastric tube; the mean plasma omeprazole concentration area under the curve (AUC) was 2.02±0.79 after oral delivery and 1.74±1.89 after nasogastric tube delivery. There was no significant difference in these parameters between the two routes of administration, and there was excellent intrasubject correlation between oral and nasogastric percent acid suppression and AUC. There was a close correlation between AUC and percent acid suppression at AUC values below 0.6, and complete acid suppression at AUC values above 0.6, regardless of the delivery route. We conclude that omeprazole delivered as enteric-coated granules via nasogastric tube provides equal bioavailability and gastric acid suppression as omeprazole given orally in its proprietary formulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MH, Ostrosky JD, Kirkwood CF: Drug review. Therapeutic evaluation of ompeprazole. Clin Pharmacol 7:725–745, 1988
Lind T, Cederberg C, Ekenved G, Haglund U, Olbe L: Effect of omeprazole—a gastric proton pump inhibitor—on pentagastrin stimulated acid secretion in man. Gut 24:270–276, 1983
Cederberg C, Thomson AB, Mahachai V, Westin JA, Kirdeikis P, Fisher D, Zuk L, Marriage B: Effect of intravenous and oral omeprazole on 24-hour intragastric acidity in duodenal ulcer patients. Gastroenterology 103:913–918, 1992
Pilbrant A, Cederberg C: Development of an oral formulation of omeprazole. Scand J Gastroenterol 20(suppl 108):113–120, 1985
Woods DJ, McClintock AD: Omeprazole administration. Ann Pharmacother 27:651, 1993 (letter)
Earnest DL: Controlling gastric pH: The impact of newer agents on the critically ill patient. DICP Ann Pharmacother 24(suppl):S31-S34, 1990
Astra Merck: Administration of PRILOSEC through a tube into the stomach or small intestine. In house literature, 1995
Jansen J, Lundborg P, Baak L, Green J, Ohman M, Stover C, Rohss K, Lamers C: Effect of single and repeated intravenous doses of omeprazole on pentagastrin-stimulated gastric acid secretion and pharmacokinetics. Gut 29:75–80, 1988
Anon: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists drug monograph for pentagastrin (selected revision). Jan 1992:1475–1476
Lagerstrom PO, Persson BA: Determination of omeprazole and metabolites in plasma and urine by liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 309:347–356, 1984
Howden CW, Forrest JAH, Reid JL: Effects of single and repeated doses of omeprazole on gastric acid and pepsin secretion in man. Gut 25:707–710, 1984
Wilson JA, Boyd EJS, Wormsley KG: Omeprazole inhibits nocturnal and pentagastrin-stimulated gastric secretion in man. Dig Dis Sci 29:797–801, 1984
Wallmark B, Brandstrom A, Larsson H: Evidence for acid-induced transformation of omeprazole into an active inhibitor of (H+/K+)-ATPase within the parietal cell. Biochim Biophys Acta 778:549–558, 1984
Andersson T: Pharmacokinetics of omeprazole in man, with special reference to single and repeated administration, drug interactions and polymorphic metabolism. PhD thesis. University of Goteberg, 1991
Pilbrant A, Cederberg C: Development of an oral formulation of omeprazole. Scand J Gastroenterol 108(suppl):113–120, 1985
Bogentoft C, Carlsson I, Ekenved G, Magnusson A: Influence of food on the absorption of acetylsalicylic acid from enteric-coated dosage forms. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 14:351–355, 1978
Utley RJ, Wright R, Beastall GH, Carter DC: The effect of omeprazole on insulin-induced gastric secretion in man. Scott Med J 30:96–100, 1985
Londong W, Londong V, Cedeberg C, Steffen H: Doseresponse study of omeprazole on meal-stimulated gastric acid secretion and gastrin release. Gastroenterology 85:1373–1378, 1983
Anderson T, Andren K, Cederberg C, Lagerstrom PO, Lundborg P, Skanberg I: Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of omeprazole after single and repeated oral administration in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 29:557–563, 1990
Andersson T, Regardh CG, Dahl-Puustinen ML, Bertilsson L: Slow omeprazole metabolizers are also poorS-mephenytoin hydroxylators. Ther Drug Monit 12:415–416, 1990
Balian JD, Sukhova N, Harris JW, Hewett J, Pickle L, Goldstein JA, Woosley RL, Flockhart DA: The hydroxylation of omeprazole correlates withS-mephenytoin metabolism: A population study. Clin Pharmacol Ther 57:662–669, 1995
Kupfer A, Preisig R: Pharmacogenetics of mephenytoin: A new drug hydroxylation polymorphism in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26:753–759, 1984
Nakamura K, Goto F, Ray WA, McAllister CB, Jacqz E, Wilkinson GR, Branch RA: Interethnic differences in genetic polymorphism of debrisoquin and mephenytoin hydroxylation between Japanese and Caucasian populations. Clin Pharmacol Ther 38:402–408, 1985
Bertilsson L, Lou Y, Du Y, Liu Y, Kuang T, Liao X, Wang K, Reviriego J, Iselius L, Sjoqvist F: Pronounced differences between native Chinese and Swedish populations in the polymorphic hydroxylations of debrisoquin andS-mephenytoin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 51:388–397, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the General Clinical Research Center of The Bowman Gray School of Medicine, M01-RR07122, and an educational grant from Astra-Merck.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larson, C., Cavuto, N.J., Flockhart, D.A. et al. Bioavailability and efficacy of omeprazole given orally and by nasogastric tube. Digest Dis Sci 41, 475–479 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02282321
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02282321