Abstract
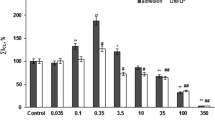
We analyzed DNA-fragmentation in human polymorphonuclear neutrophil granulocytes (PMNs) from healthy donors after addition of exogenous arachidonic acid (AA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by flow cytometry (propidium iodide staining of DNA and DNA strand break detection). The PMNs were incubated from 30 min up to 48 hours in RPMI 1640 which was supplemented with different concentrations of AA or EPA (5–40 μM). In contrast to EPA the addition of AA led to a significant increase in apoptosis up to 67.8% compared to the RPMI-control whereas the addition of EPA led to an inhibition of DNA-fragmentation. When the cells were incubated with MK 886 (1μM, inhibitor of leukotriene biosynthesis) an increase in DNA-fragmentation (up to 63.3%) was observed. Conversely, in the presence of indomethacin (1μM, inhibitor of prostanoid synthesis) an inhibition in DNA-fragmentation (up to 60.9%) occurred. Furthermore, preincubation of PMNs with pentoxifylline (1mM, phosphodiesterase inhibitor) reduced AA-stimulated DNA-fragmentation up to 43.4%. These data provide evidence for the involvement of AA and distinct AA metabolites in the regulation of apoptosis in human PMNs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
SQUIER, M. K. T., A. J. SEHNERT, and J. J. COHEN. 1995. Apoptosis in leukocytes. J. Leuko. Biol. 57:2–10.
COHEN, J. J. 1993. Apoptosis. Immunol. Today 14:26–130.
COHEN, J. J., and R. C. DUKE. 1992. Apoptosis and programmed cell death in immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 10:267–293.
WYLLIE, A. H., J. F. KERR, and A. R. CURRIE. 1980. Cell death: The significance of apoptosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 68:251–306.
COLOTTA, F., F. RE, N. POLENTARUTTI, S. SOZZANI, and A. MANTOVANI. 1992. Modulation of granulocyte survival and programmed cell death by cytokines and bacterial products. Blood 80:2012–2020.
SAVILL, J. S., A. H. WYLLIE, J. E. HENSON, M. J. WALPORT, P. M. HENSON, and C. HASLETT. 1989. Macrophage phagocytosis of aging neutrophils in inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 83:865–875.
GRIGG, J. M., J. S. SAVILL, C. SARRAF, C. HASLETT, and M. SILVERMAN. 1991. Neutrophil apoptosis and the clearance from neonatal lungs. Lancet 338:720–722.
WESTCOTT, J. Y., R. C. MURPHY, and K. STENMARK. 1987. Eicosanoids in human ventricular cerebrospinal fluid following severe brain injury. Prostaglandins 34:877–887.
BARR, R. M., K. J. MISCH, C. N. HENSBY, A. I. MALLET, and M. W. GREAVES. 1983. Arachidonic acid and prostaglandin levels in ditranol erythema: time course study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 16:715–717.
KÖOLLER, M., and W. KÖNIG. 1990. Arachidonic acid metabolism in heat shock treatment human leukocytes. Immunology 70:458–464.
NICOLETTI, I., G. MIGLIORATI, M. C. PAGLIACCI, F. GRIGNANI, and C. RICCARDI. 1991. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J. Immunol Meth. 123:271–279.
SGONC, R., G. BOECK, H. DIETRICH, J. GRUBER, H. RECHEIS, and G. WICK. 1994. Simultaneous determination of cell surface antigens and apoptosis. Trends Genet. 10:41–42.
ELBIM, C., M. LEFEBVRE, J. HAKIM, and M. A. GOUGEROT-POCIDALO. 1995. Effect of pentoxifylline on human polymorphonuclear neutrophil responses to TNF in whole blood. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 6:113–120.
HORIGUCHI, J., D. SPRIGGS, K. IMAMURA, R. STONE, R. LUEBBERS, and D. KUFE. 1989. Role of arachidonic acid metabolism in transcriptional induction of tumor necrosis factor gene expression by phorbol ester. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:252–258.
SMITH, J. A. 1994. Neutrophils, host defense, and inflammation: a double-edged sword. J. Leuko. Biol. 56:672–686.
GAVRIELI, Y., Y. SHERMAN, and S. A. BEN-SASSON. 1992. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J. Cell. Biol. 119:493–501.
COLLINS, R. J., B. V. HARMON, G. C. GOBÉ, and J. F. R. KERR. 1992. Internucleosomal DNA cleavage should not be the sole criterion for identifying apoptosis. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 61:451–453.
GORCZYCA, W., K. BIGMAN, A. MITTELMAN, T. AHMET, J. GONG, M. R. MELAMED, and Z. DARZYNKIEWIECZ. 1993. Induction of DNA strand breaks associated with apoptosis during treatment of leukemias. Leukemia 7:659–670.
GOLD, R., M. SCHMIED, G. GIEGERICH, H. BREITSCHOPF, H. P. HARTUNG, K. V. TOYKA, and H. LASSMANN. 1994. Differentiation between cellular apoptosis and necrosis by the combined use of in situ tailing and nick translation techniques. Lab. Invest. 71:219–225.
LEE, A., M. K. S. WHYTE, and C. HASLETT. 1993. Inhibition of apoptosis and prolongation of neutrophil functional longevity by inflammatory mediators. J. Leuko. Biol. 54:283–288.
BELL, A. C., M. K. MAGILL, R. MCKANE, and A. E. IRVINE. 1995. Human blood and synovial fluid neutrophils cultured in vitro undergo programmed cell death which is promoted by the addition of synoial fluid. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 54:910–913.
TERANO, T., J. A. SALMON, and S. MONCADA. 1984. Biosynthesis and biological activity of leukotriene B5. Prostaglandins 27:217–223.
LILES, W. C., D. C. DALE, and S. J. KLEBANOFF. 1995. Glucocorticoids inhibit apoptosis of human neutrophils. Blood 86:3181–3188.
AVIS, I. M., M. JETT, T. BOYLE, M. D. VOS, T. MOODY, A. M. TRESTON, A. MARTINEZ, and J. L. MULSHINE. 1996. Growth control of lung cancer by interruption of 5-lipoxygenase-mediated growth factor signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 97:806–813.
ANDERSON, K., T. SEED, F. ONDREY, and J. HARRIS. 1994. The selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor A63162 reduces PC3 proliferation and initiates morphologic changes consistent with secretion. Anticancer Res. 14:1951–1960.
KROEMER, G., P. PETIT, N. ZAMZAMI, J.-L. VAYSSIERE, and B. MIGNOTTE. 1995. The biochemistry of programmed cell death. FASEB J. 9:1277–1287.
HACHIYA, O., Y. TAKEDA, H. MIYATA, H. WATERNABE, T. YAMASHITA, and F. SENDO. 1995. Inhibition of bacterial lipopolysaccharide of spontaneous and TNF-α-induced human neutrophil apoptosis in vitro. Microbiol. Immunol. 39:715–723.
SPIEGEL, S., D. FOSTER, and R. KOLESNICK. 1996. Signal transduction through lipid second messengers. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 8:159–167.
CHANG, D. J., G. M. RINGOLD, and R. A. HELLER, 1992. Cell killing and induction of manganous superoxide dismutase by tumor necrosis factor-α is mediated by lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 188:538–546.
ROSSI, A. G., J. M. COUSIN, I. DRANSFIELD, M. F. LAWSON, E. R. CHILVERS, and C. HASLETT. 1995. Agents that elevate cAMP inhibit human neutrophil apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 217:892–895.
LILES, W. C., and S. J. KLEBANOFF. 1995. Regulation of apoptosis in neutrophils-Fas track to death? J. Immunol. 154:3289–3291.
YOUSEFI, S., D. R. GREEN, K. BLASER, and H. U. SIMON. 1994. Protein-tyrosin phosphorylation regulates apoptosis in human eosinophils and neutrophils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91:10868–10872.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köller, M., Wachtler, P., Dávid, A. et al. Arachidonic Acid Induces DNA-Fragmentation in Human Polymorphonuclear Neutrophil Granulocytes. Inflammation 21, 463–474 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027326712091
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027326712091