Abstract
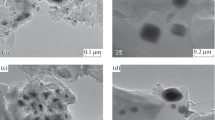
Air-stable new carbon composites containing uniformly dispersed ultrafine Fe, Co, Ni, Ru, Pd, Rh, or Ag particles were obtained by thermal degradation of coal pitches mixed homogeneously with 1–10% of poly(vinyl ferrocene), cobaltocene, nickelocene, (acenaphthylene) Ru3(CO)7, PdCl2(COD), RhCp(COD), and AgC6H4CH2NMe2, respectively, at 400–1200°C in Ar. Carbonization yields are 45–55% and the size of metal particles varied from 5 to 65 nm depending upon the treatment temperature and identity of the metal. The carbon composites containing Fe particles showed high Vicat hardness and good electrical conductivity. Pd- and Rh-dispersed materials exhibited good catalysis in hydrogenation of 1-hexene. The composite containing ultrafine Ag particles showed excellent bacteriostatic activity forEscherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, andBatchillus subtilis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. F. McClune, ed.,Powder Diffraction File, Inorganic Phase (JCPDS-International Center for Diffraction Data, Swarthmore, Pa., 1989).
J. G. Stevens, V. E. Stevens, P. T. Deason, Jr., A. H. Muir, Jr., H. M. Coogan, and R. W. Grant, eds.,Mössbauer Effect Data Index (1966–1968) (Plenum, New York, 1975).
H. Yasuda, S. Miyanaga, A. Nakamura, and H. Sakai,J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 1, 135 (1991).
Hayashi,J. Vacuum Sci. Tech.,A4, 1375 (1987).
J. O. Williams,Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. Adv. Mater. 28, 1110 (1989).
K. L. Kompa,Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 27, 13124 (1988).
H. Sato,Appl. Organomet. Chem. 3, 363 (1989).
H. Nagashima, T. Fukahori, and K. Itoh,Proc. 36th Symp. Organometal. Chem. Jap. A204 (1989).
J. J. Venter and M. A. Vannice,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111, 2377 (1989).
J. Chatt and L. M. Venanz,J. Chem. Soc. 4735 (1975).
D. Drew and J. R. Doyle,Inorg. Synth. 12, 52 (1972).
J. Gozum, D. M. Pollina, J. A. Jensen, and G. S. Gilolami,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110, 2688 (1988).
T. Chang, S. L. Bernasek, and J. Schwartz,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111, 758 (1989).
A. J. Leusink, G. Van Koten, and J. G. Noltes,J. Organomet. Chem. 56, 379 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasuda, H., Hiwara, A., Nakamura, A. et al. New carbon composites containing ultrafine metal particles. 2. Synthesis by pyrolisis of pitch-organometallic blends. J Inorg Organomet Polym 1, 239–244 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00701323
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00701323