Abstract
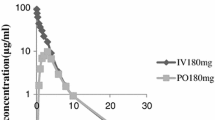
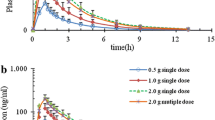
The pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime were investigated in human volunteers given constant intravenous infusions, intravenous bolus, and intramuscular doses of the drug. After intravenous dosing, the plasma levels of cefotaxime declined in a biphasic manner with a terminal half-life varying between 0.92 and 1.65 hr. Moreover, the pharmacokinetics were linear up to at least a 2.0 g dose for volume of distribution based on area (23.3–31.31), plasma clearance (249–288 ml/min), and renal clearance (151–177 ml/min). Renal tubular secretion of intact cefotaxime and each of its metabolites was demonstrated by its interaction with probenecid, although the ratio of drug to metabolites ultimately excreted in urine after probenecid was similar to that seen normally (54±6, 19±4, 6.5±0.7 and 5.5±0.7% for cefotaxime, DACM, M2, and M3, respectively, when calculated as a percentage of the dose). The observed half-lives of DACM, M2, and M3 were 2.3±0.4, 2.2 ±0.1 and 2.2 hr, respectively. However, when the true half-life of DACM was calculated (0.83±0.23 hr) it was not only significantly shorter than that observed but also shorter than that for intact cefotaxime. The plasma clearance of DACM (744 ±226 ml/min) was much higher than that of cefotaxime while the volume of distribution was of a similar order (56 ±241). When administered intramuscularly, there was good absorption of cefotaxime from the site of injection (92–94%) giving maximum plasma levels of the drug of between 30 and 35 mg/l at approximately 40 min after dosing. Thereafter, the plasma levels of cefotaxime declined in a monophasic manner with a half-life (1.0–1.2 hr) similar to that of the terminal half-life seen after intravenous administration. Lidocaine had no significant effect on either its absorption or elimination kinetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. A. Draser, W. Farrell, A. J. Howard, C. Hince, T. Leung, and J. D. Williams. Activity of HR 756 againstHaemophilus Influenzae, Bacteriodes fragilis, and gram-negative rods.J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 4:445–450 (1978).
G. Peters and G. Pulverer. Comparativein vitro activity of cefotaxime (HR756).Chemotherapy 26:177–183 (1980).
J. B. Sosna, P. R. Murray, G. Modoff. Comparison ofin vitro activities of HR756 with cephalothin, cefoxitin and cepharnandole.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 14:876–879 (1978).
M. H. Richmond.β-Lactamase stability of cefotaxime.J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 6(suppl A):13–17 (1980).
D. S. Reeves, L. O. White, H. A. Holt, D. Bahari, M. J. Bywater, and R. P. Bax. Human metabolism of cefotaxime.J. Antimicrob. Chemotherapy 6(suppl A):93–101 (1980).
J. Chamberlain, J. D. Coombes, D. Dell, J. M. Fromson, R. M. J. Ings, C. M. Macdonald, and J. McEwen. Metabolism of cefotaxime in animals and man.J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 6(suppl A):69–78 (1980).
E. Schrinner, M. Limbert, L. Penasse, and A. Lutz. Antibacterial activity of cefotaxime and other newer cephalosporins (in vitro andin vivo).J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 6(suppl A):25–30 (1980).
L. O. White, H. A. Holt, D. S. Reeves, M. J. Bywater, and R. P. Bax. Separation of assay of cefotaxime (HR756) and its metabolites in serum, urine, and bile. In J. D. Nelson, and C. Grassi (eds.),Current Chemotherapy and Infectious Disease. Proceedings of the 11th International Congress of Chemotherapy and the 19th Interscience Conference oq Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. The American Society for Microbiology, Washington D.C., 1980, pp. 153–154.
J. V. Bennett, J. L. Brodie, E. J. Benner, and W. M. N. Kirby. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens.Appl. Microbiol. 14:170–177 (1966).
F. Esmieu, J. Guilbert, H. C. Rosenkilde, I. Ho, and A. Le Go. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in normal human volunteers.J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 6(suppl A):83–92 (1980).
K. C. Yeh and K. C. Kwan. A comparison of numerical integrating algorithms by trapezoidal, lagrange, and spline approximation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:79–98 (1978).
J. B. Houston. Drug metabolite kinetics.Pharmacol. Ther. 15:521–552 (1982).
W. J. Dixon and F. J. Massey. Analysis of variance. InIntroduction to Statistical Analysis. McGraw-Hill Book Co. Inc., New York, 1969, pp. 150–187.
R. E. Walpole. Tests for paired observation. InIntroduction to Statistics. Collier-Macmillan International, London, 1972, pp. 236–241.
W. J. Westlake. Design and statistical evaluation of bioequivalence studies in man. In J. Blanchard, R. J. Sawchuk, and B. B. Brodie (eds.),Principles and Perspectives in Drug Bioavailability. S. Karger, Basel, 1979, pp. 192–209.
W. J. Westlake. The design and analysis of comparative blood-level trials. In J. Swarbrick (ed.),Current Concepts in Pharmaceutical Sciences, Dosage Form Design and Bioavailability. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 1973, pp. 149–179.
N. R. Draper and H. Smith. Fitting a straight line by least squares. In N. R. Draper and H. Smith (ed.),Applied Regression Analysis. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, 1966, pp. 7–26.
K. A. Browlee. Simple linear regression. In W. J. Dixon and F. J. Massey, Jr. (eds.),Introduction to Statistical Analysis. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1969, pp. 334–396.
K. P. Fu, P. Aswapokee, I. Ho, C. Matthigssen, and H. C. Neu. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 16:592–597 (1970).
R. Lüthy, R. Munch, J. Blaser, H. Bhend, and W. Siegenthaler. Human pharmacology of cefotaxime (HR756), a new cephalosporin.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 16:127–133 (1979).
R. Lüthy, J. Blaser, A. Bonetti, H. Simson, R. Wise, and W. Siegenthaler. Comparative multiple dose pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime, moxalactam and ceftazidime.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 20:567–575 (1981).
H. C. Neu, P. Aswapokee, K. P. Fu, I. Ho, and C. Matthigssen. Cefotaxime kinetics after intravenous and intramuscular injection of single and multiple doses.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 27:677–685 (1980).
P. Brazeau. Inhibitors of tubular transport of organic compounds. In L. S. Goodman and A. Gilman (eds.),The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 3rd edition, The Macmillan Company, New York, 1965, pp. 873–875.
M. Gibaldi and M. A. Schwartz. Apparent effect of probenecid on the distribution of penicillin in man.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 9:345–349 (1968).
D. S. Reeves, D. W. Bullock, M. J. Bywater, H. A. Holt, L. O. White, and D. P. Thornhill. The effect of probenecid on the pharmacokinetics and distribution of cefoxitin in healthy volunteers.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 11:353–359 (1981).
R. M. J. Ings, J. P. Fillastre, M. Godin, A. Leroy, and G. Humbert. The pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime and its metabolites in subjects with normal and impaired renal function.Rev. Infect. Dis. 4(suppl):S379–S391 (1982).
P. E. Gower and C. H. Dash. The pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime after intravenous injection.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 12:221–227 (1977).
M. Osmosu, O. Togashi, and K. Fugimoto. Pharmacokinetic study of cefotaxime in rabbits.Chemotherapy 28:116–121 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ings, R.M.J., Reeves, D.S., White, L.O. et al. The human pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime and its metabolites and the role of renal tubular secretion on their elimination. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 13, 121–142 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059394
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059394