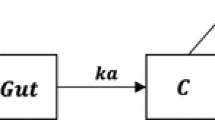
Abstract
Single input, single output experiments can result in nonunique solutions for the rate constants of a linear compartmental model used to describe the pharmacokinetics. Where a finite number of solutions exists, a priori knowledge has to be used to distinguish between the solutions. Where there is an infinite number of solutions, assumptions have to be made about the values of some rate constants in order to obtain a unique solution for the others. This paper considers such experiments and determines whether either the addition of an extra input (simultaneously with the first input) or the taking of an extra measurement would result in a unique solution. It is found that perturbing a second input can be useful, but only if the perturbation is of different shape from the first input. Measurements of drug in urine and metabolite in plasma are generally not helpful in resolving identifiability of the drug dynamic model. If a radioactive tracer is used, though, the second measurement (for example, by externally scanning the radioactivity of the liver) can prove useful, but only if the gain of the measuring device is known.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Bellman and K. J. Åström. On structural identifiability.Math. Biosci. 7:329–339 (1970).
K. Glover and J. C. Willems. Parametrization of linear dynamical systems: canonical forms and identifiability.IEEE Trans. Autom. Control AC-19:640–645 (1974).
R. F. Brown and K. R. Godfrey. Problems of determinacy in compartmental modelling with application to bilirubin kinetics.Math. Biosci. 40:205–224 (1978).
H. d'A. Heck, K. Maloney, and M. Anbar. Long-term urinary excretion of methaqualone in a human subject.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:111–122 (1978).
J. A. Jacquez.Compartmental Analysis in Biology and Medicine, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1972.
J. B. Waide, J. E. Krebs, S. P. Clarkson, and E. M. Setzler. A linear systems analysis of the calcium cycle in a forested watershed ecosystem.Prog. Theor. Biol. 3:261–345 (1974).
J. Wei.Catalysis and Reactors, Am. Inst. Chem. Eng., Monograph Series 6, Vol. 65, 1969.
M. Espana and I. M. Landau. Reduced-order bilinear models for distillation columns.Automatica 14:345–355 (1978).
R. F. Brown and J. P. Norton. Identifiability of large compartmental models. In2nd IFAC Symp. Large-Scale Systems, Toulouse, June 1980.
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier.Pharmacokinetics, Vol. 1 ofDrugs and the Pharmaceutical Sciences, J. Swarbrick (ed.), Marcel Dekker, New York, 1975.
J. G. Wagner.Fundamentals of Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamilton, Ill., 1975.
D. J. Cutler. On the definition of the compartment concept in pharmacokinetics.J. Theor. Biol. 73:329–345 (1978).
M. Rowland, L. Z. Benet, and S. Riegelman. Two-compartment model for a drug and its metabolite: application to acetylsalicylic acid pharmacokinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 59:364–367 (1970).
D. M. Foster, R. L. Aamodt, R. I. Henkin, and M. Berman. Zinc metabolism in humans: a kinetic model.Am. J. Physiol. 237:R340-R349 (1979).
S. Riegelman, M. Rowland, and L. Z. Benet. Use of isotopes in bioavailability testing.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:83–87 (1973).
R. F. Brown, E. R. Carson, L. Finkelstein, K. R. Godfrey, and R. P. Jones. Adequacy of measurements in compartmental modelling of metabolic systems.Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 17:216–222 (1979).
R. F. Brown. The identifiability of nonlinear compartmental models. InFifth IFAC Symp. Identification and System Parameter Estimation, Darmstadt, September 1979, Paper M11.5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The work described in this paper was supported by Grant No. GR/A 14827 from the U.K. Science Research Council.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Godfrey, K.R., Jones, R.P. & Brown, R.F. Identifiable pharmacokinetic models: The role of extra inputs and measurements. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 8, 633–648 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060058
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060058