Abstract
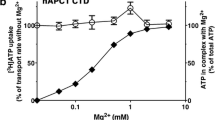
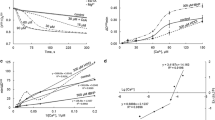
The regulatory role of Ca2+-stimulated adenosine 5′-triphosphatase (Ca2+-ATPase) in Ca2+ transport system of rat liver nuclei was investigated. Ca2+ uptake and release were determined with a Ca2+ electrode. Ca2+-ATPase activity was calculated by subtracting Mg2+-ATPase activity from (Ca2+−Mg2+)-ATPase activity. The release of Ca2+ from the Ca2+-loaded nuclei was evoked progressively after Ca2+ uptake with 1.0 mM ATP addition, while it was only slightly in the case of 2.0 mM ATP addition, indicating that the consumption of ATP causes a leak of Ca2+ from the Ca2+-loaded nuclei. The presence of N-ethylmaleimide (NEM; 0.1 mM) caused an inhibition of nuclear Ca2+ uptake and induced a promotion of Ca2+ release from the Ca2+-loaded nuclei. NEM (0.1 and 0.2 mM) markedly inhibited nuclear Ca2+-ATPase activity. This inhibition was completely blocked by the presence of dithiothreitol (DTT; 0.1 and 0.5 mM). Also, DTT inhibited the effect of NEM (0.1 mM) on nuclear Ca2+ uptake and release. Meanwhile, verapamil and diltiazem (10 μM), a blocker of Ca2+ channels, did not prevent the NAD+ (1.0 and 2.0 mM), zinc sulfate (1.0 and 2.5 μM) and arachidonic acid (10 μM)-induced increase in nuclear Ca2+ release, suggesting that Ca2+ channels do not involve on Ca2+ release from the nuclei. These results indicates that an inhibition of nuclear Ca2+-ATPase activity causes the decrease in nuclear Ca2+ uptake and the release of Ca2+ from the Ca2+-loaded nuclei. The present finding suggests that Ca2+-ATPase plays a critical role in the regulatory mechanism of Ca2+ uptake and release in rat liver nuclei.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rasmussen J: Cell communication, calcium ion, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science 170: 404–412, 1970
Williamson JR, Cooper RK, Hoek JB: Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 639: 243–295, 1981
Reinhart PH, Taylor WM, Bygrave FL: The role of calcium ions in the mechanisms of action of α-adrenergic agonists in rat liver. Biochem J 223: 1–13, 1984
Boyton AL, Whitfield JF, MacManus JP: Calmodulin stimulates DNA synthesis by rat liver cells. Biochim Biophys Res Commun 95: 745–749, 1980
Cruise J, Houck KA, Michalopoulos GK: Induction of DNA synthesis in cultured rat hepatocytes through stimulation of α-adrenoreceptor by norepinephrine. Nature 227: 749–751, 1985
Bachs O, Carafolli E Calmodulin and calmodulin-binding proteins in liver cell nuclei. J Biol Chem 262: 10786–10790, 1987
Jones DP, McConkey DJ, Nicotera P, Orrenius S: Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem 264: 6398–6403, 1989
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett 279: 281–284, 1991
Cheung WY: Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science 202: 19–27, 1980
Bachs O, Lanini L, Serratosa J, Coll MJ, Bastors R, Alique R, Rius E, Carafolli E: Calmodulin-binding proteins in the nuclei of quiescent and proliferatively activated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem 265: 18595–18600, 1990
Nicotera P, McConkey DJ, Jones DP, Orrenius S: ATP stimulates Ca2+ uptake and increases the free Ca2+ concentration in isolated rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 453–457, 1989
Yamaguchi M: Effect of calmodulin-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+ transport system in rat liver nuclei: Stimulation of Ca2+ release. Mol Cell Biochem 113: 63–70, 1992
Yamaguchi M: Regulatory effect of zinc and copper on the calcium transport system in rat liver nuclei. Relation to SH groups in the releasing mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol 45: 943–948, 1993
Oishi K, Yamaguchi M: Regulatory effect of arachidonic acid on the calcium transport system in rat liver nuclei. Biochem Pharmacol 45: 1471–1475, 1993
Oishi K, Yamaguchi M: Effect of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotides on Ca2+ transport system in rat liver nuclei: stimulation of Ca2+ release by NAD+. Mol Cell Biochem 121: 127–133, 1993
Yamaguchi M, Oishi K: Characterization of Ca2+-stimulated adenosine 5′ triphosphatase and Ca2+ sequestering in rat liver nuclei. Mol Cell Biochem 125: 43–49, 1993
Burton K: A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62: 315–323, 1956
Nakamura M, Mori K: Colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphorus in the presence of glucose-1-phosphate and adenosine triphosphate. Nature 182: 1441–1442, 1958
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall FJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–273, 1951
Graf P, Sies H: Hepatic uptake of cadmium and its biliary release as affected by dithiothreitol and glutathione. Biochem Pharmacol 33: 639–643, 1984
Cullen PJ, Conerford JG, Dowson AP: Heparin inhibits the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-induced Ca2+ release from rat liver microsomes. FEBS Lett 228: 57–59, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, M., Oishi, K. Involvement of Ca2+-stimulated adenosine 5′-triphosphatase in the Ca2+ releasing mechanism of rat liver nuclei. Mol Cell Biochem 131, 167–172 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925953
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925953