Abstract
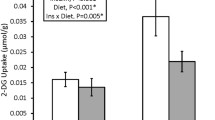
We have examined the independent and combined effects of insulin insufficiency (streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, 85 mg/kg i.p.) and reduced muscle activity (denervation) (7 days) on basal, insulin-stimulated and contraction-stimulated glucose transport in rat muscles (soleus, red and white gastrocnemius). There were four treatments: control, denervated, diabetic, and denervated + diabetic muscles. Contraction-stimulated glucose transport was lowered (~ 50%) (p < 0.05) to the same extent in all experimental groups. In contrast, there was a much smaller reduction insulin-stimulated glucose transport in muscles from diabetic animals (18-24% reduction, p < 0.05) than in denervated muscles (40-60% reduction, p < 0.05) and in denervated + diabetic muscles (40-60% reduction, p < 0.05). GLUT-4 mRNA reduction was greatest in denervated + diabetic muscles (~ -75%, p < 0.05). GLUT-4 protein was decreased (p < 0.05) to a similar extent in all three experimental conditions (~ -30-40%). In conclusion, (1) muscle inactivity (denervation) and STZ-induced diabetes had similar effects on reducing contraction-stimulated glucose transport, but (2) muscle inactivity (denervation), rather than severe diabetes, produced a 2-fold greater impairment in skeletal muscle insulin-stimulated glucose transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell GI, Kayano T, Buse JB, Burant CF, Takeda J, Lin D, Fukumoto H, Seino S: Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diab Care 13: 198–208, 1990
Brozinick JT Jr, Etgen GJ Jr, Yaspelkis BB III, Ivy JL: The effects of muscle contraction and insulin on glucose transporter translocation in rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J 297: 539–545, 1994
James DE, Brown R, Navarro J, Pilch PF: Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature 333: 183–185, 1988
Garvey TW, Hueckstadt TP, Birnbaum MJ: Pretranslational suppression of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter in rats with diabetes mellitus. Science: 60–63, 1989
Richardson JM, Balon TW, Treadway JL, Pessin JE: Differential regulation of glucose transporter activity and expression in red and white skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 266: 12690–12694, 1991
Sivitz WI, DeSautel SL, Kayano T, G.I. B, Pessin JR: Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA in insulin-deficient states. Nature 340: 72–74, 1989
Block NE, Menick DR, Robinson KA, Buse MG: Effect of denervation on the expression of two glucose transporter isoforms in rat hindlimb muscles. J Clin Invest 88: 1546–1552, 1991
Han X-X, Galbo H: The effect of putative insulin-like substances released by the motor nerve on glucose transport in perfused rat muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 151: 181–189, 1994
Handberg A, Megeney LA, McCullagh KJA, Kayser L, Bonen A: Reciprocal GLUT1 and GLUT4 expression and glucose transport in denervated muscles. Am J Physiol 271: E50–E57, 1996
Henriksen EJ, Rodnick KJ, Mondon CE, James DE, Holloszy JO: Effect of denervation or unweighting on GLUT-4 protein in rat soleus muscle. J Appl Physiol 70: 2322–2327, 1991
Megeney LA, Michel RN, Boudreau CS, Fernando PK, Prasad M, Tan MH, Bonen A: Regulation of muscle glucose transport and GLUT-4 by nerve-derived factors and activity-related processes. Am J Physiol 269: R1148–R1153, 1995
Turinsky J: Dynamics of insulin resistance in denervated slow and fast-twitch muscles in vivo. Am J Physiol 252: R531–R537, 1987
Ahmad F, Goldstein B: Alterations in specific protein-tyrosine phosphatases accompany insulin resistance of streptozozotocin diabetes. Am J Physiol 268: E932–E940, 1995
Hayashi T, Wojtaszewski JFP, Goodyear LJ: Exercise regulation of glucose transport. Am J Physiol 273: E1039–E1051, 1997
Wilkes JJ, Bonen A: Reduced insulin-stimulated plasma membrane GLUT-4 appearance in denervated skeletal muscle is associated with reductions in total Akt but not phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitated IRS-1. FASEB J 12: (abstr) A355, 1998
Han X-X, Bonen A: Epinephrine translocates GLUT-4 but inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat muscle. Am J Physiol 274: E700–E707, 1998
Han X-X, Ploug T, Galbo H: Effect of diet on insulin-and contractionmediated glucose transport and uptake in rat muscle. Am J Physiol 269: R544–R551, 1995
Ploug T, Galbo H, Vinten J, Jorgensen M, Richter EA: Kinetics of glucose transport in rat muscle: effects of insulin and contractions. Am J Physiol 253: E12–E20, 1987
Megeney LA, Prasad M, Tan MH, Bonen A: Expression of the insulin-regulatable transporter GLUT-4 is influenced by neurogenic factors. Am J Physiol 266: E813–E816, 1994
Camps M, Castello A, Munoz P, Monfar M, Testar X, Palacin M, Zorzano A: Effect of diabetes and fasting on GLUT-4 (muscle/fat) glucose-transporter expression in insulin sensitive tissue. Heterogeneous response in heart, red and white muscle. Biochem J 282: 765–772, 1992
Klip A, Tsakiridis T, Marette A, Ortiz PA: Regulation of expression of glucose transporters by glucose: A review of studies in vivo and in cell cultures. FASEB J 8: 45–93, 1994
Richter EA, Ploug T, Galbo H: Increased muscle glucose uptake after exercise: No need for insulin during exercise. Diabetes 34: 1041–1048, 1985
Megeney LA, Neufer PD, Dohm GL, Tan MH, Blewtt CA, Elder GCB, Bonen A: Effects of muscle activity and fiber composition on glucose transport and GLUT4. Am J Physiol 264: E583–E593, 1993
Wallberg-Henriksson H, Holloszy JO: Contractile activity increases glucose uptake by muscle in severely diabetic rats. J Appl Physiol 57: 1045–1049, 1984
Youn JH, Gulve EA, Holloszy JO: Calcium stimulates glucose transport in skeletal muscle by a pathway independent of contraction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 260: C555–C561, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, XX., Fernando, P.K. & Bonen, A. Denervation provokes greater reductions in insulin-stimulated glucose transport in muscle than severe diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem 210, 81–89 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007108025929
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007108025929