Abstract
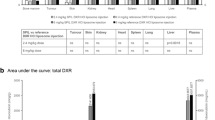
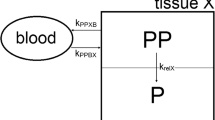
The effects of liposome formulation on interleukin-7 (IL-T)-dependent lymphopoietic activity was investigated based on the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution profile of soluble and liposome-formulated recombinant human IL-7. Using 125I-IL-7, we determined the role of liposome formulation on in vivoIL-7 disposition by analyzing injection site, blood, tissue, and urinary kinetics. Following a 30- to 40-µg subcutaneous dose of soluble IL-7, most of the IL-7 was eliminated through urinary excretion within 24 hr. An equivalent subcutaneous dose of liposome-encapsulated IL-7 resulted in a peak level less than one-tenth that seen with soluble drug but produced sustained blood and urinary levels for 5 days. The bioavailability of liposome-encapsulated IL-7 was comparable to that of soluble IL-7, as determined by both blood and urinary data. Kinetic analysis of IL-7 at the subcutaneous injection site indicated that liposome encapsulation significantly reduced the rate of disappearance at the injection site. Studies with a mixture of 40% liposome-encapsulated and 60% soluble IL-7 gave an intermediate response between that of soluble IL-7 and that of liposome-encapsulated IL-7. Characterization of blood cells from IL-7-treated animals indicated that treatment with two weekly doses of mixed IL-7 liposomes (40% liposome encapsulated IL-7) significantly increased the total numbers of lymphocytes by day 14. In contrast, animals treated with soluble IL-7 on an identical dose and schedule did not produce any effect on blood lymphocytes. Collectively, liposome formulation provided a lower, but significantly sustained blood IL-7 level that enhanced IL-7 effects on blood lymphocyte numbers.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. Bocci. Interleukins: Clinical pharmacokinetics and practical applications. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 21:274–284 (1991).
A. E. Namen, A. E. Schmierer, C. J. March, R. W. Overall, L. S. Park, D. L. Urdal, and D. Y. Mochizuki. B-cell precursor growth-promoting activity: Purification and characterization of a growth factor active on lymphocyte precursors. J. Exp. Med. 167:988–1102 (1988).
A. E. Namen, S. Lupton, K. Hjerrid, J. Wignall, D. Y. Mochizuki, A. Schmierer, B. Mosley, C. J. March, D. Urdal, S. Gillis, D. Cosman, and R. G. Goodwin. Stimulation of B-cell progenitors by cloned murine interleukin-7. Nature 333:571–573 (1988).
R. G. Goodwin, S. Lupton, A. Schmierer, K. J. Hjerrid, R. Jerzy, W. Clevenger, S. Gillis, D. Cosman, and A. E. Namen. Human interleukin-7: Molecular cloning and growth factor activity on human and murine B-lineage cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:302–306 (1989).
P. J. Morrissey, R. G. Goodwin, R. P. Nordan, D. Anderson, K. H. Grabstein, D. Cosman, J. Sims, S. Lupton, B. Acres, S. G. Reed, D. Y. Mochizuki, J. Eisenman, P. J. Conlon, and A. E. Namen. Recombinant interleukin-7, pre-B cell growth factor, has co-stimulatory activity on purified mature T cells. J. Exp. Med. 169:707–716 (1989).
G. D. Chazen, G. M. Pereira, G. LeGros, S. Gillis, and E. M. Shevach. Interleukin-7 is a T-cell growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 86:5923–5927 (1989).
R. Murray, T. Suda, N. Wrighton, F. Lee, and A. Zlotnik. IL-7 is a growth and maintenance factor for mature and immature thymocyte subsets. Int. Immunol. 1:526–531 (1989).
M. Fabbi, V. Groh, and J. L. Strominger. IL-7 induces proliferation of CD3−/low CD4− CD8− human thymocyte precursors by an IL-2 independent pathway. Int. Immunol. 4:1–5 (1992).
P. A. Welch, A. E. Namen, R. G. Goodwin, R. Armitage, and M. D. Cooper. Human IL-7: A novel T cell growth factor. J. Immunol. 143:3562–3567 (1989).
R. J. Armitage, A. E. Namen, H. M. Sassenfeld, and K. H. Grabstein. Regulation of human T cell proliferation by IL-7. J. Immunol. 144:938–941 (1990).
M. Londei, A. Verhoef, C. Hawylowicz, J. Groves, P. DeBerardinis, and M. Feldmann. Interleukin-7 is a growth factor for mature human T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 20:425–428 (1990).
C. Varma, D. Chantry, F. Brennan, M. Turner, F. Katz, and M. Feldmann. Interleukin-7 and interleukin-4 stimulate human thymocyte growth through distinct mechanisms. Cytokine 2:55–59 (1990).
R. J. Tsuhinski, I. B. McAlister, D. E. Williams, and A. E. Namen. The effects of interleukin-7 (IL-7) on bone marrow in vitro. Exp. Hematol. 19:749–754 (1991).
P. J. Morrissey, P. Conlon, K. Charrier, S. Braddy, A. Alpert, D. Williams, A. E. Namen, and D. Y. Mochizuki. Administration of IL-7 to normal mice stimulates B-lymphopoiesis and peripheral lymphadenopathy. J. Immunol. 147:561–568 (1991).
P. J. Morrissey, P. Conlon, S. Braddy, D. E. Williams, A. E. Namen, and D. Y. Mochizuki. Administration of IL-7 to mice with cyclophosphamide-induced lymphopenia accelerates lymphocyte repopulation. J. Immunol. 146:1547–1552 (1991).
J. Samaridis, G. Casorati, A. Traunecker, A. Iglesias, J. C. Gutierez, U. Müller, and R. Palacios. Development of lymphocytes in interleukin-7-transgenic mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 21:453–460 (1991).
C. R. Faltynek, S. Wang, D. Miller, E. Young, L. Tiberio, K. Koss, M. Kelley, and E. Kloszewsk. Administration of human recombinant IL-7 to normal and irradiated mice increases the numbers of lymphocytes and some immature cells of the myeloid lineage. J. Immunol. 149:1276–1282 (1992).
T. Bui, C. Faltynek, and R. J. Y. Ho. Biologic response of recombinant interleukin-7 on herpes simplex virus infection in guinea pigs. Vaccine, in press (1994).
D. S. Wilbur, S. W. Hadley, M. D. Hylarides, P. G. Abrams, P. A. Beaumier, A. C. Morgan, J. M. Reno, and A. R. Fritzberg. Development of a stable radiciodination reagent to label monoclonal antibodies for radiotherapy of cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 30:216–226 (1989).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Fan, and R. J. Randall. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275 (1951).
R. J. Y. Ho, R. L. Burke, and T. C. Merigan. Liposome-formulated interleukin-2 as an adjuvant for the treatment of recurrent genital HSV-2 in guinea pigs with recombinant HSV glycoprotein gD. Vaccine 10:209–213 (1992).
M. Gibaldi. Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3rd ed., Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 1984.
G. Post, R. Kirsh, and T. Koestler. The challenge of liposome targeting in vivo. In G. Gregoriadis (ed.), Liposome Technology, Vol. III, 1st ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1984, pp. 1–28.
G. L. Scherphof, R. J. Vonk, H. J. Verkade, J. T. P. Derksen, and F. Kuipers. Application of lipidic liposome labels to study hepatic lipid metabolism in rats. In G. Gregoriadis (ed.), Liposome Technology, Vol. III, 2nd ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1993, pp. 74–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bui, T., Faltynek, C. & Ho, R.J.Y. Differential Disposition of Soluble and Liposome-Formulated Human Recombinant Interleukin-7: Effects on Blood Lymphocyte Population in Guinea Pigs. Pharm Res 11, 633–641 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018955708443
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018955708443