Summary
Adult diabetics were divided into 4 groups according to therapy before and after a therapeutic trial with diet and glibenclamide:
I: insulin before — insulin afterwards, II: tablets — insulin, III: insulin — tablets and IV: tablets — tablets. The secretion capacity of the beta-cells, determined by C-peptide was examined in 6 healthy subjects and in 10 diabetics of each group following an i.v. glibenclamide-glucose load.
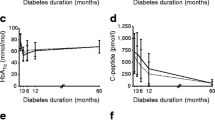
A decreased insulinogenic reserve showing itself in a reduced and delayed rise of immunomeasurable C-peptide (IMCP) was found in all diabetics. However, the secretion of IMCP lasted longer in the diabetics requiring tablets than in the healthy subjects. The average values for the increment of IMCP and the integrated stimulation areas were much more considerable in the patients treated with tablets (III+IV) than in the insulin-dependent patients (I+II).
An analysis of variance was performed for the diabetics depending on insulin, on the one hand, and the patients depending on tablets on the other. Between groups I and II the group average values for IMCP are significantly different while differences in the time course of the IMCP mean values of both groups are accidental. Neither the group average values of IMCP nor the time course of the IMCP mean values show significant differences between groups III and IV. The time course of IMCP was described by a regression polynomial of 2nd degree in insulin-dependent diabetics and a polynomial of 4th degree in diabetics depending on tablets; the corresponding curves differ considerably as to extent and steepness of their rise.
Prediction of suitable diabetes therapy from an i.v. glibenclamide-glucose load based on blood glucose evaluation up to now is easier and more reliable since C-peptide levels are known.
A development of the residual beta-cell function from the stage in groups III and IV via group II to the stage in group I is likely to be the natural course of adult diabetes.
Zusammenfassung
Erwachsene Diabetiker wurden je nach Therapie vor und nach einem Behandlungsversuch mit Diät und Glibenclamid in 4 Gruppen eingeteilt:
I: vorher Insulin — nachher Insulin, II: Tabletten — Insulin, III: Insulin — Tabletten und IV: Tabletten — Tabletten. Bei 6 Stoffwechselgesunden und 10 Patienten aus jeder Diabetikergruppe wurde die Sekretionskapazität der Beta-Zellen nach i.v. Belastung mit Glibenclamid-Glukose mittels C-Peptid Messungen untersucht.
Bei den Diabetikern aller Gruppen kam eine Sekretionsstarre in einem verminderten und verzögerten Anstieg von immunologisch meßbarem C-Peptid (IMCP) zum Ausdruck. Bei tablettenbedürftigen Patienten hielt die Sekretion allerdings länger an als bei Stoffwechselgesunden. Im Mittel waren der Zuwachs von IMCP und die integrierten Stimulationsflächen bei tablettenbedürftigen Patienten (III+IV) viel größer als bei insulinbedürftigen (I+II).
Eine Varianzanalyse wurde für die insulinbedürftigen Fälle einerseits und die tablettenbedürftigen Patienten andererseits durchgeführt. Die Gruppen I und II unterscheiden sich überzufällig bezüglich der Gruppenmittelwerte für IMCP, während der zeitliche Verlauf der IMCP Mittelwerte der beiden Gruppen nur zufällig von der Parallelität abweicht. In den Gruppen III und IV unterscheiden sich weder die Gruppenmittelwerte überzufällig, noch konnte eine Abweichung der jeweiligen zeitlichen Verläufe von der Parallelität nachgewiesen werden. Der zeitliche Verlauf konnte für Insulinbedürftige durch ein Regressionspolynom 2. Grades, für Tablettenbedürftige durch ein Regressionspolynom 4. Grades dargestellt werden. Die Kurven unterscheiden sich erheblich in Ausmaß und Steilheit ihres Anstiegs.
Die Therapievorhersage nach i.v. Belastung mit Glibenclamid-Glukose, die bisher auf Kriterien des Blutglukoseverlaufs beruhte, ist bei Kenntnis des IMCP Verlaufs leichter und zuverlässiger möglich.
Als natürlicher Verlauf des Diabetes mellitus im Erwachsenenalter ist die Entwicklung der Restsekretion der Beta-Zellen vom Stadium der Gruppen III und IV über Gruppe II zum Stadium der Gruppe I wahrscheinlich.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Beischer, W., Heinze, E., Keller, L., Rapits, S., Kerner, W., Pfeiffer, E.F.: Human C-peptide, part II: clinical studies. Klin. Wschr.54, 717 (1976)
Beischer, W., Keller, L., Heinze, E., Raptis, S., Tamás, Gy., Thum, Ch., Pfeiffer, E.F.: Nachweis von körpereigenen Insulinreserven beim insulinbehandelten Diabetiker mittels C-Peptid Bestimmung. XII. Kongreß d. Süddeutschen Gesellschaft f. Innere Medizin, Stuttgart, 1975. Therapiewoche26, 1936 (1976)
Beischer, W., Keller, L., Maas, M., Schiefer, E., Pfeiffer, E.F.: Human C-peptide, part I: radioimmunoassay. Klin. Wschr.54, 709 (1976)
Beischer, W., Melani, F., Keller, L., Pfeiffer, E.F.: Chromatographic heterogeneity of insulin extracted from insulomas. J. clin. Endocr.40, 393 (1975)
Block, M.B., Mako, M.E., Steiner, D.F., Rubenstein, A.H.: Diabetic ketoacidosis: evidence for C-peptide and proinsulin secretion following recovery. J. clin. Endocr.35, 402 (1972)
Block, M.B., Pildes, R.S., Mossabhoy, N.A., Steiner, D.F., Rubenstein, A.H.: C-peptide immunoreactivity (CPR): a new method for studying infants of insulin-treated diabetic mothers. Pediatrics53, 923 (1974)
Cerasi, E., Luft, R.: Clinical diabetes and theories of pathogenesis. In: Handbook of Physiology. Section 7, Vol. I, Steiner, D.F., Freinkel, N., eds. American Physiological Society, Washington D.C., 1972
Fußgänger, R.D., Goberna, R., Hinz, M., Jaros, P., Karsten, C., Pfeiffer, E.F., Raptis, S.: Comparative studies and the dynamics of insulin secretion following HB 419 and tolbutamide on the perfused isolated rat pancreas and the perfused isolated islet of Langerhans. Horm. Metab. Res. Suppl.1, 34 (1969)
Grodsky, G.M., Curry, D.L., Bennett, L.L.: Effect of HB 419 on insulin secretion in vitro. Tegernsee Konferenz über das neue orale Antidiabetikum HB 419, 1969. Horm. Metab. Res. Suppl.1, 54 (1969)
Haupt, E., Köberich, W., Beyer, J., Schöffling, K.: Pharmacodynamic aspects of tolbutamide, glibenclamide, glibornuride, and glisoxepide II. Repeated administration in combination with glucose. Diabetologia7, 455 (1971)
Heding, L.G.: Determination of total serum insulin (IRI) in insulin-treated diabetic patients. Diabetologia8, 260 (1972)
Heding, L.G.: Radioimmunological determination of human C-peptide in serum. Diabetologia11, 541 (1975)
Horwitz, D.L., Starr, J.I., Mako, M.E., Blackhard, W.G., Rubenstein, A.H.: Proinsulin, insulin, and C-peptide in human portal and peripheral blood. J. clin. Invest.55, 1278 (1975)
Johnston, D.G., Alberti, K.G.M.M., Wright, R.: Mechanism of the hyperinsulinism of cirrhosis (abstr.). Diabetologia12, 401 (1976)
Kaneko, T., Oka, H., Munemura, M., Oda, T., Yamashita, K., Suzuki, S., Yanaihara, N., Hashimoto, T., Yanaihara, Ch.: Radioimmunoassay of human proinsulin C-peptide using synthetic human connecting peptide. Endocr. jap.21, 141 (1974)
Katz, A.I., Rubenstein, A.H.: Metabolism of proinsulin, insulin and C-peptide in the rat. J. clin. Invest.52, 1113 (1973)
Kerner, W., Thum, Ch., Tamás, Gy., Beischer, W., Clemens, A.H., Pfeiffer, E.F.: Attempts at perfect normalization of glucose tolerance test of severe diabetics by artificial pancreas. Horm. Metab. Res.8, 256 (1976)
Loubatières, A., Mariani, M.M., Chapal, J.: Etudes de la synergie entre le glucose et le tolbutamide dans les limites physiopathologiques de la glycémie. Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. Ser.D269, 1460 (1969)
Loubatières, A., Mariani, M.M., Chapal, J.: Etude physiologique et pharmacologique de l'insulino-sécrétion sur le pancréas isolé et perfusé du rat. J. Pharmacol. (Paris)1, 7 (1970)
Melani, F., Rubenstein, A.H., Oyer, P.E., Steiner, D.F.: Identification of proinsulin and C-peptide in human serum by a specific immunoassay. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci.67, 148 (1970)
Pfeiffer, E.F., Ditschuneit, H., Ziegler, R.: Über die Bestimmung von Insulin im Blute am epididymalen Fettanhang der Ratte mit Hilfe markierter Glukose. IV. Die Dynamik der Insulinsekretion des Stoffwechselgesunden und des Altersdiabetikers nach wiederholter Belastung mit Glukose, Sulfonylharnstoffen und menschlichem Wachstumshormon, ein Beitrag zur Pathogenese des menschlichen Altersdiabetes. Klin. Wschr.39, 415 (1961)
Pfeiffer, E.F., Pfeiffer, M., Ditschuneit, H., Chang-Su-Ahn: Über die Bestimmung von Insulin im Blute am epididymalen Fettanhang der Ratte mit Hilfe markierter Glukose. II. Experimentelleund klinische Erfahrungen. Klin. Wschr.37, 1239 (1959)
Pfeiffer, E.F., Raptis, S.: Controlled extension of oral antidiabetic therapy on former insulin-dependent diabetes by means of the combined i.v. glibenclamide-glucose response test. Diabetologia8, 41 (1972)
Pfeiffer, E.F., Raptis, S., Schröder, K.E.: Einmalige intravenöse Glibenclamid-Glukose Belastung als Vorhersagetest. Dtsch. med. Wschr.99, 1281 (1974)
Raptis, S., Rau, R.M., Schröder, K.E., Faulhaber, J.D., Pfeiffer, E.F.: Comparative study of insulin secretion following repeated administration of glucose, tolbutamide and glibenclamide (HB 419) in diabetic and non diabetic subjects. Horm. Metab. Res. Suppl.1, 65 (1969)
Rövenstrunck, U., Beischer, W., Loeprecht, H., Raptis, S., Pfeiffer, E.F.: Hepatic clearance of C-peptide and insulin. Symposium on C-peptide, Mainz, February 11th, 1977
Rubenstein, A.H., Clark, J.L., Melani, F., Steiner, D.F.: Secretion of proinsulin C-peptide by pancreatic beta-cell and its circulation in blood. Nature224, 697 (1969)
Schmidt, F.H.: Enzymatische Methode zur Bestimmung von Blut- und Harnzucker unter Berücksichtigung von Vergleichsuntersuchungen mit klassischen Methoden. Internist (Berlin)4, 554 (1963)
Seltzer, H.S., Smith, L.W.: Plasma insulin activity after glucose. Diabetes8, 417 (1959)
Steiner, D.F., Kemmler, W., Clark, J.L., Oyer, P.E., Rubenstein, A.H.: The biosynthesis of insulin. In: Handbook of Physiology, Section 7, Vol. I, Steiner, D.F., Freinkel, N., eds. American Physiological Society, Washington D.C., 1972
Stoll, R.W., Touber, J.L., Menahan, L.A., Williams, R.A.: Clearance of porcine insulin, proinsulin, and connecting peptide by the isolated rat liver. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol.133, 894 (1970)
Werner, W., Rey, H.G., Wielinger, H.: Über die Eigenschaften eines neuen Chromogens für die Blutzuckerbestimmung nach der GOD/POD-Methode. Z. Anal. Chem.252, 224 (1970)
Yalow, R.S., Berson, S.A.: Immuno-assay of endogeneous plasma insulin in man. J. clin. Invest.39, 1157 (1960)
Ziegler, R.: Die Dynamik der Insulinsekretion beim Stoffwechselgesunden und beim Altersdiabetiker nach wiederholter Belastung mit Glukose und Sulfonylharnstoffen. Dissertation, Frankfurt/Main, 1963
Zilker, Th., Kränzlin, Th., Schweigart, U., Ermler, R., Bottermann, P.: Radioimmunologische Seruminsulinbestimmung beim manifesten Diabetes mellitus als Parameter der Therapieplanung. Med. Klin.71, 761 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Durchgeführt mit Unterstützung der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft, SFB 87 Endokrinologie, Ulm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beischer, W., Raptis, S., Keller, L. et al. Humanes C-Peptid. Klin Wochenschr 56, 111–120 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01478566
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01478566