Abstract
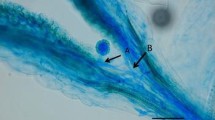
Pistil squashes were used to examine the growth of Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa Deg pollen tubes in self-compatible and self-incompatible crosses. Compatible tubes typically showed a uniform layer of callose deposition in the walls and in small plugs spaced at regular intervals within the tube. Two sites of rejection were observed in incompatible crosses: the stigma and on some occasions the style, especially in anomalous crosses. In the style the inhibition of pollen-tube growth occurred in both the upper and middle parts of the transmitting tract. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that suggests the presence of a gametophytic gene which acts in association with the sporophytic S-gene in P. edulis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 October 1998 / Accepted: 2 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rêgo, M., Rêgo, E., Bruckner, C. et al. Pollen tube behavior in yellow passion fruit following compatible and incompatible crosses. Theor Appl Genet 101, 685–689 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051531
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051531