Summary
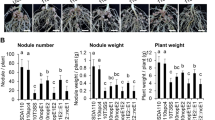
To determine the relationship between nodulation restriction by the Rj4 allele of soybean, rhizobitoxine-induced chlorosis, and taxonomic grouping of bradyrhizobia, 119 bradyrhizobial isolates were tested in Leonard jar culture for nodulation response and chlorosis induction. In addition to strain USDA 61, the strain originally reported as defining the Rj4 response, eight other isolates (i.e., USDA 62, 83, 94, 238, 252, 259, 260, and 340) were discovered to elicit the nodulation interdiction of the Rj4 allele. Only 16% of all the bradyrhizobial strains tested induced chlorosis, but seven of the nine strains (78%) interdicted by the Rj4 allele were chlorosis-inducing strains. Furthermore, in tests for antibiotic resistance profile, eight of the nine interdicted strains (89%) were classed in DNA homology group II. This evidence suggests that the Rj4 allele has a positive value to the host plant in shielding it from nodulation by certain chlorosis-inducing bradyrhizobia of a DNA homology group with impaired efficiency of nitrogen fixation with soybean.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devine TE (1985a) Host range and compatibility of soybean with rhizobial microsymbionts. In: Shibles R. (ed) Proc 3rd World Soybean Res Conf Ames/IA, 1984. Westview Press, Boulder/CO, pp 484–492
Devine TE (1985b) Modulation of soybean plant introduction lines with the fast-growing rhizobial strain USDA 205. Crop Sci 25:354–356
Devine TE (1987) A comparison of rhizobial strain compatibilities of Glycine max and its progenitor species Glycine soja. Crop Sci 27:635–639
Devine TE (1988) Role of the nodulation restrictive allele Rj4 in soybean evolution. J Plant Physiol 132:453–455
Devine TE Breithaupt BH (1980a) Phenotypic stability of rhizobitoxine-induced chlorosis and the nodulation controlling gene, rj1. Crop Sci 20:394–396
Devine TE, Breithaupt BH (1980b) Significance of incompatibility reactions of Rhizobium japonicum strains with soybean host genotypes. Crop Sci 20:269–271
Devine TE, Breithaupt BH (1981) Frequency of nodulation response alleles, Rj2 and Rj4, in soybean plant introduction and breeding lines. USDA Tech Bull 1628
Devine TE, O'Neill (1986) Registration of BARC-2(Rj4) and BARC-3(rj4) soybean germ plasm. Crop Sci 26:1263–1264
Devine TE, Kuykendall LD, Breithaupt BH (1983) Nodule-like structures induced on peanut by chlorosis-producing strains of Rhizobium classified as R. japonicum. Crop Sci 23:394–397
Devine TE, Kuykendall LD, O'Neill JJ (1988) DNA homology group and the identity of bradyrhizobial strains producing rhizobitoxine-induced foliar chlorosis on soybean. Crop Sci 28:939–941
Erdman LW, Johnson HW, Clark F (1957) Varietal responses of soybeans to a bacterial-induced chlorosis. Agron J 49:267–271
Fuhrmann J (1990) Symbiotic effectiveness of indigenous soybean bradyrhizobia as related to serological, morphological, rhizobitoxine, and hydrogenase phenotypes. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:224–229
Hollis AB, Kloos WE, Elkan GH (1981) DNA:DNA hybridization studies of Rhizobium japonicum and related Rhizobiaceae. J Gen Microbiol 123:215–222
Johnson HW, Means UM (1960) Interactions between genotypes of soybeans and genotypes of nodulating bacteria. Agron J 52:651–654
Keyser HH, Griffin RF (1987) Beltsville Rhizobium culture collection catalog. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Research Service, ARS-60
Kuykendall LD (1979) Transfer of R factors to and between genetically marked sublines of Rhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:862–866
Kuykendall LD, Roy MA, O'Neill JJ, Devine TE (1988) Fatty acids, antibiotic resistance, and deoxyribonucleic acid homology groups of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:358–361
Leonard LT (1943) A simple assembly for use in the testing of culture rhizobia. J Bacteriol 45:523–527
Owens LD, Wright DA (1965) Rhizobial-induced chlorosis in soybeans: Isolation, production in nodules, and varietal specificity of the toxin. Plant Physiol 40:927–930
Vest G, Caldwell BE (1972) Rj4-a gene conditioning ineffective nodulation in soybeans. Crop Sci 12:692–694
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. R. Hallauer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devine, T.E., Kuykendall, L.D. & O'Neill, J.J. The Rj4 allele in soybean represses nodulation by chlorosis-inducing bradyrhizobia classified as DNA homology group II by antibiotic resistance profiles. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 80, 33–37 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224012
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224012