Abstract
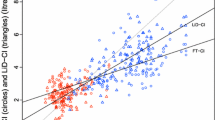
Values obtained for cardiac output (CO) were compared using thermodilution (TD) with those obtained using bioimpedance (Bi) as measured using the Bomed NCCOM3 (Revision 6) in 28 consecutive patients in the first 24h after coronary artery bypass surgery (CABS). In 46 paired measurements made in the first 12 h after CABS Bi values for CO were significantly lower than TD values, the limits of agreement between the two methods were also unacceptably large (mean Bi 4.38 (SD 1.40) l/min, mean TD 5.46 (SD 1.19) l/min, limits of agreement−3.05 to +0.89). In 55 paired measurements made after 12h (all in spontaneously breathing patients) there was no significant difference between the two methods and acceptable limits of agreement, mean Bi 5.69 (SD 1.2) l/min mean TD 5.6 (SD 1.2) l/min, limits of agreement−0.99 to +1.17). The significantly lower BiCO values obtained in the first 12h after CABS show that BiCO measurement is not consistently reliable in the intensive care setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein DP (1986) A new stroke volume equation for thoracic electrical bioimpedance: theory and rationale. Crit Care Med 14:905–909
Northridge DB, Findlay IN, Wilson J, Henderson E, Dargie HJ (1990) Non-invasive determination of cardiac output by Doppler echocardiography and electrical impedance. Br Heart J 63:93–97
Bernstein DP (1986) Continuous noninvasive real-time monitoring of stroke volume and cardiac output by thoracic electrical impedance. Crit Care Med 14:899–901
Bland MJ, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet I:307–310
Appel PL, Kram HB, Mackabee J, Fleming AW, Shoemaker WC (1986) Comparison of measurements of cardiac output by bio-impedance and thermodilution in severely ill surgical patients. Crit Care Med 14:933–935
Gotshall RW, Wood VC, Miles DS (1989) Comparison of two impedance cardiographic techniques for measuring cardiac output in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 117:806–811
Spinale FG, Reines HD, Crawford FA (1988) Comparison of bioimpedance and thermodilution methods for determining cardiac output: Experimental and clinical studies. Ann Thorac Surg 45:421–425
Spahn DR, Schmid ER, Torni CM, Jenni R, Segesser LV, Turina M, Baetscher A (1990) Noninvasive versus invasive assessment of cardiac output after cardiac surgery: clinical validation. J Cardiothorac Anaesth 4:46–59
Okamoto K, Komatsu T, Kumar V et al. (1986) Effects of intermittent positive pressure ventilation on cardiac output measurements by thermodilution. Crit Care Med 14:977–980
Jansen JRC, Schrevder JJ, Settels JJ, Kloek JJ, Versprille A (1990) An adequate strategy for the thermodilution technique in patients during mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med 16:422–425
Preiser JC, Daper A, Parquier JN, Contempre B, Vincent JL (1989) Transthoracic electrical bioimpedance versus thermodilution technique for cardiac output measurement during mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med 15:221–223
Thomas AN, Ryan JP, Doran BH, Pollard BJ (1990) Non-invasive measurement of cardiac output, thoracic electrical impedance and index of contractility before and after coronary artery bypass grafting. (Abstract) Br Hosp Med 44:432–433
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, A.N., Ryan, J., Doran, B.R.H. et al. Bioimpedance versus thermodilution cardiac output measurement: The bomed NCCOM3 after coronary bypass surgery. Intensive Care Med 17, 383–386 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01720674
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01720674