Abstract
The inhibition of fructose utilization by whole cells of Hydrogenomonas eutropha H 16, following the addition of hydrogen to the gas phase, has been explained as an inhibition of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (Blackkolb and Schlegel, 1968a, b).
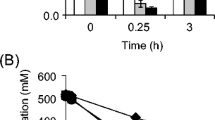
The intracellular concentrations of glucose 6-phosphate, 6-phosphogluconate, three inhibitors of the enzyme (NADH, ATP and phosphoenolpyruvate) and some related metabolites were measured in cells incubated in the presence and absence of hydrogen.
Inhibition of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase was confirmed by an increase in the glucose 6-phosphate pool and a decrease in the 6-phosphogluconate concentration. The regulatory control is apparently due to a threefold increase in the NADH concentration while the concentrations of the other two inhibitors fell slightly. When the measured intracellular concentrations of intermediates were used in the in vitro assay of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity, an almost total inhibition of the dehydrogenase was observed, therefore further regulatory factors must be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens, W.: CO2-bedürftige Mutanten von Hydrogenomonas H 16. Diss., Universität Göttingen 1970
Atkinson, D. E.: Regulation of enzyme function. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 23, 47–68 (1969)
Bächi, B., Ettlinger, L.: Influence of glucose on adenine nucleotide levels and energy charge in Acetobacter aceti. Arch. Mikrobiol. 93, 155–164 (1973)
Blackkolb, F., Schlegel, H. G.: Katabolische Repression und Enzymemmung durch molekularen Wasserstoff bei Hydrogenomonas. Arch. Mikrobiol. 62, 129–143 (1968a)
Blackkolb, F., Schlegel, H. G.: Regulation der Glucose-6-phosphat-Dehydrogenase aus Hydrogenomonas H 16 durch ATP und NADH2. Arch. Mikrobiol. 63, 177–196 (1968b)
Blair, J. McD.: Magnesium, potassium, and the adenylate kinase equilibrium. Magnesium as a feedback signal from the adenine nucleotide pool. Europ. J. Biochem. 13, 384–390 (1970)
Bonsignore, A., de Flora, A.: Regulatory properties of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. In: B. L. Horecker, E. R. Stadtman, Eds., Current topics in cellular regulation, vol. 6, pp. 21–62. New York: Academic Press 1972
Chance, B., Williams, G. R.: The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Advanc. Enzymol. 17, 65–134 (1956)
Chapman, A. G., Fall, L., Atkinson, D. E.: Adenylate energy charge in Escherichia coli during growth and starvation. J. Bact. 108, 1072–1086 (1971)
Cook, A. M., Bowien, B.: The fluorimetric determination of metabolic pool sizes in Hydrogenomonas eutropha strain H 16. J. gen. Microbiol. 75, XIX (1973)
Davis, B. D., Dulbecco, R., Eisen, H. N., Ginsberg, H. S., Wood, W. B.: Microbiology, internat. Edt., pp. 36–42. New York: Harper & Row 1969
Estabrook, R. W., Maitra, P. K.: A fluorimetric method for the quantitative microanalysis of adenine and pyridine nucleotides. Analyt. Biochem. 3, 369–382 (1962)
Gottschalk, G.: Verwertung von Glucose durch Hydrogenomonas H 16. II. Cryptisches Verhalten gegenüber Glucose. Arch. Mikrobiol. 49, 96–102 (1964)
Gottschalk, G.: Die Verwertung organischer Substrate durch Hydrogenomonas in Gegenwart von molekularem Wasserstoff. Biochem. Z. 341, 260–270 (1965)
Gottschalk, G., Eberhardt, U., Schlegel, H. G.: Verwertung von Fructose durch Hydrogenomonas H 16. Arch. Mikrobiol. 48, 95–108 (1964)
Gutfreund, H.: Transient and relaxation kinetics of enzyme reactions. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 40, 315–344 (1971)
Krebs, H. A.: Die Steuerung von Stoffwechselvorgängen. Endeavour 16, 125–132 (1957)
MacNab, R., Moses, V., Mowbray, J.: Evidence for metabolic compartmentation in Escherichia coli. Europ. J. Biochem. 34, 15–19 (1973)
Maitra, P. K., Estabrook, R. W.: A fluorimetric method for the enzymic determination of glycolytic intermediates. Analyt. Biochem. 7, 472–484 (1964)
Reid, D. F., Frank, H. A.: Isotopic method for estimating microbial cell volumes. J. Bact. 92, 639–644 (1966)
Reeves, R. E., Sols, A.: Regulation of Escherichia coli phosphofructokinase in situ. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 50, 459–466 (1973)
Rolleston, F. S.: A theoretical background to the use of measured concentrations of intermediates in study of the control of intermediary metabolism. In: B. L. Horecker, E. R. Stadtman, Eds., Current topics in cellular regulation, vol. 5, pp. 47–75. New York: Academic Press 1972
Schlegel, H. G., Gottschalk, G., Bartha, R. von: Formation and utilization of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid by Knallgas bacteria (Hydrogenomonas). Nature (Lond.) 191, 463–465 (1961b)
Schlegel, H. G., Kaltwasser, H., Gottschalk, G.: Ein Submersverfahren zur Kultur wasserstoffoxydierender Bakterien: Wachstumsphysiologische Untersuchungen. Arch. Mikrobiol. 38, 209–222 (1961a)
Schramm, V. L.: Allosteric AMP nucleosidase (AMPase): Regulation and a proposed metabolic role. Abstracts, 9th International Congress of Biochemistry (1973)
Sols, A., Marco, R.: Concentrations of metabolites and binding sites. Implications in metabolic regulation. In: B. L. Horecker, E. R. Stadtman, Eds., Current topics in cellular regulation, vol. 2, pp. 227–273, New York: Academic Press 1970
Tunail, N., Schlegel, H. G.: Phosphoenolpyruvate, a new inhibitor of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 49, 1554–1560 (1972)
Webb, J. L.: Enzyme and metabolite inhibitors, vol. 1, pp. 383–392. London-New York: Academic Press 1963
Wilde, E.: Untersuchungen über Wachstum und Speicherstoffsynthese von Hydrogenomonas. Arch. Mikrobiol. 43, 109–137 (1962)
Williamson, J. R., Corkey, B. E.: Assay of intermediates of the citric acid cycle and related compounds by fluorimetric enzyme methods. Meth. Enzymol. 13, 434–513 (1969)
Wilson, A. T., Calvin, M.: The photosynthetic cycle. CO2 dependent transients. J. Amer. chem. Soc. 77, 5948–5957 (1955)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bowien, B., Cook, A.M. & Schlegel, H.G. Evidence for the in vivo regulation of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in Hydrogenomonas eutropha H 16 from measurements of the intracellular concentrations of metabolic intermediates. Arch. Microbiol. 97, 273–281 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403067
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403067