Summary
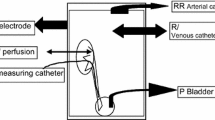
The metabolic pathway of 3H-noradrenaline released spontaneously and by nerve stimulation was studied in the isolated perfused spleen of the cat. The deaminated glycol, DOPEG, (3,4 dihydroxyphenylglycol) was the main metabolite in spontaneous outflow, accounting for 62.5±1.6% of the total radioactivity (n=13). Of the total increase in radioactive products elicited by nerve stimulation at 5 Hz or 10 Hz around 30% was accounted for by the noradrenaline metabolites, particularly DOPEG and the O-methylated fraction. In the presence of 2.9×10−6 M of cocaine the total overflow of radioactivity induced by stimulation was unchanged but DOPEG formation from released noradrenaline was abolished. These findings indicate that DOPEG formation results from the recapture of the released transmitter by adrenergic nerve endings and subsequent intraneuronal deamination. The total overflow of noradrenaline was reduced by flow-stop while the metabolism of the released transmitter was increased significantly. Cocaine, 2.9×10−6 M, prevented the increase in DOPEG when stimulation was applied under flow-stop conditions. The decrease in noradrenaline overflow induced by flow-stop is partly due to the increase in the metabolism of the released transmitter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler-Graschinsky, E., Langer, S. Z., Rubio, M. C.: Metabolism of norepinephrine released by phenoxybenzamine in isolated guinea-pig atria. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 180, 286–301 (1972).
Anton, A. H., Sayre, D. F.: A study of the factors affecting the aluminium oxide trihydroxyindole procedures for the analysis of catecholamines. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 138, 360–375 (1962).
Burn, J. H.: Practical pharmacology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications 1952.
Crout, J. R.: In: Standard methods of clinical chemistry. Ed. by D. Seligson, vol. 3, pp. 62–80. New York: Academic Press 1961.
Enero, Ma. A., Langer, S. Z., Rothlin, R. P., Stefano, F. J. E.: Role of the alpha-adrenoceptor in regulating noradrenaline overflow by nerve stimulation. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 44, 672–688 (1972).
Farnebo, L. O., Hamberger, B.: Drug induced changes in the release of 3H-noradrenaline from field stimulated rat iris. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 43, 97–106 (1971).
Graefe, K. H., Stefano, F. J. E., Langer, S. Z.: Preferential metabolism of (-)-3H-norepinephrine through the deaminated glycol in the rat vas deferens. Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 1147–1161 (1973).
Hertting, G.: Effect of drugs and sympathetic denervation on noradrenaline uptake and binding in animal tissues. Pharmacol. of Cholinergic and adrenergic transmission. Proc. Soc. Intern. Pharmacol. Meeting, 1963, vol. 3, pp. 277–289. Pergamon Press 1965.
Kirpekar, S. M., Puig, Margarita: Effect of flow-stop on noradrenaline release from normal spleens treated with cocaine, phentolamine or phenoxybenzamine. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 43, 359–369 (1971).
Langer, S. Z.: The metabolism of 3H-noradrenaline released by electrical stimulation from the isolated nictitating membrane of the cat and from the vas deferens of the rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 208, 515–546 (1970).
Langer, S. Z., Adler, E., Enero, Ma. A., Stefano, F. J. E.: The role of the alpha receptor in regulating noradrenaline overflow by nerve stimulation. XXVth. Int. Congr. Physiol. Sciences, p. 335 (1971).
Langer, S. Z., Stefano, F. J. E., Enero, Ma. A.: Pre- and postsynaptic origin of the norepinephrine metabolites formed during transmitter release elicited by nerve stimulation. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 183, 90–102 (1972).
Laverty, R., Taylor, K. M.: The fluorometric assay of catecholamines and related compounds: Improvements and extensions to the hydroxyindole technique. Analyt. Biochem. 22, 269–279 (1968).
Levin, J. A.: Metabolism of 3H-norepinephrine by the adventitia and media of rabbit aorta. V th. Int. Congr. Pharmac., p. 139 (1972).
Paton, D. M., Gillis, G. N.: Effect of altered perfusion rates on the retention of noradrenaline by the spleen. Nature (Lond.) 208, 391–392 (1965).
Roffler-Tarlov, S., Langer, S. Z.: The fate of 3H-norepinephrine released from isolated atria and vas deferens: effect of field stimulation J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 179, 186–197 (1971).
Snedecor, G. W., Cochran, W. G.: Statistical methods, 6th ed. The Iowa State University Press 1967.
Starke, K.: Influence of extracellular noradrenaline on the stimulation evoked secretion of noradrenaline from sympathetic nerves: Evidence for an alphareceptor-mediated feed back inhibition of noradrenaline release. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 275, 11–23 (1972).
Starke, K., Montel, H., Schümann, M. J.: Influence of cocaine and phenoxybenzamine on noradrenaline uptake and release. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 270, 210–214 (1971).
Su, C., Bevan, S. A.: Blockade of the nicotine-induced norepinephrine release by cocaine, phenoxybenzamine and desipramine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 175, 533–540 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubocovich, M., Langer, S.Z. Effects of flow-stop on the metabolism of noradrenaline released by nerve stimulation in the perfused spleen. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 278, 179–194 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500649
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500649