Summary
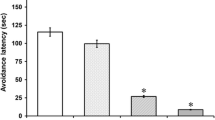
[d-Arg1, dTrp7,9, Leu11]-substance P (spantide) was tested for antagonism against the licking, biting and scratching response induced by various neurokinin (NK) receptor agonists and bombesin (Bom) in mice. When co-administered with substance P (SP) intrathecally, spantide reduced the SP-induced behavioural responses in a dose-dependent manner. The duration of this antagonistic effect was approximately 30 min. Behavioural responses induced by physalaemin (Phy), [pGlu6, l-Pro9]-SP (6–11) (septide), [pGlu6, d-Pro7]-SP (6–11) (d-septide) and eledoisin (Ele) were also dose-dependently decreased by relatively small doses of spantide. Higher doses of spantide were needed to reduce the behavioural responses induced by [Sar9, Met (O2)11]-SP, neurokinin A (NK A) and neurokinin B (NK B). No significant effect of spantide was observed against the behavioural responses elicited by Bom. Pretreatment with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, resulted in a reversible effect on the behavioural reduction of NK-2 and NK-3 receptor agonists produced by spantide. However, the effect of spantide on the NK-1 receptor agonist-induced response was unchanged by naloxone. In homogenates of mouse spinal cord, competition studies confirmed that the binding of the opioid ligand [3H]naloxone was displaced by spantide with a low but measurable affinity. These results suggest that the behavioural response to NK-2 and NK-3 receptor agonists may be partially inhibited by spantide through the activation of opioid system in the mouse spinal cord.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkerman B, Rosel S, Folkers K (1982) Intrathecal (D-Pro2, D Trp7,9)-SP elicits hypoalgesia and motor blockade in the rat and antagonizes noxious responses induced by substance P. Acta Physiol Scand 114:631–633
Atweh SF, Kuhar MJ (1977) Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res 124:63–67
Barthó L, Holzer P, Leander S, Lembeck F (1989) Evidence for an involvement of substance P, but not cholecystokinin-like peptides in hexamethonium-resistant intestinal peristalsis. Neuroscience 28:211–217
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Buck SH, Burcher E (1986) The tachykinins: A family of peptides with a brood of receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 7:65–68
Buck SH, Shatzer SA (1988) Agonist and antagonist binding to tachykinin peptide NK-2 receptors. Life Sci 42:2701–2708
Buck SH, Helke CJ, Burcher E, Shults CW, O'Donohue TL (1986) Pharmacological characterization and autoradiographic distribution of binding sites for iodinated tachykinins in the rat central nervous system. Peptides 7:1109–1120
Caranikas S, Mizrahi J, D'Oreans-Juste R, Regoli D (1982) Antagonists of substance P. Eur J Pharmacol 77:205–206
Chahl LA (1985) Effects of substance P antagonists on the atropine-sensitive and atropine-resistant responses of guinea-pig ileum to substance P. Neurosci Lett 55:35–40
Chang K-J, Cuatrecasas P (1979) Multiple opiate receptors. J Biol Chem 254:2610–2618
Eide PK, Hole K (1991) Interactions between serotonin and substance P in the spinal regulation of nociception. Brain Res 550:225–230
Folkers K, Hörig J, Rosell S, Björkroth U (1981) Chemical design of antagonists of substance P. Acta Physiol Scand 111:505–506
Folkers K, Håkanson R, Hörig J, Jie-Chang X, Leander S (1984) Biological evaluation of substance P antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 83:449–456
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A, Terenius L, Elde R, Nilsson G (1977) Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: Enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3081–3085
Hwang AS, Wilcox GL (1986) Intradermal hypertonic saline-induced behavior as a nociceptive test in mice. Life Sci 38:2389–2396
Hylden JLK, Wilcox GL (1980) Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol 67:313–316
Hylden JLK, Wilcox GL (1981) Intrathecal substance P elicits a caudally-directed biting and scratching behavior in mice. Brain Res 217:212–215
Hylden JLK, Wilcox GL (1983) Intrathecal opioids block a spinal action of substance P in mice: Functional importance of both µ- and δ-receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 86:95–98
Johnston PA, Chahl LA (1991) Tachykinin antagonists inhibit the morphine withdrawal response in guinea-pigs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343:283–288
Karlsson JA, Finney MJB, Persson CGA, Post C (1984) Substance P antagonists and the role of tachykinins in non-cholinergic bronchoconstriction. Life Sci 35:2681–2691
Larson AA (1988) Desensitization to intrathecal substance P in mice: Possible involvement of opioids. Pain 32:367–374
Litchfield JT Jr, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose effect experiment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 96:99–113
Maggio JE (1988) Tachykinins. Ann Rev Neurosci 11:13–28
Matsumura H, Sakurada T, Hara A, Kuwahara H, Ando R, Sakurada S, Kisara K (1985) Intrathecal substance P analogue causes motor dysfunction in the rat. Neuropharmacology 24:811–813
Ninkovic M, Beaujouan JC, Torrens Y, Saffroy M, Hall MD, Glowinski J (1985) Differential localization of tachykinin receptors in rat spinal cord. Eur J Pharmacol 106:463–464
Otsuka M, Yanagisawa M (1988) Effect of a tachykinin antagonist on a newborn rat. J Physiol 395:255–270
Pernow B (1983) Substance P. Pharmacol Rev 35:85–141
Piercey MF, Schroeder LA, Folkers K, Xu J-C, Horig J (1981) Sensory and motor functions of spinal cord substance P. Science 214:1361–1363
Post C, Folkers K (1985) Behavioural and antinociceptive effects of intrathecally injected substance P analogues in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 113:335–343
Post C, Freedman J, Paulsson I, Hökfelt T (1987) Antinociceptive effects in mice after intrathecal injection of a substance P receptor antagonist. Spantide: lack of ‘neurotoxic action’. Regul Pept 18:243–252
Quirion R, Dam T-V (1988) Multiple neurokinin receptors: recent development. Regul Pept 22:18–25
Sakurada T, Takahashi K, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Folkesson R, Terenius L (1988) Enkephalins interact with substance P-induced aversive behaviour in mice. Brain Res 442:191–194
Sakurada T, Yamada T, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Ohba M (1989) Substance P analogues containing d-histidine antagonize the behavioural effects of intrathecally co-administered substance P in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 174:153–160
Sakurada T, Manome Y, Tan-No K, Sakurada S, Kisara K (1990) The effect of substance P analogues on the scratching, biting and licking response induced by intrathecal injection of N-methyl-d-aspartate in mice. Br J Pharmacol 101:307–310
Sakurada T, Tan-No K, Manome Y, Sakurada S, Kisara K (1991a) Aversive response produced by intrathecal injection of NMDA in mice: Effects of substance P and 5-HT antagonists. In: Kameyama T, Domino EF (eds) NMDA receptor related agents: Biochemistry, pharmacology and behavior, NPP Books, pp 219–225
Sakurada T, Yamada T, Tan-No K, Manome Y, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Ohba M (1991b) Differential effects of substance P analogs on neurokinin 1 receptor agonists in the mouse spinal cord. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259:205–210
Scatchard G (1949) The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions. Ann NY Acad Sci 51:660–672
Takahashi K, Sakurada T, Sakurada S, Kuwahara H, Yonezawa A, Ando R, Kisara K (1987) Behavioural characterization of substance P-induced nociceptive response in mice. Neuropharmacology 26:1289–1293
Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Duranti R (1987) D-Arg1,9, DTrp7,9, Leu11-Substance P (spantide) does not antagonize substance P-induced hyper-excitability of the nociceptive flexion withdrawal reflex in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 129:55–59
Yachnis AT, Crawley JN, Jensen RT, McGrane MM, Moody TW (1984) The antagonism of bombesin in the CNS by substance P analogues. Life Sci 35:1963–1969
Yanagisawa M, Otsuka M (1990) Pharmacological profile of a tachykinin antagonist, spantide, as examined on rat spinal motoneurones. Br J Pharmacol 100:711–716
Yashpal K, Dam T-V, Quirion R (1990) Quantitative autoradiographic distribution of multiple neurokinin binding sites in rat spinal cord. Brain Res 506:259–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to T. Sakurada at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakurada, T., Manome, Y., Katsumata, K. et al. Naloxone-reversible effect of spantide on the spinally mediated behavioural response induced by neurokinin-2 and -3 receptor agonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 346, 69–75 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167573
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167573