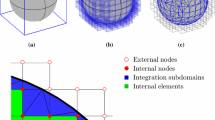
Abstract
The computational advantages associated with the utilization of preconditioned iterative equation solvers are quantified for the reanalysis of perturbed shapes using continuum structural boundary element analysis (BEA). Both single- and multizone three-dimensional problems are examined. Significant redutions in computer time are obtained by making use of previously computed solution vectors and preconditioners in subsequent analyses. The effectiveness of this technique is demonstrated for the computation of shape response sensitivities required in shape optimization. Computer times and accuracies achieved using the preconditioned iterative solvers are compared with those obtained via direct solvers and implicit differentiation of the boundary integral equations. It is concluded that this approach employing preconditioned iterative equation solvers in reanalysis and sensitivity analysis can be competitive with if not superior to those involving direct solvers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Kassim, A.M.; Topping, B.H.V. 1987: Static reanalysis: a review.J. Struct. Engng. 113, 1011–1028
Argyris, J.H.; Roy, J.R. 1972: General treatment of structural modifications.J. Struct. Div. ASCE 98, 465–492
Arora, J.S. 1976: Survey of structural reanalysis techniques.J. Struct. Div. ASCE 102, 783–802
Cook, R.D.; Young, W.C. 1985:Advanced mechanic of materials. New York: McMillan
Dervieux, A.; Fezoui, L.; Steve, H.; Periaux, J.; Stoufflet, B. 1989: Low-storage implicit upwinf-FEM schemes for the Euler equation.Proc. 11-th Int. Conf. Numer. Meth. in Fluid Dynamics, pp. 215–219. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer
Fox, R.L.; Mura, H. 1971: An approximate analysis technique for design calculations.AIAA J. 9, 177–179
Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. 1983:Matrix computations. Baltimore: John Hopkins Univ. Press
Guru Prasad, K.; Kane, J.H. 1992: Three dimensional boundary element thermal shape sensitivity analysis.Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer (in press)
Kane, J.H. 1986: Shape optimization utilizing a boundary element formulation.Proc. BETECH 86
Kane, J.H. 1987: A second generation structural shape optimization capability employing a boundary element formulation. In: Pande, G.N.; Middleton, J. (eds.)Proc. Int. Conf. on numerical methods in engineering, pp. D43/1–13. Dordrecht: Martinus Nijhoff
Kane, J.H. 1990: Boundary element design sensitivity analysis formulations for coupled problems.Engng. Analysis 7, 21–32
Kane, J.H. 1992:Boundary element analysis formulations in engineering continuum mechanics. New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Kane, J.H.; Gupta, A.; Saigal, S. 1989: Reusable intrinsic sample point (RISP) algorithm for the efficient numerical integration of three dimensional curved boundary elements.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 28, 1661–1676
Kane, J.H.; Keyes, D.E.; Guru Prasad, K. 1991: Iterative equation solution techniques in boundary element analysis.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 31, 1511–1536
Kane, J.H.; Kumar, B.L.K.; Gallagher, R.H. 1990: Boundaryelement iterative reanalysis for continuum structures.J. Engng. Mech., ASCE 116, 2293–2309
Kane, J.H.; Kumar, B.L.K.; Stabinsky, M. 1991: Transient thermoelasticity and other body force effects in boundary element shape sensitivity analysis.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 31, 1203–1230
Kane, J.H.; Mao, S.; Everstine, G. 1991: A boundary element formulation for acoustic shape sensitivity analysis.J. Acoustical Society of America 90, 561–573
Kane, J.H.; Saigal, S. 1988: Design sensitivity analysis of solids using BEM.J. Engng. Mech., ASCE 114, 1703–1722
Kane, J.H.; Saigal, S. 1990: An arbitrary multi-zone condensation technique for boundary element design sensitivity analysis.AIAA J. 28, 1277–1284
Kane, J.H.; Stabinsky, M. 1988: Simultaneous computation of multiple sensitivities by a boundary element structural analysis formulation.Proc. Third Int. Conf. on CAD/CAM Robotics and Factories of the Future
Kane, J.H.; Wang, H. 1991: Boundary element shape sensitivity analysis formulations for thermal problems with nonlinear boundary conditions.AIAA J. 29, 1978–1989
Kane, J.H.; Wang, H. 1992: Boundary formulations for shape sensitivity of temperature dependent conductivity problems.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. (in press)
Kane, J.H.; Zhao, G.; Wang, H.; Guru Prasad, K. 1992: Boundary formulations for three dimensional continuum structural shape sensitivity analysis.Tranactions, ASME J. Appl. Mech. 31 (in press)
Kardestuncer, H.; Norrie, D. 1987:Finite element handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill
Kavlie, D.; Powell, G.H. 1971: Efficient reanalysis of modified structures.J. Struct. Div. ASCE 97, 377–392
Kirsch, U. 1981:Optimum structural design. New York: McGraw-Hill
Kirsch, U.; Rubenstein, M.F. 1972: Reanalysis for limited structural design modifications.J. Engng. Mech. ASCE 98, 61–70
Kirsch, U.; Toledano, G. 1983: Approximate reanalysis for modifications of structural geometry.Comp. & Struct. 9, 269–277
Nachtigal, N.M.; Reddy, S.C.; Trefethen, L.N. 1992: How fast are nonsymmetric matrix iterations?SIAM J. Matrix Applics. July
Navarra, A. 1992: An application of GMRES to indefinite problems in meteorology.Appl. Numer. Mathem. (to appear)
Noor, A.K. 1974: Multiple configuration analysis via mixed methods.ASCE J. Struct. Div. ST9, 1991–1997
Noor, A.K.; Lowder, H.E. 1974: Approximate techniques of structural reanalysis.Comp. & Struct. 4, 801–812
Noor, A.K.; Lowder, H.E. 1975: Structural reanalysis via a mixed method.Comp. & Struct. 5, 9–12
Ortega, J.M. 1988:Introduction to parallel and vector solution of linear systems. New York: Plenum Press
Phansalkar, S.R. 1974: Matrix iterative methods for structural reanalysis.Comp. & Struct. 4, 779–800
Saad, Y.; Schultz, M.H. 1986: GMRES: a generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems.SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput. 7, 856–869
Saigal, S.; Borggaard, J.T.; Kane, J.H. 1989: Boundary element implicit differentiation equations for design and sensitivities of axisymmetric structures.Int. J. Solids & Struct. 25, 527–538
Saigal, S.; Kane, J.H. 1990: An arbitrary multi-zone condensation technique for boundary element design sensitivity analysis.AIAA J. 28, 1203–1204
Saigal, S.; Kane, J.H.; Aithal, R. 1989: Semi-analytical structural sensitivity formulation using a boundary elements.AIAA J. 27, 1615–1621
Shakib, F.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Johan; Z. 1989: Element-by-element algorithms for nonsymmetric matrix problems arising in fluids. In: Kane, J.H.; Carlson, A.D.; Cox, D.L. (eds.)Solution of superlarge problems in computational mechanics, pp. 1–33. New York: Plenum Press
Storaasli, O.O.; Sobieszczanski, J. 1974: On the accuracy of Taylor approximation for structure resizing.AIAA J. 12, 231–233
Wigton, L.B.; Yu, N.J.; Young, D.P. 1985: GMRES acceleration of computational fluid dynamics codes.Proc. AIAA 7-th Computational Fluid Dynamic Conf., 85–1494, Washington DC: AIAA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Sobieski
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guru Prasad, K., Kane, J.H. Shape reanalysis and sensitivities utilizing preconditioned iterative boundary solvers. Structural Optimization 4, 224–235 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01742749
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01742749