Abstract
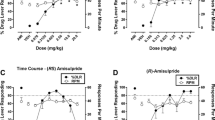
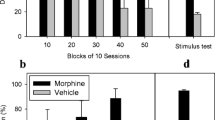
Zolpidem is a non-benzodiazepine hypnotic drug which displaces benzodiazepines from their binding sites in different brain structures. Previous work has demonstrated several differences between zolpidem and benzodiazepines, including differences between the stimulus properties of zolpidem and chlordiazepoxide. In the present study the discriminative stimulus properties of zolpidem were analysed by training rats to discriminate between this drug and saline. It was found that stimulus control developed readily with 2 mg/kg but not with 1 mg/kg zolpidem. The effect was dose-related, had a short duration of action and was antagonised by Ro 15-1788. Furthermore, stimulus control produced by zolpidem was associated with marked reductions in rates of responding. Injections of chlordiazepoxide, triazolam, lorazepam, zopiclone, CL 218,872 and pentobarbital produced dose-related responding on the zolpidem-associated lever but haloperidol did not. However, in general, the doses of those drugs which produced drug-lever responding also reduced response rates. It is possible that the above mentioned differences between the discriminative stimulus produced by zolpidem in rats and those produced by other sedatives may be due to a selective action of zolpidem on a sub-type of benzodiazepine binding site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbilla S, Depoortere H, George P, Langer SZ (1985) Pharmacological profile of zolpidem at benzodiazepine receptors and electrocorticogram in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 330:248–251
Ator NA, Griffiths RR (1983) Lorazepam and pentobarbital drug discrimination in baboons: Cross-drug generalization and interaction with Ro 15–1788. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:776–782
Ator NA, Griffiths RR (1985) Lorazepam and pentobarbital discrimination: interactions with CGS 8216 and caffeine. Eur J Pharmacol 107:169–181
Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) (1982) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Colpaert FC, Desmedt LKC, Janssen PAJ (1976) Discriminative stimulus properties of benzodiazepines, barbiturates and pharmacologically related drugs: relation to some intrinsic and anticonvulsant effects. Eur J Pharmacol 37:113–123
Dantzer R, Perio A (1982) Behavioural evidence for partial agonist properties of Ro 15–1788, a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 81:655–658
Depoortere H, Zivkovic B, Lloyd KG, Sanger DJ, Perrault G, Langer SZ, Bartholini G (1986) Zolpidem, a novel non-benzodiazepine hypnotic. I — Neuropharmacological and behavioral effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (in press)
Garcha HS, Rose IC, Stolerman IP (1985) Midazolam cue in rats: Generalization tests with anxiolytic and other drugs. Psychopharmacology 87:233–237
Haug T (1983) Neuropharmacological specificity of the diazepam stimulus complex: effects of agonists and antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 93:221–227
Haug T, Gotestam KG (1982) The diazepam stimulus complex: specificity in a rat model. Eur J Pharmacol 80:225–230
Herling S, Shannon HE (1982) Ro 15–1788 antagonizes the discriminative stimulus effects of diazepam in rats but not similar effects of pentobarbital. Life Sci 31:2105–2112
Hunkeler W, Mohler H, Pieri L, Polc L, Bonetti EP, Cumin R, Schaffner R, Haefely W (1981) Selective antagonists of benzodiazepines. Nature 290:514–516
Johansson JO, Jarbe TUC (1975) Diazepam as a discriminative cue: its antagonism by bemegride. Eur J Pharmacol 30:372–375
Lippa AS, Coupet J, Greenblatt EN, Klepner CA, Beer B (1979) A synthetic non-benzodiazepine ligand for benzodiazepine receptors: A probe for investigating neuronal substrates of anxiety. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 11:99–106
Litchfield JT, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 96:99–113
McElroy JF, Feldman RS (1982) Generalization between benzodiazepine-and triazolopyridazine-elicited discriminative cues. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:709–713
Nicholson AN, Pascoe DA (1986) Hypnotic activity of an imidazopyridine (zolpidem). Br J Clin Pharmacol 21:205–211
Overton DA (1966) State-dependent learning produced by depressant and atropine-like drugs. Psychopharmacologia 10:6–31
Overton DA (1976) Discriminable effects of benzodiazepines. Psychopharmacol Commun 2:339–343
Sanger DJ, Joly D, Zivkovic B (1985) Behavioral effects of non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic drugs: A comparison of CGS 9896 and zopiclone with chlordiazepoxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:831–837
Schechter MD (1984) Specific antagonism of the behavioral effects of chlordiazepoxide and pentobarbital in the rat. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 8:359–364
Shannon HE (1984) Stimulus control by diazepam of behavior maintained under fixed-ratio stimulus-shock termination schedules in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:715–720
Shannon HE, Davis SL (1984) CGS 8216 non competitively antagonizes the discriminative effects of diazepam in rats. Life Sci 34:2589–2596
Shannon HE, Herling S (1983) Discriminative stimulus effects of diazepam in rats: Evidence for a maximal effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:160–166
Winter JC (1978) Drug-induced stimulus control, In: Blackman DE, Sanger DJ (eds) Contemporary research in behavioral pharmacology, Plenum, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: D.J. Sanger
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanger, D.J., Zivkovic, B. The discriminative stimulus properties of zolpidem, a novel imidazopyridine hypnotic. Psychopharmacology 89, 317–322 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174367
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174367