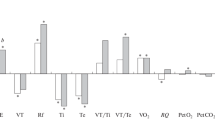
Abstract
The contribution of pulmonary stretch receptor (SR) activity to the changes in breathing pattern (f,V T,t I,t E,t I:t E) following inhalation of ammonia vapour has been studied in rabbits at three levels of lung distension, i.e., three levels of SR activity, and during reversible SO2-blockade of SR.
The results show that the increase in breathing frequency (f) and the decrease in tidal volume (V T) due to ammonia inhalation are almost identical for animals with and without blockade of SR, whereas the duration of inspiration and expiration (t I,t E) as well as their relationship (t I:t E) vary considerably, the variations dependeing on the level of SR activity. For a givent I the expiration was longer in animals with SR intact than in animals with SR blocked.
It is concluded that in rabbits the increased activity of SR after inhalation of ammonia counteracts significantly the predominant effects of irritant (deflation) receptor stimulation, thus rendering possible a longer expiration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callanan D, Dixon M, Widdicombe JG (1975) The acute affects of SO2 on pulmonary mechanics, breathing patterns and pulmonary vagal afferent receptors in the rabbit. J Physiol (London) 247:23–24P
Davies A (1976) Respiratory reflexes in rabbits without pulmonary stretch receptor activity. In: Duron B (ed) Respiratory Centres and Afferent Systems, INSERM, Amiens, Vol 59, pp 235–262
Davies A, Dixon M, Callanan D, Huszczuk A, Widdicombe JG, Wise JGM (1978) Lung reflexes in rabbits during pulmonary stretch receptor block by sulphur dioxide. Respir Physiol 34:83–101
Kohl J, Koller EA (1980) Stretch receptor activity during irritant-induced tachypnoea in the rabbit. Pflügers Arch 386:231–237
Koller EA (1968) Atmung und Kreislauf im anaphylaktischen Asthma bronchiale des Meerschweinchens. III. Die Lungenveränderungen im Asthmaanfall und die inspiratorische Reaktion. Helv Physiol Acta 26:153–170
Koller EA, Ferrer P (1970) Studies on the role of the lung delfation reflex. Respir Physiol 10:172–183
Koller EA, Ferrer P (1973) Discharge patterns of the lung stretch receptors and activation of deflation fibres in anaphylatic bronchial asthma. Respir Physiol 17:113–126
Koller EA, Kohl J (1975) The Hering-Breuer reflexes in the bronchial asthma attack. Pflügers Arch 357:165–171
Koller EA, Rüegg DG, Ferrer P (1971) Approach to quantitative differentiation between the respiratory effects evoked from the lung stretch and the lung deflation receptors during thoracic compression. Experimentia 27:163–164
Mills JE, Sellick H, Widdicombe JG (1969) Activity of lung irritant receptors in pulmonary microembolism, anaphylaxis and drug-induced bronchoconstriction. J Physiol (London) 203:337–357
Miserocchi G, Trippenbach T, Mazzarelli M, Jaspar N, Hazucha M (1978) The mechanism of rapid shallow breathing due to histamine and phenyldiguanide in cats and rabbits. Respir Physiol 32:141–153
Oberholzer RJH (1944) Narkoseeinfluß auf vagale Atmungsreflexe. Helv Physiol Acta 2:449–459
Widdicombe JG (1961) The activity of pulmonary stretch receptors during bronchoconstriction, pulmonary oedema, atelectasis and breathing against a resistance. J Physiol (London) 159:436–450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohl, J., Koller, E.A. The effect of pulmonary stretch receptor activity on the respiratory response to ammonia-inhalation. Pflugers Arch. 392, 279–283 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584311
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584311