Summary
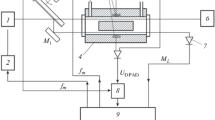
A relatively simple instrument for the detection and measurement of atmospheric trace constituents by longpath absorption spectroscopy in the visible and UV spectral ranges is described. A selected wavelength interval is scanned with high repetition rate (∼ 100 Hz). After averaging over several ten thousand scans molecular absorption bands with optical densities below 10−4 can be detected. Using a 10-km lightpath the following detection limits are reached: SO2: 17ppt(1 ppt = 1 part in 1012); NO2: 100 ppt; NO3: 0.5 ppt; HNO2: 20 ppt; O3: 2100 ppt; CH2O: 120 ppt.
Zusammenfassung
Beschrieben wird ein relativ einfach aufgebautes Gerät zur Identifikation und Konzentrationsbestimmung von atmosphärischen Spurenstoffen mittels Langpfad-Absorptionsspektroskopie im sichtbaren und ultravioletten Spektralbereich. Ein voreingestellter Wellenlängenbereich wird mit hoher Wiederholfrequenz (∼ 100 Hz) abgetastet. In über einige zehntausend Abtastungen gemittelten Spektren sind Molekülbanden mit optischen Dichten von unter 10−4 noch nachweisbar. Bei 10 km Lichtweg in der freien Atmosphäre werden folgende Nachweisgrenzen erreicht: SO2: 17 ppt (1ppt = 1 Teil in 1012); NO2: 100 ppt; NO3: 0.5 ppt; HNO2: 20ppt; O3: 2100ppt; CH2O: 120 ppt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Hanst PL (1971) Adv Environ Sci Technol 2:91
Bonafe G, Caesari G, Giovanelli G, Tirabassi T, Vittori O (1976) Atmos Environ 10:469–474
Millan MM, Hoff RM (1978) Atmos Environ 12:853–864
Connell PS, Perry RA, Howard CJ (1980) Geophys Res Lett 7:1093–1096
Noxon JF, Norton RB, Henderson RB (1980) Geophys Res Lett 7:125–128
Noxon JF (1981) Geophys Res Lett 8:1223–1226
Tuazon EC, Winer AM, Pitts JN (1981) Environ Sci Technol 15:1232–1237
Haugen DA (ed) (1973) Workshop on micrometeorology. Science Press, Ephrata, PA
Menyuk N, Killinger DK, Menyuk CR (1983) Optical and laser remote sensing. Springer Ser, Optical Sci 39:185–190
Platt U, Perner D, Pätz HW (1979) J Geophys Res 84:6329–6335
Perner D, Platt U (1979) Geophys Res Lett 6:917–920
Platt U, Perner D, Winer AM, Harris GW, Pitts JN (1980) Geophys Res Lett 7:89–92
Platt U, Perner D, Winer AM, Harris GW, Pitts JN (1980) Nature 285:312–314
Platt U, Perner D (1980) J Geophys Res 85:7453–7458
Platt U, Perner D, Schröder J, Kessler C, Tönnissen A (1981) J Geophys Res 86:11965–11970
Harris GW, Carter WPL, Winer AM, Pitts JN, Platt U, Perner D (1982) Environ Sci Technol 16:414–419
Perner D, Platt U (1980) Geophys Res Lett 7:1053–1056
Magnotta F, Johnston HS (1980) Geophys Res Lett 7:769–772
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. W. Fresenius zum 70. Geburtstag gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Platt, U., Perner, D. Ein Instrument zur spektroskopischen Spurenstoffmessung in der Atmosphäre. Z. Anal. Chem. 317, 309–313 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00494483
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00494483