Summary
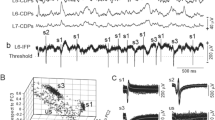
27 cells in the S I group I projection area of the cerebral cortex, identified as activated by group I afferent fibres by electrical stimulation of the deep radial nerve, were examined by natural stimulation in 4 awake cats.
Sixty-four percent of the cells responded to wrist and/or digital ventroflexion only. Another 28% of the cells responded also to elbow flexion or extension. Only one cell responded to stretch of antagonistic muscles.
Half of the cells responded to pulling of only one out of four available muscle tendons of wrist and digital dorsiflexors. The rest of the cells responded to pulling of two adjacent tendons.
All cells tested responded to light tapping stimulation of skin areas overlying the muscles providing excitation, presumably as a result of mechanical stimulus spread to sensitive muscle spindles. 20% of the cells responded to deflection of hairs located on the paw.
The receptive fields obtained were compared with those obtained in the cortex and at lower levels of the pathway with electrical nerve stimulation on nembutalized animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asanuma, H., Sakata, H.: Functional organization of a cortical efferent system examined with focal depth stimulation in cats. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 35–54 (1967).
Grampp, W., Oscarsson, O.: Inhibitory neurones in the group I projection area of the cat's cerebral cortex. In: Structure and Functions of Inhibitory Neuronal Mechanisms. Proceedings of the Fourth International Meeting of Neurobiologists. New York: Pergamon Press 1968.
Granit, R., Henatsch, H.D.: Gamma control of dynamic properties of muscle spindles. J. Neurophysiol. 19, 356–366 (1956).
Körner, L., Landgren, S.: Projections of low threshold joint afferents to the cerebral cortex of the cat. Acta physiol. scand. 76, 5A-7A (1969).
Landgren, S., Silfvenius, H., Wolsk, D.: Somato-sensory paths to the second cortical projection area of the group I muscle afferents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 191, 543–559 (1967).
Oscarsson, O.: Functional organization of spinocerebellar paths. Handbook of Sensory Physiology. Volume II. Somatosensory System. Ed. by A. Iggo. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1972. (In Press).
— Rosén, I.: Projection to cerebral cortex of large muscle spindle afferents in forelimb nerves of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 924–945 (1963).
—: Short-latency projections to the cat's cerebral cortex from skin and muscle afferents in the contralateral forelimb. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 182, 164–184 (1966).
— Sulg, I.: Organization of neurones in the cat cerebral cortex that are influenced from group I muscle afferents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 183, 189–210 (1966).
Rosén, I.: Afferent connections to group I activated cells in the main cuneate nucleus of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 205, 209–236 (1969b).
—: Excitation of group I activated thalamo-cortical relay neurones in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 205, 237–255 (1969b).
Rosén, I.: Projection of forelimb group I muscle afferents to the cat cerebral cortex. Lund: Thesis 1970.
— Asanuma, H.: Receptive fields of group I activated cells in the cerebral cortex examined by natural stimulation. Fed. Proc. 30, 664 (1971).
— Sjölund, B.: Organization of group I activated cells in the main and external cuneate nuclei of the cat: Identification of muscle receptors. Exp. Brain Res. 16, 221–237 (1973a).
—: Organization of group I activated cells in the main and external cuneate nuclei of the cat: Convergence patterns demonstrated by natural stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 16, 238–246 (1973b).
Silfvenius, H.: Cortical peojections of large muscle afferents from the cat's forelimb. Acta physiol. scand. 74, 25A-26A (1968).
—: Projections to the cerebral cortex from afferents of the interosseous nerves of the cat. Acta physiol. scand. 80, 196–214 (1970b).
Swett, J.E., Bourassa, C.M.: Short latency activation of pyramidal tract cells by group I afferent volleys in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 189, 101–117 (1967a).
—: Comparison of sensory discrimination thresholds with muscle and cutaneous nerve volleys in the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 530–545 (1967b).
Thompson, W.D., Stoney, S.D., Jr., Asanuma, H.: Characteristics of projections from primary sensory cortex to motorsensory cortex in cats. Brain Res. 22, 15–27 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosén, I., Asanuma, H. Natural stimulation of group I activated cells in the cerebral cortex of the awake cat. Exp Brain Res 16, 247–254 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233329
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233329