Summary
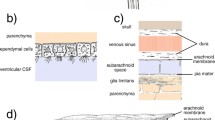
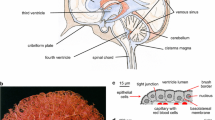
The ventriculo-cisternal perfusion technique was utilized in anaesthetized goats to investigate the clearance of urea and sucrose from isotonic and hypertonic perfusion fluids. Diffusional outflux coefficients of 0.114±0.015 (SEM) and 0.030±0.003 ml/min were found for urea and sucrose, respectively, in the isotonic (control) perfusions; these coefficients increased by 40% and 83%, respectively, in the hypertonic (0.40 osmolal) perfusions. Changes in ventricular hydrostatic pressure were not of sufficient magnitude, and changes in fluid accretion (osmotic flow from brain to ventricular fluid) were not in the right direction, to explain the enhanced clearance of nonelectrolytes in the experimental perfusions. The outflux coefficient data, together with previously reported osmometric data, support the hypothesis that the increased clearance of urea and sucrose from the hypertonic perfusion fluids is primarily the result of expansion of intercellular channels (due to cell shrinkage) between ependymal and parenchymal cells.
Some of the factors affecting indicator clearance from isotonic perfusion fluid (e.g. perfusion rate, unilateral vs. bilateral ventriculo-cisternal perfusion, anesthetic, and anatomical barriers) have been further evaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, W.F.: Effects of plasma tonicity on the distribution of water and solutes in brain and muscle. Exp. Neurol. 13, 58–70 (1965)
Bentley, P.J.: Physiological properties of the isolated frog bladder in hyperosmotic solutions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 12, 233–239 (1964)
Bering, E.A., Jr., Sato O.: Hydrocephalus: Changes in formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid within the cerebral ventricles. J. Neurosurg. 20, 1050–1063 (1963)
Bradbury, M.W.B., Bagdoyan, H., Berberian, A., Kleeman, C.R.: Effect of osmolarity on cell water and electrolytes in the isolated frog brain. Amer. J. Physiol. 215, 730–735 (1968)
Bradbury, M.W.B., Davson, H.: The transport of urea, creatinine and certain monosaccharides between blood and fluid perfusing the cerebral ventricular system of rabbits. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 170, 195–211 (1964)
Brightman, M.W., Reese, T.S.: Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J. Cell Biol. 40, 648–677 (1969)
Calhoun, M.C., Hurt, H.D., Eaton, H.D., Rousseau, J.E., Jr., Hall, R.C., Jr.: Rates of formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid in bovine hypovitaminosis A. J. Dairy Sci. 50, 1486–1494 (1967)
Calhoun, M.C., Hurt, H.D., Eaton, H.D., Rousseau, J.E., Jr., Hall, R.C., Jr.: Osmotic flow during ventriculocisternal perfusion of vitamin A deficient calves. J. Dairy Sci. 51, 1781–1786 (1968)
Cserr, H.: Potassium exchange between cerebrospinal fluid, plasma, and brain. Amer. J. Physiol. 209, 1219–1226 (1965)
Curl, F.D., Pollay, M.: Transport of water and electrolytes between brain and ventricular fluid in the rabbit. Exp. Neurol. 20, 558–574 (1968)
Dainty, J., Ginzburg, B.Z.: The permeability of the cell membranes of Nitella translucens to urea, and the effect of high concentrations of sucrose on this permeability. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 79, 112–121 (1964)
Davson, H., Kleeman, C.R., Levin, E.: Quantitative studies of the passage of different substances out of the cerebrospinal fluid. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 161, 126–142 (1962)
Davson, H., Pollay, M.: The turnover of 24Na in the cerebrospinal fluid and its bearing on the blood-brain barrier. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 167, 247–255 (1963)
Diamond, J.M.: Non-linear osmosis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 183, 58–82 (1966)
Domer, F.R., Hiatt, R.A.: Effects of quaternary ammonium compounds on the movement of potassium out of the cerebrospinal fluid. Arch. int. Pharmaeodyn. 173, 306–315 (1968)
Feldberg, W., Fleischhauer, K.: Penetration of bromophenol blue from the perfused cerebral ventricles into the brain tissue. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 150, 451–462 (1960)
Fenstermacher, J.D.: Studies of transport between csf, brain and blood by ventriculocisternal perfusion. The Proceedings of a Symposium on the Blood-Brain Barrier, pp. 49–58. Oxford: Truex Press 1970
Ferguson, R.K., Woodbury, D.M.: Penetration of 14C-inulin and 24C-sucrose into brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and skeletal muscle of developing rats. Exp. Brain Res. 7, 181–194 (1969)
Fishman, R.A.: Factors influencing the exchange of sodium between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. J. clin. Invest. 38, 1698–1708 (1959)
Franz, T.J., Van Bruggen, J.T.: A possible mechanism of action of DMSO. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 141, 302–309 (1967)
Heisey, S.R., Held, D., Pappenheimer, J.R.: Bulk flow and diffusion in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the goat. Amer. J. Physiol. 203, 775–781 (1962)
Henderson, L.W.: Peritoneal ultrafiltration dialysis: enhanced urea transfer using hypertonic peritoneal dialysis fluid. J. clin. Invest. 45, 950–955 (1966)
Hochwald, G.M., Wallenstein, M.: Exchange of albumin between blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain in the cat. Amer. J. Physiol. 212, 1199–1204 (1967)
Johnson, J.A., Cavert, H.M., Lifson, N., Visscher, M.B.: Permeability of the bladder to water studied by means of isotops. Amer. J. physiol. 165, 87–92 (1951)
Levin, V.A., Fenstermacher, J.D., Patlak, C.S.: Sucrose and inulin space measurements of cerebral cortex in four mammalian species. Amer. J. Physiol. 219, 1528–1533 (1970)
Lorenzo, A.V., Hammerstad, J.P., Cutler, R.W.P.: The effect of anaesthetic agents on the cerebrospinal fluid clearance of 35S-sulphate and 125I-iodide. Biochem. Pharmacol. 17, 1279–1283 (1968)
Milhorat, T.H.: Hydrocephalus and the cerebrospinal fluid, pp. 237. Baltimore: The Williams and Wilkins Company 1972
Morain, W.D., Replogle, C.A., Curran, P.F.: Effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on permeability and electrical properties of frog skin. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 154, 298–302 (1966)
Pappenheimer, J.R., Heisey, S.R., Jordan, E.F.: Active transport of Diodrast and phenolsulfonphthalein from cerebrospinal fluid to blood. Amer. J. Physiol. 200, 1–10 (1961)
Pappenheimer, J.R., Heisey, S.R., Jordan, E.F., Downer, J. deC.: Perfusion of the cerebral ventricular system in unanesthetized goats. Amer. J. Physiol. 203, 763–774 (1962)
Pierce, E.C., Jr., Lambertsen, C.J., Deutsch, S., Chase, P.E., Linde, H.W., Dripps, R.D., Price, H.L.: Cerebral circulation and metabolism during thiopental anesthesia and hyperventilation in man. J. clin. Invest. 41, 1664–1671 (1962)
Pollay, M., Kaplan, R.J.: Diffusion of non-electrolytes in brain tissue. Brain Res. 17, 407–416 (1970)
Rall, D.P.: Transport through the ependymal linings. In: Progress in Brain Research, (vol. 29): Brain Barrier Systems, pp. 159–172. Ed. by A. Lajtha and D.H. Ford. New York: Elsevier Publishing Co. 1968
Rall, D.P., Oppelt, W.W., Patlak, C.S.: Extracellular space of brain as determined by diffusion of inulin from the ventricular system. Life Sci. 1, 43–48 (1962)
Rapoport, S.I.: Effect of concentrated solutions on blood-brain barrier. Amer. J. Physiol. 219, 270–274 (1970)
Rapoport, S.I., Hori, M., Klatzo, I.: Reversible osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier. Science, N. Y. 173, 1026–1028 (1971)
Reed, D.J., Woodbury, D.M.: Effect of hypertonic urea on cerebrospinal fluid pressure and brain volume. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 164, 252–264 (1962)
Rich, G.T., Sha'afi, R.I., Romualdez, A., Solomon, A.K.: Effect of osmolality on the hydraulic permeability coefficient of red cells. J. gen. Physiol. 52, 941–954 (1968)
Schantz, E.J., Lauffer, M.A.: Diffusion measurements in agar gel. Biochemistry, N.Y. 1, 658–663 (1962)
Thompson, A.M.: Hyperosmotic effects on brain uptake of nonelectrolytes. In: Alfred Benzon Symposium II: Capillary Permeability, pp. 459–467. Ed. by C. Crone and N. A. Lassen. New York: Academic Press 1970
Urakabe, S., Handler, J.S., Orloff, J.: Effect of hypertonicity on permeability properties of the toad bladder. Amer. J. Physiol. 218, 1179–1187 (1970)
Vickers, J.L., Marshall, E.K., Jr.: Permeability of the urinary bladder to urea and sodium chloride. Amer. J. Physiol. 70, 607–612 (1924)
Voetmann, E.: On the structure and surface area of the human choroid plexuses. Acta anat. (Basel) 8, Suppl. 10, 1–116 (1949)
Welch, K., Sadler, K.: Permeability of the choroid plexus of the rabbit to several solutes. Amer. J. Physiol. 210, 652–660 (1966)
Welch, K., Sadler, K., Gold, G.: Volume flow across choroidal ependyma of the rabbit. Amer. J. Physiol. 210, 232–236 (1966)
Wright, E.M., Prather, J.W.: The permeability of the frog choroid plexus to nonelectrolytes. J. Membrane Biol. 2, 127–149 (1970)
Zadunaisky, J.A., Wald, F., DeRobertis, E.D.P.: Osmotic behavior and glial changes in isolated frog brains. In: Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 15, pp. 196–218. Ed. by E.D.P. DeRobertis and R. Carrea. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Co. 1965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study, which represents part of a doctoral thesis submitted to the University of Kansas, was supported in part by United States Public Health Service Grants 2 RO1 NS07059 and 5 SO1 RR05373. The fine technical assistance of E. Hart is gratefully acknowledged. The authors wish to thank Dr. J. Trank, Dr. D. Reed and Dr. E. Fingl for valuable consultation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johanson, C.E., Foltz, F.M. & Thompson, A.M. The clearance of urea and sucrose from isotonic and hypertonic fluids perfused through the ventriculo-cisternal system. Exp Brain Res 20, 18–31 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239015
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239015