Summary
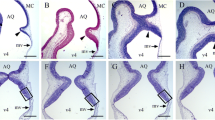
Previous results from our laboratory (Bejar et al. 1985) indicated that a single injection in mouse pups of the antimitotic/mutagenic agent methylazoxymethanol at postnatal day 5 typically produces hypogranular cerebella with no changes in foliation, in contrast to the severe alterations observed after the more usual injection on the day of birth. Here we report that injection of a higher dose (30 mg/kg) of methylazoxymethanol, always at postnatal day 5, leads to the additional presence of a ectopic cell layer in adult cerebellum. Immunostaining with several antibodies recognizing cell specific proteins ruled out the possibility that these ectopic cells were glial and electron microscopy indicated that they were morphologically mature granule cells. In the molecular layer of other cerebellar areas and apparently unrelated with granule cell ectopia, ectopic Golgi epithelial cells were observed. The reason for the presence of these ectopic cells of different type in the molecular layer was discussed in relation with analogous ectopias obtained by other means.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J (1973) Experimental reorganization of the cerebellar cortex. III Regeneration of the external germinal layer and granule cell ectopia. J Comp Neurol 149:123–152
De Barry J, Gombos G (1989) Immunohistochemistry with anti-Calbindin and anti-neurofilament antibodies in the cerebellum of methylazoxymethanol-treated mice. J Neurosci 23:330–336
De Barry J, Gombos G, Hamori J (1987) Alteration of mouse cerebellar circuits following methylazoxymethanol treatment during development: immunohistochemistry of GABAergic elements and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 261:253–265
Bejar A, Roujansky P, De Barry J, Gombos G (1985) Different effect of methylazoxymethanol on mouse cerebellar development depending on the age of injection. Exp Brain Res 57:279–285
Borrelli E, Langley OK, Ghandour MS, Delaunoy J-P, Gombos G (1982) Immunocytology of carbonic anhidrase II in the central nervous system of Jimpy mutant mice. Neuroci Lett 32:321–327
Berciano MT, Conde B, Lafarga M (1990) Interactions between astroglia and ectopic granule cells in the cerebellar cortex of normal adult rats: a morphological and cytochemical study. Exp Brain Res 80:397–408
Chen S, Hillman DE (1986) Selective ablation of neurons by methylazoxymethanol during pre- and postnatal brain development. Exp Neurol 94:103–119
Chen S, Hillman DE (1988) Developmental factors related to abnormal cerebellar foliation induced by methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM). Dev Brain Res 40:201–212
Fañanás JR (1916) Contribucion al estudio de la neuroglia del cerebelo. Trab Lab Invest Biol 14:163–179
Fujita S (1967) Quantitative analysis of cell proliferation and differentiation in the cortex of the postnatal mouse cerebellum. J Cell Biol 32:277–287
Ghandour MS, Labourdette G, Vincendon G, Gombos G (1981) A biochemical and immunohistological study of S-100 protein in developing rat cerebellum. Dev Neurosci 4:98–109
Hillman DE, Chen S, Ackman J (1988a) Perinatal methylazoxymethanol acetate uncouples coincidence of orientation of cerebellar folia and parallel fibers. Neuroscience 24:99–110
Hillman DE, Chen S, Chen V (1988b) Ectopic glial cell in rat cerebella following neonatal administration of methylazoxymethanol acetate. Brain Res 447:353–359
Johnston MV, Coyle JT (1982) Cytotoxic lesions and the development of transmitter systems. Trends Neurosci 5:153–156
Landis SC (1973) Granule cell heterotropia in normal and nervous mutant mice of the BALB/c strain. Brain Res 61:175–189
Lovell KL, Goetting MG, Jones MZ (1980) Regeneration in the cerebellum following methylazoxymethanol-induced destruction of the external germinal layer. Dev Neurosci 3:128–139
Palay SL, Chan-Palay V (1974) In: Cerebellar cortex. Cytology and organization, Springer, Berlin
Rakic P, Sidman RL (1973) Sequence of developmental abnormalities leading to granule cell deficit in cerebellar cortex of weaver mutant mice. J Comp Neurol 152:103–132
Sotelo C, Rio JP (1980) Cerebellar malformation obtained in rats by early postnatal treatment with 6-aminonicotamide. Role of neuron-glia interactions in cerebellar development. Neuroscience 5:1737–1759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia-Ladona, F.J., de Barry, J., Girard, C. et al. Ectopic granule cell layer in mouse cerebellum after methyl-azoxy-methanol (MAM) treatment. Exp Brain Res 86, 90–96 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231043
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231043