Summary
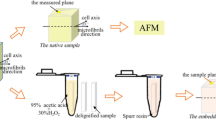
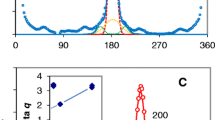
The thick-walled bamboo fibres exhibit a polylamellate structure with alternating broad and narrow lamellae. Characteristically the cellulose fibrils in the broad lamellae are oriented almost parallel to the longitudinal axis of the fibre (2–20°), whereby there is a gradual but only slight increase in the angle from middle lamella to lumen. The narrow lamellae consist of fibrils oriented almost perpendicular to the cell axis (85–90°); this angle remains constant in all the successive narrow lamellae. The concentration of lignin is higher in the narrow lamellae than in the broad ones. Xylan seems to occur in a higher concentration in the narrow lamellae. The pits between the fibres are bordered. The results are discussed in relation to earlier data on wall structure and development. A model for the thick-walled bamboo fibre is presented with a new terminology for the various lamellae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentum, A. L. K., Côté, W. A. Jr., Day, A. C., Timell, T. E. 1969. Distribution of lignin in normal and tension wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 3: 218–231
Chafe, S. C. 1970. The fine structure of the collenchyma cell wall. Planta 90: 12–21
Chafe, S. C. 1974. Cell wall structure in the xylem parenchyma of Cryptomeria. Protoplasma 81: 63–76
Chafe, S. C., Chauret, G. 1974. Cell wall structure in the xylem parenchyma of trembling aspen. Protoplasma 80: 129–147
Chafe, S. C., Doohan, M. E. 1972. Observations on the ultrastructure of the thickened sieve cell wall in Pinus strobus. Protoplasma 75: 67–78
Chafe, S. C., Wardrop, A. B. 1972. Fine structural observations on the epidermis. I. The epidermal cell wall. Planta 107: 269–278
Côté, W. A. Jr., Day, A. C., Timell, T. E. 1968. Distribution of lignin in normal and compression wood of tamarack. Wood Sci. Technol. 2: 13–37
Dietrichs, H. H., Zschirnt, K. I. 1972. Untersuchungen über den enzymatischen Abbau von Holocellulosen in vitro. Holz Roh Werkst. 30: 66–74
Fergus, B. J., Procter, A. R., Scott, J. A. N., Goring, D. A. I. 1969. The distribution of lignin in sprucewood as determined by ultraviolet microscopy. Wood Sci. Technol. 3: 117–138
Ghosh, S. S., Negi, B. S. 1959. Anatomical features of bamboo used for paper manufacture. Cellulose Research Symposium, CSIR, New Delhi, pp. 139–148
Grosser, D. 1971. Beitrag zur Histologie und Klassifikation asiatischer Bambusarten. Mitt. der Bundesforschungsanstalt für Forst- und Holzwirtschaft, Reinbek, Nr. 85, 321 S.
Grosser, D., Liese, W. 1971. On the anatomy of Asian bamboos with special reference to their vascular bundles. Wood Sci. Technol. 5: 290–312
Herzog, A. 1938. Zur Mikroskopie der Bambusfaser. Woch. Papierfabr. 69: 1025–1031
Higuchi, T. 1957. Biochemical studies of lignin formation. III. Physiol. Plant. 10: 633–648
Hoffmann, P., Parameswaran, N. 1976. On the ultrastructural localization of hemicelluloses within delignified tracheids of spruce. Holzforschung 30: 62–70
van der Houven van Oordt-Hulshof, B. 1957. Cell-wall structure of some Monocotyledones. Acta bot. neerl. 6: 420–426
Itoh, T. 1975a. Application of freeze etching technique for investigating cell wall organization of parenchyma cells in higher plants. Wood Res. 58: 20–32
Itoh, T. 1975b. Cell wall organization of cortical parenchyma of angiosperms observed by the freeze-etching technique. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 88: 145–156
Krishnagopalan, A., Kutscha, N. P., Simard, G. L. 1975. The effect of refining on the morphology and properties of bamboo paper. IPPTA 12: 9–19
Kutscha, N. P. 1965. Fibrillar orientation within the bamboo fiber. Wood Products Engg. Report 201, SUNY College of Forestry, Syracuse, New York, USA
Lüdtke, M. 1928. Zur kenntnis der pflanzlichen Zellmembran. Ann. Chem. 466:27–58
McClure, F. A. 1966. The bamboos: a fresh perspective. Cambridge, Mass. Harvard Univ. Press, 347 pp.
Nomura, T., Yamada, T. 1974a. X-ray analysis of tyrosine in growing stage of bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis A. & C. Riviere) Wood Res. 56: 21–27
Nomura, T., Yamada, T. 1974b. Crystallinity change in the growing stage of bamboo (Phyllostachys mitis). Wood Res. 57: 23–30
Nomura, T., Yamada, T. 1976. Small angle x-ray scattering of woody plants. Wood Res. 59/60: 7–18
Parameswaran, N. 1975. Zur Wandstruktur von Sklereiden in einigen Baumrinden. Protoplasma 85: 305–314
Parameswaran, N., Liese, W. 1975. On the polylamellate structure of parenchyma wall in Phyllostachys edulis Riv. IAWA Bull. 1975/4: 57–58
Parham, R. A. 1974. Distribution of lignin in kraft pulp as determined by electron microscopy. Wood Sci. 6: 305–315
Parham, R. A., Côté, W. A. Jr. 1971. Distribution of lignin in normal and compression wood of Pinus taeda L. Wood Sci. Technol. 5: 49–62
Preston, R. D. 1974. The physical biology of plant cell walls. London: Chapman and Hall, 491 pp.
Preston, R. D., Singh, K. 1950. The fine structure of bamboo fibres. I. Optical properties and x-ray data. J. exp. Bot. 1: 214–226
Preston, R. D., Singh, K. 1952. The fine structure of bamboo fibres. II. Refractive indices and wall density. J. exp. Bot. 3: 162–169
Reis, D., Roland, J.-C. 1974. Mise en évidence de l'organisation de parois des cellules végétales en croissance par extractions ménagées des polysaccharides associées à la cytochimie ultrastructurale. J. Microscopie 20: 271–284
Roland, J.-C, Vian, B., Reis, D. 1975. Observations with cytochemistry and ultracryotomy on the fine structure of the expanding walls in actively elongating plant cells. J. Cell Sci. 19: 239–259
Saiki, H., Furukawa, I., Harada, H. 1972. An observation on tensile fracture of wood by scanning electron microscope. Bull. Kyoto Univ. For. no. 43: 309–319
Sarkanen, K. V., Hergert, H. L. 1971. Classification and distribution. In: Sarkanen, K. V., Ludwig, C. H. (eds.). Lignins., pp. 43–94, New York: Wiley Intersci.
Schlotmann, A. 1933. Untersuchungen über die Struktur pflanzlicher Haare und Fasern. Planta 19: 313–334
Sinner, M., Parameswaran, N., Dietrichs, H. H., Liese, W. 1973. Spezifischer xylanolytischer Abbau der delignifizierten Zellwand von Rotbuchenholz (Fagus sylvatica L.). Holzforschung 27: 36–42
Sinner, M., Parameswaran, N., Yamazaki, N., Liese, W., Dietrichs, H. H. 1976. Specific enzymatic degradation of polysaccharides in delignified wood cell walls. J. Appl. Polymer. Sci., Appl. Pol. Symposia 28: 993–1024
Thomas, R. J., Nicholas, D. D. 1966. Pit membrane structure in loblolly pine as influenced by solvent exchange drying. For. Prod. J. 16: 53–56
Tono, T., Ono, K. 1962a, b. Researches on the morphological structure and the physical properties of bamboo fibers for paper making. I. Relation between the behaviour of swelling and the morphological structure. II. The layered structure and its morphological transformation by acid treatment. J. Jap. Wood Res. Soc. 8: 238–244, 245–249
Yamanaka, K., Harada, H. 1968. The ultrastructure of vessel wall in certain species of Dipterocarpaceae wood. Bull. Kyoto Univ. For. 40: 293–300
Yu, C. H., Chang, J. W. 1963. A quantitative investigation on the arrangement of the mechanical tissue in bamboo culm. Acta bot. Sin. 11: 308–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We are thankful to Mrs. R. Schultze and Miss B. Schröder for their technical assistance. Grateful acknowledgement is also due to Dr. D. Keyser and Mrs. K. Hoffmann for the SEM facilities and to Prof. Dr. J. Bauch and Mrs. R. Endeward for the UV-microspectrophotometry. Prof. T. E. Timell (Syracuse) and Dr. O. Faix were helpful with the preparation of hydrofluoric acid concentrations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parameswaran, N., Liese, W. On the fine structure of bamboo fibres. Wood Science and Technology 10, 231–246 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350830
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350830