Abstract
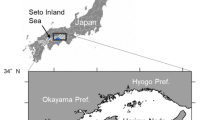
The ontogenetic diel vertical migration of the planktonic copepodCalanus sinicus was investigated in the Inland Sea of Japan in summer 1988, when the water was thermally stratified with a thermocline of ca 5 °C between 35 and 45 m. Stage-specific differences in the diel vertical migration behavior ofC. sinicus were found. Eggs were spawned primarily within the surface-waters between midnight and dawn by ascending females, and sank gradually to deeper waters until they hatched into nauplii. Non-feeding nauplius stages (NI and II) were distributed throughout the water column, but the first feeding stage (NIII) performed an ontogenetic upward migration. NIV to VI and copepodite (C) stages I to III continuously aggregated in the phytoplankton-rich euphotic layer. However, the depth of the median CI to III populations descended as stage progressed. The onset of prominent diel vertical migration took place in CIV, and the amplitude of vertical migration increased with age, being maximal in adult females (CVI♀). Adult males (CVI♂), however, remained in the layer below 20 m, and did not migrate dielly. The ecological significance of ontogenetic diel vertical migration is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Banse, K. (1964). On the vertical distribution of zooplankton in the sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2: 55–125
Bradford, J. M. (1988). Review of the taxonomy of the Calanidae (Copepoda) and the limits to the genusCalanus. Hydrobiologia 167/168: 73–81
Brodsky, K. A. (1965). Variability and systematics of the species of the genusCalanus Copepoda. I.Calanus pacificus Brodsky, 1948, andCalanus sinicus Brodsky sp. n. Issled. Fauny Morei 3: 22–71 [in Russ., cited in Kidachi 1979a, b]
Brodsky, K. A. (1975). Phylogeny of the family Calanidae (Copepoda) on the basis of a comparative morphological analysis of its characters. In: Zvereva, Z. A. (ed.) Geographical and seasonal variability of marine plankton. Keter Publishing House, Jerusalem, p. 1–127
Cushing, D. H. (1951). The vertical migration of planktonic crustacea. Biol. Rev. 26: 158–192
Dagg, M. J. (1985). The effects of food limitation on diel migratory behavior in marine zooplankton. Ergeb. Limnol. 21: 247–255
Dagg, M. J., Frost, B. W., Walser, W. E. (1989). Copepod diel migration, feeding, and the vertical flux of pheopigments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34: 1062–1071
Enright, J. T. (1977). Diurnal vertical migration: Adaptive significance and timing. Part 1. Selective advantage: a metabolic model. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22: 856–872
Fancet, M. S., Kimmerer, W. J. (1985). Vertical migration of the demersal copepodPseudodiaptomus as a means of predator avoidance. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 88: 31–43
Harding, J. P., Marshall, S. M., Orr, A. P. (1951). Time of egg-laying in the planktonic copepodCalanus. Nature, Lond. 167: 953
Harris, R. P., Malej, A. (1986). Diel patterns of ammonium excretion and grazing rhythms inCalanus helgolandicus in surface stratified waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 31: 75–85
Hirota, R. (1964). Zooplankton investigation in Hiuchi-nada in the Setonaika (Inland Sea of Japan). I. The seasonal occurrence of Copepoda at the three stations in Hiuchi-nada. J. oceanogr. Soc. Japan 20: 24–31
Hirota, R. (1979). Seasonal occurrence of zooplankton at a definite station off Mukaishima from July of 1976 to June of 1977. Publs Amakusa mar. biol. Lab. 5: 9–17
Huntley, M., Brooks, E. R. (1982). Effects of age and food availability on diel vertical migrations ofCalanus pacificus. Mar. Biol. 71: 23–31
Kadota, S. (1984). Distributional characteristics of the copepodCalanus sinicus in coastal waters of southern part of middle Japan. In: Marumo, R. and co-authors (eds.) Biological processes in the ocean. Koseisha-Koseikaku, Tokyo, p. 121–123 [in Jap.]
Kidachi, T. (1979a). Systematics ofCalanus in the Japanese waters, with special reference to morphological differentiations ofCalanus in Sagami Bay. Part 1. Aquabiology, Tokyo 2: 9–15 [in Jap.]
Kidachi, T. (1979b). Systematics ofCalanus in the Japanese waters, with special reference to morphological differentiations ofCalanus in Sagami Bay. Part 2. Aquabiology, Tokyo 3: 25–31 [in Jap.]
Koslow, J. A. (1981). Feeding selectivity of schools of northern anchovy,Engraulis mordax, in the Southern California Bight. Fish. Bull. U.S. 79: 143–150
Landry, M. R. (1983). The development of marine calanoid copepods with comments on the isochronal rule. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28: 614–624
Li, S., Fang, J. (1983). The developmental stages ofCalanus sinicus Brodsky. Taiwan Strait 2: 110–118 [in Chin. with Eng. abstract]
Lin, Y., Li, S. (1984). A preliminary study on the life cycle ofCalanus sinicus Brodsky in Xiamen Harbour. J. Xiamen Univ. (nat. Sci.) 23: 111–117 [in Chin. with Eng. abstract]
Lin, Y., Li, S. (1986). Laboratory survey on egg production of the marine planktonic copepodCalanus sinicus in Xiamen Harbour. J. Xiamen Univ. (nat. Sci.) 25: 107–112 [in Chin. with Eng. abstract]
Marcus, N. H. (1985). Endogenous control of spawning in a marine copepod. J. exp. mar. biol. Ecol. 91: 263–269
Marshall, S. M., Orr, A. P. (1955). The biology of a marine copepodCalanus finmarchicus (Gunnerus). Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh
McLaren, I. A. (1963). Effects of temperature on growth of zooplankton and the adaptive value of vertical migration. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 20: 685–727
McLaren, I. A. (1974). Demographic strategy of vertical migration by a marine copepod. Am. Nat. 108: 91–102
Mullin, C. H. (1968). Egg-laying in the planktonic copepodCalanus helgolandicus (Claus). Crustaceana (Suppl.) 1968 (1): 29–34
Ohman, M. D., Frost, B. W., Cohen, E. B. (1983). Reverse diel vertical migration: an escape from invertebrate predators. Science, N.Y. 220: 1404–1407
Peterson, W. P. (1986). Development, growth, and survivorship of the copepodCalanus marshallae in the laboratory. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 29:61–72
Runge, J. A. (1985). Relationship of egg production ofCalanus pacificus to seasonal changes in phytoplankton availability in Puget Sound, Washington. Limnol. Oceangr. 30: 382–396
Russell, R. S. (1927). The vertical distribution of plankton in the sea. Biol. Rev. 2: 213–262
Simard, Y., Lacroix, G., Legendre, L. (1985). In situ twilight grazing rhythm during diel vertical migrations of a scattering layer ofCalanus finmarchicus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30: 598–606
Stearns, D. E., Tester, P. A., Walker, R. L. (1989). Diel changes in the egg production rate ofAcartia tonsa (Copepoda: Calanoida) and related environmental factors in two estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 52: 7–16
Strickland, J. D. H., Parsons, T. R. (1972). A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Fish Res. Bd Can.
Uotani, I., Izuha, A., Asai, K. (1978). Food habit and selectivity of anchovy larvae (Engraulis japonica). Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 44: 427–434 [in Jap. with Eng. abstract]
Uye, S. (1988). Temperature-dependent development and growth ofCalanus sinicus (Copepoda: Calanoida) in the laboratory. Hydrobiologia 167/168: 285–293
Uye, S., Kuwata, H., Endo, T. (1986). Standing stocks and production rates of phytoplankton and planktonic copepods in the Inland Sea of Japan. J. oceanogr. Soc. Japan 42: 421–434
Williams, R. (1985). Vertical distribution ofCalanus finmarchicus andC. helgolandicus in relation to the development of the seasonal thermocline in the Celtic Sea. Mar. Biol. 86: 145–149
Williams, R., Conway, D. V. P. (1980). Vertical distributions ofCalanus finmarchicus andC. helgolandicus (Crustacea: Copepoda). Mar. Biol. 60: 57–61
Williams, R., Conway, D. V. P. (1984). Vertical distribution, and seasonal and diurnal migration ofCalanus helgolandicus in the Celtic Sea. Mar. Biol. 79: 63–73
Williams, R., Conway, D. V. P. (1987). Vertical distribution of eggs, nauplii and copepodites ofCalanus helgolandicus (Copepoda: Crustacea) in the Celtic Sea. Mar. Biol. 96: 247–252
Wright, D., O'Brien, W. J., Vinyard, G. L. (1980). Adaptive value of vertical migration: a simulation model argument for the predation hypothesis. In: Kerfoot, W. C. (ed.) Evolution and ecology of zooplankton communities. University Press New England, London, p. 138–147
Zaret, T. M., Suffern, J. S. (1976). Vertical migration in zooplankton as a predator avoidance mechanism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 21: 804–813
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Anraku, Tokyo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uye, S., Huang, C. & Onbe, T. Ontogenetic diel vertical migration of the planktonic copepodCalanus sinicus in the Inland Sea of Japan. Mar. Biol. 104, 389–396 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314341
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314341