Summary
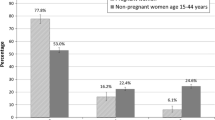
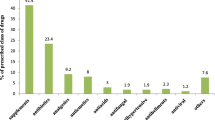
Prescription data have been analysed in order to study drug exposure of women before, during and after pregnancy as compared to non-pregnant controls. During full term pregnancy (n=341) drug exposure increased markedly, mostly due to prescription of drugs such as iron and vitamins. Excluding these drugs, the increase was statistically significant only for one third of the women whose case records revealed some intercurrent disease during pregnancy. Women whose pregnancy ended in a spontaneous abortion (n=29) did not differ significantly from controls in terms of drug exposure before, during or after pregnancy. In an induced abortion group (n=60), drug exposure was more pronounced before pregnancy than in the other pregnant patients or controls. On comparing the drug history obtained from delivery records with that obtained in this study it was found that only diuretics and urinary tract chemotherapeutics had been noted fairly consistently in the former records.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smithells, R. W.: Environmental teratogens of man. Br. med. Bull.32, 27–33 (1976)
Peckham, C. H., King, R. W.: A study of intercurrent conditions observed during pregnancy. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynecol.87, 609–624 (1963)
Forfar, J. O., Nelson, M. M.: Epidemiology of drugs taken by pregnant women: Drugs that may affect the fetus adversely. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.14, 632–642 (1973)
Hill, R. M.: Drugs ingested by pregnant women. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.14, 654–659 (1973)
Medalie, J. H. and others: The use of medicines before and during pregnancy — preliminary results from an epidemiological study of congenital defects. Adv. exp. Med. Biol.27, 481–487 (1972)
Boethius, G., Wiman, F.: Recording of drug prescriptions in the County of Jämtland, Sweden: I. Methodological aspects. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.12, 31–35 (1977)
Kullander, S., Källén, B., Sandahl, B.: Exposure to drugs and other possibly harmful factors during the first trimester of pregnancy. Comparison of two prospective studies performed in Sweden 10 years apart. Acta obstet. gynecol. scand. In press.
Eklund, L. H., Wessling, A.: Personal communication
Kullander, S., Källén, B.: A prospective study of drugs and pregnancy. I. Psychopharmaca. Acta obstet. gynecol. scand.55, 25–33 (1976)
Miller, R. W.: How environmental effects on child health are recognized. Pediatrics53, 792–799 (1974)
Lundborg, P.: Abnormal ontogeny in young rabbits after chronic administration of haloperidol to the nursing mothers. Brain Res.44, 684–687 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boethius, G. Recording of drug prescriptions in the county of Jämtland, Sweden. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 12, 37–43 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561403
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561403