Summary
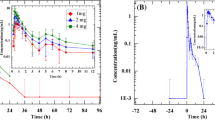
A tablet formulation of nifedipine was given to 8 hospitalized hypertensive men, W.H.O. stage I or II, mean age 45 years. After an initial placebo test, nifedipine 20, 40 or 60 mg was given in random order at 72-h intervals, in a single administration crossover study. The placebo and the active drug were given at 8 a.m. Blood pressure and heart rate were measured twice by the same observer, every 20 min from 7 to 8 a.m., and then hourly until 8 p.m., first in recumbency and again after 1 min of standing upright. Plasma nifedipine was assayed in samples taken hourly from 8 a.m. to noon, every 2 h from noon to 8 p.m., and 24 and 48 h after drug administration. All 3 doses significantly lowered blood pressure; the fall during recumbency was significantly larger (−18%) and lasted longer (12 h) after 60 mg than after 20 mg (−11% and 7 h). All 3 doses caused a similar increase in heart rate (+29 to +38%), which reached its maximum after 2 h and lasted for 5 h. The maximum plasma concentration and the area under the plasma concentration — time curve were dose-dependent despite large inter-subject variation. Absorption, bioavailability and elimination were linear between the 20 and 60 mg doses. Plasma nifedipine levels were strongly correlated with the concomitant decrease in mean arterial blood pressure (r=0.61,p<0.001). Four patients experienced mild side effects (headaches, flushes, drowsiness or weakness). This tablet form of nifedipine has a potent antihypertensive action which lasts longer than that of the capsule presentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki K, Kondo S, Mochizuki A, Yoshida T, Kato SUK, Jakikawa K (1978) Antihypertensive effect of cardiovascular Ca2+-antagonist in hypertensive patients in the absence and presence of beta adrenergic blockade. Am Heart J 96: 218–226
Guazzi MD, Fiorentini C, Olivari MT, Bartorelli A, Necci G, Polese A (1980) Short and long term efficacy of a calcium antagonist agent (nifedipine combined with methyl dopa in the treatment of severe hypertension. Circulation 61:913–919
Horster FA, Duhm B, Maul W, Medenwald H, Patschke K, Wegner LA (1972) Klinische Untersuchungen zur Pharmakokinetik von radioaktiv markiertem 4-(2-Nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarbonsaure-dimethylester. Arzneim Forsch 22:330–334
Jakobsen P, Lederballe Pedersen O, Mickelsen E (1979) Gas chromatographic determination of nifedipine and one of its metabolites using electron capture detection. J Chromatogr 162:81–87
Leary WP, Asmal AC (1979) Treatment of hypertension with verapanil. Curr Ther Res 25:747–752
Lederballe Pedersen O, Mikkelsen E (1978) Acute and chronic effects of nifedipine in arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 14:375–381
Lederballe Pedersen O, Mikkelsen O, Christensen NJ, Kornerup HJ, Pedersen EB (1979) Effect of nifedipine on plasma renin, aldosterone and catecholamines in arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15:235–240
Lederballe Pedersen O, Christensen CK, Mikkelsen E, Ramsch KD (1980a) Relationship between the antihypertensive effect and steady state plasma concentration of nifedipine given alone or in combination with a beta adrenoreceptor blocking agent. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18:287–293
Lederballe Pedersen O, Christensen WJ, Ramsch KD (1980b) Comparison and acute effect of nifedipine in normotensive and hypertensive men. J Cardio Vasc Pharmacol 2:357–366
Menard J, Bertagna X, N'Guyen PT, Degoulet P, Corvol P (1976) Rapid identification of patients with essential hypertension sensitive to acebutolol (a new cardioselective beta-blocker). Am J Med 60:886–890
Murakami MUE, Takekoshi N, Tsuchiya M, Kin T, Onde T, Takeuchi N, Funatsu T, Harai S, Ishise S, Mifune J, Maeda M (1972) Antihypertensive effect of 4(-2′nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyrine-3,5-dicarbonic acid dimethylester (Nifedipine, Bay-a-1040), a new coronary dilator. Jpn Heart J 13:128–135
Olivari MT, Bartorelli C, Polese A, Fiorentini C, Moruzzi F, Guazzi MD (1979) Treatment of hypertension with nifedipine, a calcium antagonist agent. Circulation 59:1056–1062
Patzschke K, Schlossmann K, Horster FA (1975) Nifedipin (Adalat). Pharmakokinetik und Biotransformation. Ther Ber 47:197–203
Ramsch KD (1981) Zur Pharmakokinetik von Nifedipin. Schwerpunkt Medizin 4:55–61
Stone PH, Antman EM, Muller JE, Braunwald E (1980) Calcium channel blocking agents in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. Part II: hemodynamic effects and clinical application. Ann Int Med 93:886–904
Thibonnier M, Bonnet F, Corvol P (1980) Antihypertensive effect of fractionated sublingual administration of nifedipine in moderate essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17:161–164
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design, Vol 7. McGraw Hill, London, pp 514–603
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banzet, O., Colin, J.N., Thibonnier, M. et al. Acute antihypertensive effect and pharmacokinetics of a tablet preparation of nifedipine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24, 145–150 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613808
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613808