Summary
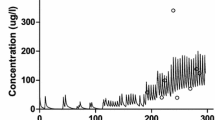
Morphine concentrations in plasma in five patients following intrathecal (i.t.) administration and in five other patients following intravenous (i.v.) administration were measured by a specific RIA sensitive to 0.1 ng/ml. Pharmacokinetic analysis showed a similar apparent total body clearance of morphine following both i.t. and i.v. administration, and complete bioavailability of i.t. morphine to the systemic circulation. This indicates that morphine is probably not metabolised in the CNS and that all of an i.t. dose diffuses from CSF to the plasma compartment. However a marked decrease in the i.t. terminal rate constants, involving a flip-flop phenomenon, contributed to the prolonged terminal half-life of i.t. morphine. The slow diffusion of morphine from the i.t. space to the plasma compartment can account for the prolonged analgesia following i.t. administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chauvin M, Samii K, Scherrmann JM, Sandouk P, Bourdon R, Viars P (1982) Plasma pharmacokinetics of morphine after i.m., extradural and intrathecal administration. Br J Anaesth 54: 843–847
Nordberg G, (1984) Pharmacokinetic aspects of spinal morphine analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scan [Suppl 79] 28: 1–38
Moore RA, Paterson GMC, Bullingham RES, Allen MC, Baldwin D, Mc Quay HJ (1984) Controlled comparison of intrathecal cinchocaine with intrathecal cinchocaine and morphine. Br J Anaesth 56: 837–841
Samii K, Chauvin M, Viars P (1981) Postoperative spinal analgesia with morphine. Br J Anaesth 53: 817–820
Sandouk P (1982) Dosage de la morphine par radioimmunologie et contribution à l'étude de sa pharmacocinétique après administration médullaire. Thèse de Doctorat de 3ème cycle (Sciences Pharmaceutiques) Université René Descartes, Paris, France
Gintzler AR, Mohacsi E, Spector S (1976) Radioimmunoassay for the simultaneous determination of morphine and codeine. Eur J Pharmacol 38: 149–156
Abraham GE (1969) Solid phase radioimmunoassay of oestradiol-17 β. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 29: 866–868
Nielsen-Kudsk F (1983) A microcomputer program in basic for iterative, non-linear data-fitting to pharmacokinetic functions. Int J Biomed Comput 14: 95–107
Wagner JG (1975) Fundamentals of clinical pharmacokinetics. Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamilton, Ill
Dahlstrom B, Tamsen A, Paalzow L, Hartvig P (1982) Patient controlled analgesic therapy, part IV: pharmacokinetics and analgesic plasma concentrations of morphine. Clin Pharmacokinet 7: 266–279
Murphy MR, Hug CC (1981) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous morphine in patients anesthetised with enflurane-nitrous oxide. Anesthesiology 54: 187–192
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1983) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Schill G, Gustavii K (1964) Acid dissociation constants of morphine. Acta Pharm Suec 1: 24–35
Yeh SY (1975) Urinary excretion of morphine and its metabolites in morphine dependent subjects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 192: 201–210
Kaufman JJ, Semo NM, Koski WS (1975) Microelectrometric titration measurement of the pKa's and partition and drug distribution coefficients of narcotics and narcotics antagonists and their pH and temperature dependance. J Med Chem 18: 647–655
Hansch CLA, Elkibs D (1971) Partition coefficients and their uses. Chem Rev 71: 525–555
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandouk, P., Scherrmann, J.M. & Chauvin, M. Rate-limiting diffusion processes following intrathecal administration of morphine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 30, 575–579 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542417
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542417