Summary
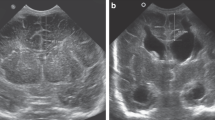
Cranial computed tomography (CT) of 108 cases with dilated lateral ventricles was reviewed to elucidate the relationship between focal vulnerability of developing brain and disproportional dilatation of lateral ventricles. CT findings of 108 cases with symmetrical dilatation of lateral ventricles were classified into three types by morphometry of lateral ventricles: anterior horn predominant type (31 cases), diffuse type (36 cases), posterior horn predominant type (41 cases). Posterior horn predominant type has a tendency to occur in congenital anomalies and premature brain damage, and anterior horn predominant type in infantile brain damage. This disproportional dilatation of anterior or posterior horns suggests a vulnerability of periventricular structure in developing brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benda CE (1940) Microcephaly. Am J Psychiatr 97:1135–1146
Garg BP (1982) Colpocephaly: An error of morphogenesis? Arch Neurol 39:243–246
Fitz CR (1981) Computed tomography in the newborn. In: Korobkin R, Guilleminault C (eds) Progress in perinatal neurology, vol 1. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore London, pp 85–120
Banker BQ, Larroche JC (1962) Periventricular leucomalacia of infancy: a form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol 7:386–410
Shuman RM, Selednik LJ (1980) Periventricular leucomalacia. A one-year autospy study. Arch Neurol 37:231–235
Takashima S, Tanaka K (1978) Development of cerebrovascular architecture and its relationship to periventricular leucomalacia. Arch Neurol 35:11–16
Friede RL (1961) A histochemical study of DPN diaphorase in human white matter with some notes on myelination. J Neurochem 8:17–30
Yakovlev PI, Lecours AR (1967) The myelogenetic cycles of regional maturation of brain. In: Minkowski A (ed) Regional development of the brain in early life. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford Edinburgh, pp 3–70
Takashima S, Becker LE (1983) Developmental changes of glial fibrillary acidic protein in cerebral white matter. Arch Neurol 40:14–18
Takashima S, Armstrong DL, Becker LE (1978) Subcortical leucomalacia. Relationship to cerebral sulcus and its vascular supply. Arch Neurol 35:470–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishimura, M., Ieshima, A., Takashima, S. et al. Focal vulnerability of developing brain: CT studies on disproportionally dilated lateral ventricles. Neuroradiology 28, 30–33 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341762
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341762