Abstract
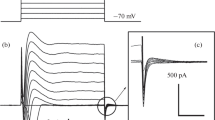
Anion-selective channels from apical membranes of cultured CFPAC-1 cells were isolated and incorporated into giant liposomes for patch clamp recording. Liposomes were formed from L-α-lecithin by a dehydration-hydration method. Ion channels were characterized using the excised inside-out patch clamp configuration. The most commonly observed anion channels were similar to those observed in native epithelial tissues. The linear 20 pS Cl channel had the halide permeability sequence Cl− > I− ≥ Br− > F−, and showed anomalous mole-fraction behavior in solutions containing different proportions of Cl− and F−, ions. The autwardly rectifying Cl− channel had the halide permeability sequence I− > Br− > Cl− > F−, and also showed anomalous molefraction behavior, indicating that both these channels probably contain multi-ion pores. The third, voltage-dependent anion channel showed at least five different substrates, had a conductance of 390 pS in the main state, and showed two types of kinetics, fast (openings and closings < 1 ms), and slow (openings and closings > 1 s). The channel was seen more frequently after reconstitution into giant liposomes than in intact cells. It was not selective amongst the halides, and there was no deviation from a linear dependence of relative current on molar fractions, indicating relatively simple permeation through the pore. Differences in halide permeabilities suggest that different anion channels may be related to different membrane proteins. Comparison with the chloride channel proteins isolated biochemically from epithelial cell membranes is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alton EWF, Manning SD, Schlatter PJ, Geddes DM, Williams AJ (1991) Characterization of a Ca++-dependent anion channel from sheep tracheal epithelium incorporated into planar bilayers. J Physiol 443:137–159
Anderson MP, Sheppard DN, Berrer HA, Welsh MJ (1992) Chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis airway and intestinal epithelia. Am J Physiol 263: L1-L14
Berrier C, Coulombe A, Houssin C, Ghazi A (1992) Fast and slow kinetics of porin channels from Escherichia coli reconstituted into giant liposomes and studied by patch-clamp. FEBS Lett 306:251–256
Bollag DM, Edelstein SJ (1991) Protein Methods, Wiley-Liss, New York
Breuer W (1990) Reconstitution of a kidney chloride channel and its identification by covalent labeling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1922: 229–236
Colquhoun D, Sigworth FJ (1985) Fitting and statistical analysis of single-channel records. In: Sakmann B, Neher E (eds) Single-channel recording, Plenum Press, New York, pp 191–236
Duszyk M, French AS, Man SFP (1990) The 20 pS chloride channel of the human airway epithelium. Biophys J 57:223–230
Duszyk M, French AS, Man SFP (1989) Cystic fibrosis affects chloride and sodium channels in human airway epithelia. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 67:1352–1365
Finn A, Tsai LM, Falk RJ (1989) Monoclonal antibodies to the apical Cl− channel in Necturus gallbladder inhibit the chloride conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7649–7652
Germs RB (1989) Biomembranes, molecular structure and function. Springer, New York, p 208
Halm DR, Frizzell RA (1992) Anion permeation in an apical membrane chloride channel of a secretory epithelial cell. J Gen Physiol 99:339–366
Hanrahan JW, Alles WP, Lewis SA (1985) Single anion-selective channels in basolateral membrane of a mammalian tight epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7791–7795
Hamill OP, Marty A, Nehrer E, Sackman B, Sigworth F, (1981) Improved patch clamp techniques for high resolution current recordings from cells and cell free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hille B (1992) Ion channels of excitable membranes. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass.
Keller BU, Hedrich R, Vaz WLC, Criado M (1988) Single channel recordings of reconstituted ion channel proteins: an improved technique. Pflügers Arch 411:94–100
Kolb HA, Brown C, Murer H (1985) Identification of a voltage-dependent anion channel in the apical membrane of a Cl− secretory epithelium (MDCK). Pflügers Arch 415:262–265
Langridge-Smith JE, Field M, Dubinsky WP (1983) Isolation of transporting plasma membrane vesicles from bovine tracheal epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta 731:318–328
McInnes DA (1939) The principles of electrochemistry. Rheinhold Publ Co, Washington DC
Murer H, Amman E, Biber J, Hopfer U (1976) The surface membrane of the small intestinal epithelial cell. 1. Localization of adenyl cyclase. Biochim Biophys Acta 433:509–519
Neher E (1992) Correction for liquid junction potentials in patch clamp experiments. Methods Enzymol 207:123–131
Nelson D, Tang JM, Palmer L (1984) Single-channel recordings of apical membrane chloride conductance in A6 epithelial cells. J Membr Biol 80:81–89
Neubig RR, Krodel EE, Boyd ND, Cohen JB (1979) Aceylcholine and local anaesthetic binding to Torpedo nicotinic postsynaptic membranes after removal of nonreceptor peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:690–694
Ran S, Benos DJ (1991) Isolation and functional reconstitution of a 38-kDa chloride channel protein from bovine tracheal membranes. J Biol Chem 266:4782–4788
Riquelme G, Lopez E, Garcia-Segura LM, Ferragut JA, Gonzalez-Ros JM (1990) Giant liposomes: a model system in which to obtain patch-clamp recordings of ionic channels. Biochemistry 29:11215–11222
Schoumacher RA, Ram J, Iannuzzi MC, Bradbury NA, Wallace RW, Hon CT, Kelly DR, Schmid SM, Gelder FB, Rado TA, Frizzell RA (1990) A cystic fibrosis pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4012–4016
Schneider G, Cook DI, Gage PW, Young JA (1985) Voltage sensitive, high-conductance chloride channel in the luminal membrane of cultured pulmonary alveolar (type II) cells. Pflügers Arch 404:354–357
Shoemaker RL, Frizzell RA, Dwyer TM, Farley JM (1986) Single chloride channel currents from canine tracheal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 858:235–242
Tsai L-M, Dillard M, Rosenberg RL, Falk RJ, Gaido ML, Finn AL (1991) Reconstitution of an epithelial chloride channel. Conservation of the channel from mudpuppy to man. J Gen Physiol 98:723–750
Vaughan P, French AS (1989) Non-ligand-gated anion channels in muscles and epithelia. Prog Biophys Molec Biol 54:59–79
Wilk-Blaszczak MA, French AS, Man SFP (1992) Halide permeability through 10 pS and 20 pS anion channels in human airway epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1104:160–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: M. Duszyk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duszyk, M., Liu, D., French, A.S. et al. Halide permeation through three types of epithelial anion channels after reconstitution into giant liposomes. Eur Biophys J 22, 5–11 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00205807
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00205807