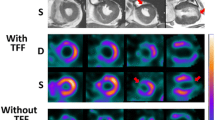
Abstract
Rest and exercise radionuclide ventriculograms were performed in 61 non infarcted, male, patients who underwent cardiac catheterization for chest pain and in 16 normal control subjects. Studies were performed using the first pass method with a fast single crystal gamma camera, which allowed a count rate of 140±19 Kcounts/sec to be reached during left ventricular filling; the count integral on left ventricular area was 10.8±1.6 Kcounts and the maximum count/pixel 155±16. We analyzed sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value of global ejection fraction (EF) and of the regional wall motion in identifying ventricular function abnormalities due to obstructive coronary artery disease. The regional wall motion was evaluated with four functional images: regional ejection fraction (REF), amplitude (A) and phase (PH) from Fourier analysis and systolic transit times (TT). Sensitivity was near 90% for EF, REF, A and TT, while PH was less sensitive (80%); all functional images were more specific (nearly 90%) than EF (80%). Both sensitivity and specificity were lower for the exercise EKG (59% and 63%, respectively) in this patient group. Significant differences between single vessel and multiple vessel disease were also observed either for the EF increase/decrease (-1.34±7.4 and-7.82±9.96; P<0.05) or for the number of segments which developed wall motion abnormalities during exericise (1.22±0.73 and 2.15±1.04; P<0.02). In conclusion, with our method, a fast single crystal gamma camera is suitable for obtaining optimal first pass radionuclide ventriculograms with a count density sufficient either for global or regional left ventricular function evaluation. First pass radionuclide ventriculography seems to provide very high diagnostic accuracy in the detection of cornorary artery disease in non infarcted, male, subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger HJ, Reduto AL, Johnstone DE, Borkowski H, Sands JM, Cohen LS, Langou RA, Gottshalk A, Zaret BL (1979) Global and regional left ventricular response to bicycle exercise in coronary artery disease. Assessment by quantitative radionuclide angiocardiography. Am J Cardiol 66:13–21
Bodenheimer MM, Banka VS, Agarwal JB, Weintraub WS, Helfant RH (1983) Relative value of isotonic and isometric exercise radionuclide angiography to detect coronary heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1:790–796
Borer JS, Bacharach SL, Green MV, Kent KM, Epstein SE, Johnston GS (1977) Real-time radionuclide cineangiography in the noninvasive evaluation of global and regional left ventricular function at rest and during exercise in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 296:839–844
Borer JS, Kent KM, Bacharach SL, Green MV, Rosing DR, Seides SF, Epstein SE, Johnston GS (1979) Sensitivity, specificity and predictive accuracy of radionuclide cineangiography during exercise in patients with coronary artery disease. Comparison with exercise electrocardiography. Circulation 60:572–580
DePace NL, Iskandrian AS, Hakki A, Kane SA, Segal BL (1983) Value of left ventricular ejection fraction during exercise in predicting the extent of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1:1002–1010
Diamond GA, Forrester JS (1981) Analysis of probability as an aid in the clinical diagnosis of coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 300:1350–1358
Freeman MR, Berman DS, Staniloff H, Elkayam U, Maddahi J, Swan HJC, Forrester J (1981) Comparison of upright and supine bicycle exercise in the detection and evaluation of extent of coronary artery disease by equilibrium radionuclide ventriculography. Am Heart J 102:182–188
Gibbons RJ, Lee KL, Cobb F, Jones RH (1981) Ejection fraction response to exercise in patients with chest pain and normal coronary arteriograms. Circulation 64:952–957
Gibbons RJ, Lee KL, Pryor D, Harrell FE, Coleman RE, Cobb FR, Rosati RA, Jones RH (1983) The use of radionuclide angiography in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease — a logistic regression analysis. Circulation 68:740–746
Higginbotham MB, Morris KG, Coleman E, Cobb FR (1984) Sexrelated differences in the normal cardiac response to up-ght exercise. Circulation 70:357–366
Iskandrian AS, Hakki AH (1984) Left ventricular function in patients with coronary heart disease in the presence or absence of angina pecoris during exercise radionuclide ventriculography. Am J Cardiol 53:1239–1243
Jengo JA, Oren V, Conant R, Brizendine M, Nelson T, Uszler M, Mena I (1979) Effects of maximal exercise stress on left ventricular function in patients with coronary artery disease using first pass radionuclide angiocardiography. A rapid noninvasive technique for determining ejection fraction and segmental wall motion. Circulation 59:60–65
Jones RH, McEwan P, Newman GE, Port S, Rerych S, Scholz PM, Upton MT, Peter CA, Austin EH, Leong K, Gibbons RJ, Cobb FR, Coleman RE, Sabiston DC (1981) Accuracy of the diagnosis of coronary artery disease by radionuclide measurement of left ventricular function during rest and exercise. Circulation 64:586–601
La Canna G, Giubbini R, Metra M, Soccisi MC, Bissoli GS, Guerra UP, Arosio G, Dei Cas L (1985) Confronto del valore predittivo dell' angiocardioscintigrafia di primo transito nella diagnosis di malattia coronarica ostruttiva in soggetti di sesso femminile e maschile. Cardiologia [Suppl] 30:10–10
Manayari DE, Kostuk WJ (1983) Left and right ventricular function at rest and during bicycle exercise in the supine and sitting positions in normal subjects and patients with coronary artery disease. Assessment by radionuclide ventriculography. Am J Cardiol 51:36–42
Marshall RC, Wisenberg G, Schelbert HR, Henze E (1981) Effect of oral propranolol on rest, exercise and postexercise left ventricular performance in normal subjects and patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 63:572–583
Nickel O, Schad N, Andrews EJ, Fleming JW, Mello M (1978) Image analysis of the heart action recorded with a high speed multicrystal gamma camera. Med Progr Technol 5:163–169
Osbakken MD, Okada RD, Boucher CA, Strauss HW, Pohost GM (1984) Comparison of exercise perfusion and ventricular function imaging: an analysis of factors affecting the diagnostic accuracy of each technique. J Am Coll Cardiol 3:272–283
Osbakken MD, Boucher CA, Okada RD, Bingham JB, Strauss HW, Pohost GM (1983) Spectrum of global left ventricular responses to supine exercise. Limitation in the use of ejection fraction in identifying patients with coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 51:28–35
Pedroli G, Buraggi G (1983) I controlli di qualità in medicina nuclear — Atti Convegno Nazionale processi di ottimizzazione nella diagnostic con radiazioni ionizzanti: situazione attuale e prospettive future. Roma 25/11/1983, 149
Shen WF, Roubin GS, Hirasowa K, Choong CY-P, Hutton BF, Harris PJ, Fletcher PJ, Kelly DT (1985) Left ventricular volume and ejection fraction response to exercise in chronic congestive heart failure: difference between dilated cardiomyopathy and previous myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 55:1027–1031
Schad N (1977) Non traumatic assessment of left ventricular wall motion and regional stroke volume after myocardial infarction. J Nucl Med 18:333–341
Schad N, Nickel O (1978) Radionuclide angiography of the heart in coronary heart disease: where do we stand? — Cardiovasc Radiol 1:27–35
Schelbert HR, Verba JW, Johnson AD, Brock GW, Alazraki NP, Rose FJ, Ashburn WL (1975) Non traumatic determination of left ventricular ejection fraction by radionuclide angiocardiography. Circulation 51:902–909
Steingart RM, Wexler J, Slagle S, Scheuer J (1984) Radionuclide ventriculographic responses to graded supine and upright exercise: critical role of the Frank-Starling mechanism at submaximal exercise. Am J Cardiol 53:1671–1671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giubbini, R., Metra, M., Guerra, P. et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rest-exercise first pass ventriculography with a fast single crystal gamma camera in detecting coronary artery disease. Eur J Nucl Med 13, 213–220 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252595
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252595