Abstract
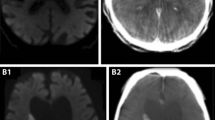
Thallium-201 brain single-photon emission tomography (201Tl-SPET) is widely used to detect viable tumour tissue with increased metabolic activity. When reperfusion takes place early in cerebrovascular lesions of embolic origin, the presence of tissue areas with increased regional blood flow and preserved metabolic activity can also be assumed. In the present study our purpose was to investigate whether or not foci of 201Tl accumulation occur in reperfused areas with sustained morphological integrity indicated by computed tomography (CT) scans not showing hypodensity in the acute or subacute period.In 16 stroke patients with possible cortical embolic infarction, dual 201Tl and technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime (99mTc-HMPAO) SPET was performed in both the acute and the subacute period. 99mTc-HMPAO SPET was performed to detect reperfusion. Follow-up CT scans from the same period were also available. In five cases 99mTc-HMPAO SPET ruled out reperfusion and 201Tl SPET was also negative. In four cases 99mTc-HMPAO studies indicated reperfusion early in the acute phase (24–72 h), and comparative CT, without showing hypodensity in the acute or subacute period, also favoured the possibility of sustained metabolic activity. In these cases 201Tl SPET was negative in both the acute and the subacute period. In seven cases CT already showed necrosis in 99mTc-HMPAO hypoperfused areas in the acute period, with negative results on corresponding 201Tl SPET. Later reperfusion occurred in the subacute period (8–14 days) as indicated by 99mTc-HMPAO SPET, at which time an unexpected focal accumulation of 201Tl was detected. We cannot give any explanation for the findings, but further studies might clarify the matter and improve our knowledge of the precise mechanism of 201Tl uptake under different conditions. Until then the phenomenon should be borne in mind as a possible pitfall when assessing tissue viability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim KT, Black KL, Marciano D, Mazziota JC, Guze BH, Grafton S, Hawkins RA, Becker DP. 201TL SPECT imaging of brain tumours: methods and results. J Nucl Med 1990;7:249–257
Biersack HJ, Grünwald F, Kropp J. Single photon emission computed tomography imaging of brain tumours. Semin Nucl Med 1991;21:2–10
Mountz JM, Raymond PA, McKeever PE, Modell JG, Hood TW, Barthel LK, Stafford-Schuck KA. Specific localization of thallium201 in human high-grade astrocytoma by microautoradiography. Cancer Res 1989;49:4053–4056
Schwartz RB, Carvalho PA, Alexander E, Loeffler JS, Folkerth R, Holman BL. Radiation necrosis vs high-grade recurrent glioma: differentiation by using dual-isotope SPECT with 201Tl and 99mTc-HMPAO. AJNR 1991; 12:1187–1192
Burkard R, Kaiser KP, Wieler H, Klawki P, Linkamp A, Mittelébach L, Goller T. Contribution of thallium-201-SPECT to the grading of tumours alterations of the brain. Neurosurg Rev 1992;15:265–273
Arai M, Hayakawa K, Takhashi T, Kato S, Niibe H, Nagai T, Inoue T, Saski Y, Shibasaki T. Study of 201Tl, 123I-IMP-SPECT before and after radiation therapy of brain tumor. Kaku Igaku 1990;27:279–283
De Jong BM, Van Royen EA. Uptake of SPECT radiopharmaceuticals in neocortical brain cultures. Eur J Nucl Med 1989;15:16–20
Carvalho PA, Schwartz RB, Alexander E 3rd, Leoffler JS, Zimmerman RE, Nagel BL. Extracranial metastatic glioblastoma: appearance on thallium-201-chloride/technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT images. J Nucl Med 1991;32:322–324
Sehweil AM, McKillop JH, Milroy R, Abdel-Dayem HM, Omar YT. Mechanism of 201 Tl uptake in tumours. Eur J Nucl Med 1989;15:376–370
Olsen TS, Lassen NA. A dynamic concept of middle cerebral artery occlusion and cerebral infarction in the acute state based on interpreting severe hyperemia as a sign of embolic migration. Stroke 1984;15:458–468
Sperling B, Lassen NA. Hyperfixation of HMPAO in subacute ischemic stroke leading to spuriously high estimates of cerebral blood flow by SPECT. Stroke 1993;24:193–195
Wang PY, Kao CH, Mui MY, Wang SJ. Leukocyte infiltration in acute hemispheric ischemic stroke. Stroke 1993;24:236–241
Tonami N, Matsuda H, Ooba H, Yokoyama K, Hisada K, Ikeda K, Yamashita J. Thallium 201 accumulation in cerebral candidiasis: unexpected finding on SPECT. Clin Nucl Med 1990; 15:397–400
Vanarthros WJ, Ganz WI, Vanarthros JC, Serafini AN, Tehranzadeh J. Diagnostic uses of nuclear medicine an AIDS. Radiographics 1992;12:731–752
Ando A, Ando I, Katayama M, Sanada S, Hiraki T, Mori H, Tonami N, Hisada K. Biodistribution of 201 Tl in tumor bearing animals and inflammatory lesion induced animals. Eur J Nucl Med 1987;12:567–572
Rubertone JA, Woo DV, Emrich JG, Brady LW. Brain uptake of thallium 201 from the cerebrospinal fluid compartment. J Nucl Med 1993;34:99–103
Traupe H, Heiss WD, Hoffken W, Zülch KJ. Hyperfusion and enhancement in dynamic computed tomography of ischemic stroke patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1979;3:627–632
Bergström M, Ericson K. Compartment analysis of contrast enhancement in brain infarction. J Comput Tomogr 1979;3:234–240
Schauwecker DS, Burt RW, Richmond DB. Comparison of CVA imaging with 99mTc phosphates, 99mTc pertechnetate and computed tomography. Neuroradiology 1981;21:199–205
Welch DM, Coleman RE, Hardin WB. Brain scanning in cerebral vascular disease. Stroke 1975;6:136–141
Campbell JK, Houser OW, Stevens JC, Wahner HW, Baker KL, Folger WN. Computed tomography and radionuclide imaging in the evaluation of ischemic stroke. Radiology 1978; 126:695–702
Gado MH, Coleman ER, Merlis AL, Alderson PO, Lee KS. Comparison of computerised tomography and radionuclide imaging of stroke. Stroke 1976;7:109–113
Chiu LC, McWilliams FE, Christie JH. Comparison of radionuclide and computed tomography scanning in non neoplastic intracranial disease. J Comput Tomogr 1978;2:295–317
Soin JS, Burdine JA. Acute cerebral vascular accident associated with hyperperfusion. Radiology 1976;118:109–112
DiChiro G, Timins EL, Jones AE, Johntston GS, Hammock MK, Swann SJ. Radionuclide scanning and microangiography of evolving and completed brain infarction. Neurology (Minneap) 1974;24:418–423
Levine SR, Helpern JA, Welch KMA, Vande Linde AMQ, Sawaya KL, Brown EE, Ramadan NM, Deveshwar RK, Ordidge RJ. Human focal cerebral ischemic: evaluation of brain pH and energy metabolism with p-31 NMR spectroscopy. Radiology 1992;185:537–544
Syrota A, Samson Y, Boullais C, Wajnberg P, Loc'h C, Crouzel C, Maziere B, Soussaline F, Baron JC. Tomographic mapping of brain intracellular pH and extracellular water space in stroke patients. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1985;5:358–368
Senda M, Alpert NM, Mackey BC, Buxton RB, Correia JA, Weise SB, Ackerman RH, Dorer D, Buonanno FS. Evaluation of the 11CO2 positron emission tomography method for measuring brain pH. J Cereb Blood Metab 1989;9:859–873
Hakim AM, Pokrupa RP, Villanueval J, Diksic M, Evans AC, Thompson CJ, Meyer E, Yamamoto YL, Feindel WH. The effect of spontaneous reperfusion on metabolic function in early human cerebral infarcts. Ann Neurol 1987;21:279–289
Yoshii Y, Satou M, Yamamoto T, Yamada Y, Hyoda A, Nose T, Ishikawa H, Hatakeyama R. The role of thallium-201 single photon emmission tomography in the investigation and characterisation of brain tumours in man and their response to treatment. Eur J Nucl Med 1993;20:39–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernat, I., Toth, G. & Kovács, L. Tumour-like thallium-201 accumulation in brain infarcts, an unexpected finding on single-photon emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 21, 191–195 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188664
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188664