Abstract
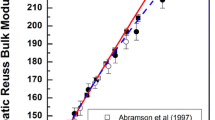
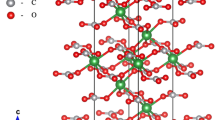
Chondrodite, a member of the humite group of minerals, forms by hydration of olivine and is stable over a range of temperatures and pressures that includes a portion of the uppermost mantle. We have measured the single crystal elastic properties of a natural chondrodite specimen at ambient conditions using Brillouin spectroscopy. The isotropic aggregate bulk (K) and shear (µ) moduli calculated from the single-crystal elastic moduli, Cij, are: KS=118.4(16) GPa and µ=75.6(7) GPa. A comparison of the structures and elasticity of olivine and chondrodite indicate that the replacement of O with (OH,F) in M2+O6 octahedra has a small effect on the elasticity of humite-group minerals. The slightly diminished elastic moduli of humite-group minerals (as compared to olivine) are likely caused by a smaller ratio of strong structural elements (SiO4 tetrahedra) to weaker octahedra, and perhaps a more flexible geometry of edge-sharing MO4(O,OH,F)2 octahedra. In contrast to the humite-olivine group minerals, the incorporation of water into garnets and spineloids leads to a more substantial decrease in the elastic properties of these minerals. This contrasting behavior is due to formation of O4H4 tetrahedra and vacant hydroxyl-bearing octahedra in the garnets and spineloids, respectively. Therefore, the mechanism of incorporation of H/OH into mineral phases, not only degree of hydration, should be taken into account when estimating the effect of water on the elastic properties of minerals. The bulk elastic wave velocities of chondrodite and olivine are very similar. If humite-like incorporation of OH is predominant in the upper mantle, then the reaction of OH with olivine will have a minor or possibly no detectable effect on seismic velocities. Thus, it may be difficult to distinguish chondrodite-bearing rocks from “anhydrous” mantle on the basis of seismically determined velocities for the Earth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 February 1998 / Revised, accepted: 18 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinogeikin, S., Bass, J. Single-crystal elastic properties of chondrodite: implications for water in the upper mantle. Phys Chem Min 26, 297–303 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050189
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050189