Abstract
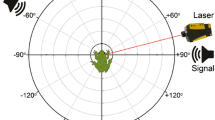
We investigated directionalities of eardrum vibration and auditory nerve response in anesthetized northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens pipiens). Simultaneous measures of eardrum velocities and firing rates from 282 auditory nerve fibers were obtained in response to free-field sounds from eight directions in the horizontal plane. Sound pressure at the external surface of the ipsilateral eardrum was kept constant for each presentation direction (± 0.5 dB). Significant effects of sound direction on eardrum velocity were shown in 90% of the cases. Maximum or minimum eardrum velocity was observed more often when sounds were presented from the lateral and posterior fields, or from the anterior and contralateral fields, respectively. Firing rates of 38% of the fibers were significantly affected by sound direction and maximum or minimum firing rate was observed more frequently when sounds were delivered from the lateral fields, or from the anterior and contralateral fields, respectively. Directionality patterns of eardrum velocity and nerve firing also vary with sound frequency. Statistically significant correlation between eardrum velocity and nerve fiber firing rate was demonstrated in only 45% of the fibers, suggesting that sound transmission to the inner ear through extratympanic pathways plays a non-trivial role in the genesis of directionality of auditory nerve responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CF:
-
characteristic frequency
- SVL:
-
snout-vent length
- TM:
-
tympanic membrane
References
Aertsen AMHJ, Vlaming MSMG, Eggermont JJ, Johannesma PIM (1986) Directional hearing in the grassfrog (Rana temporaria L.). II. Acoustics and modelling of the auditory periphery. Hearing Res 21: 17–40
Anson M, Pinder AC, Keating MJ, Chung SH (1985) Acoustic vibration of the amphibian eardrum studied by white noise analysis and holographic interferometry. J Acoust Soc Am 78: 916–923
Capranica RR (1976) Morphology and physiology of the auditory system. In: Llinas R, Precht W (eds) Frog neurobiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 551–575
Christensen-Dalsgaard J, Narins PM (1993) Sound and vibration sensitivity of VIIIth nerve fibers in the frogs Leptodactylus albilabris and Rana pipiens pipiens. J Comp Physiol A 172: 653–662
Chung SH, Pettigrew A, Anson M (1978) Dynamics of the amphibian middle ear. Nature 272: 142–147
Chung SH, Pettigrew AG, Anson M (1981) Hearing in the frog: dynamics of the middle ear. Proc R Soc Lond B 212: 459–485
Dodd F, Capranica, RR (1992) A comparison of anesthetic agents and their effects on the response properties of the peripheral auditory system. Hearing Res 62: 173–180
Eggermont JJ (1988) Mechanisms of sound localization in anurans. In: Fritzsch B, Ryan MJ, Wilczynski W, Hetherington TE, Walkowiak W (eds) The evolution of the amphibian auditory system. Wiley, New York, pp 307–336
Ehret G, Tautz J, Schmitz B, Narins PM (1990) Hearing through the lungs: Lung-eardrum transmission of sound in the frog Eleutherodactylus coqui. Naturwissenschaften 77: 192–194
Ehret G, Werth EK, Kamada T (1994) The lung-eardrum pathway in three treefrog and four dendrobatid frog species: some properties of sound transmission. J Exp Biol 195: 329–343
Feng AS (1980) Directional characteristics of the acoustic receiver of the leopard frog (Rana pipiens): A study of eighth nerve auditory responses. J Acoust Soc Am 68: 1107–1114
Feng AS (1981) Directional response characteristics of single neurons in the torus semicircularis of the leopard frog (Rana pipiens). J Comp Physiol 144: 419–428
Feng AS (1982) Quantitative analysis of intensity-rate and intensitylatency function in peripheral auditory nerve fibers of northern leopard frogs (Rana p. pipiens). Hearing Res 6: 241–246
Feng AS, Capranica RR (1976) Sound localization in anurans. I. Evidence of binaural interaction in dorsal medullary nucleus of bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). J Neurophysiol 39: 871–881
Feng AS, Capranica RR (1978) Sound localization in anurans. II. Binaural interaction in superior olivary nucleus of the green tree frog (Hyla cinerea). J Neurophysiol 41: 43–54
Feng AS, Shofner WP (1981) Peripheral basis of sound localization in anurans. Acoustic properties of the frog ear. Hearing Res 5: 201–216
Feng AS, Narins PM, Capranica RR (1975) Three populations of primary auditory fibers in the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). J Comp Physiol 100: 221–229
Feng AS, Gerhardt HC, Capranica RR (1976) Sound localization behavior of the green treefrog (Hyla cinerea) and the barking treefrog (H. gratiosa). J Comp Physiol 107: 241–252
Fletcher NH, Thwaites S (1979) Physical models for the analysis of acoustical system in biology. Q Rev Biophys 12: 25–65
Gerhardt HC, Rheinlaender J (1980) Accuracy of sound localization in a miniature dendrobatid frog. Naturwissenschaften 67: 362
Gerhardt HC, Rheinlaender J (1982) Localization of an elevated sound source by the green tree frog. Science 217: 663–664
Gooler DM, Condon CJ, Xu JH, Feng AS (1993) Sound direction influences the frequency-tuning characteristics of neurons in the frog inferior colliculus. J Neurophysiol 69: 1018–1030
Hall JC, Feng AS (1991) Temporal processing in the dorsal medullary nucleus of the northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens pipiens). J Neurophysiol 66: 955–973
Jørgensen MB (1991) Comparative studies of the biophysics of directional hearing in anurans. J Comp Physiol A 169: 591–598
Jørgensen MB, Gerhardt HC (1991) Directional hearing in the gray tree frog Hyla versicolor: Eardrum vibrations and phonotaxis. J Comp Physiol A 169: 177–183
Jørgensen MB, Schmitz B, Christensen-Dalsgaard J (1991) Biophysics of directional hearing in the frog Eleutherodactylus coqui. J Comp Physiol A 168: 223–232
Klump GM, Gerhardt HC (1989) Sound localization in the barking treefrog. Naturwissenschaften 76: 35–37
Lombard RE, Straughan IR (1974) Functional aspects of anuran middle ear structures. J Exp Biol 61: 71–93
Michelsen A, Jørgensen M, Christensen-Dalsgaard J (1986) Directional hearing of awake, unrestrained treefrogs. Naturwissenschaften 73: 682–683
Narins PM, Lewis ER (1984) The vertebrate ear as an exquisite seismic sensor. J Acoust Soc Am 76: 1384–1387
Narins PM, Ehret G, Tautz J (1988) Accessory pathway for sound transfer in a neotropical frog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 1508–1512
Palmer AR, Pinder AC (1984) The directionality of the frog ear described by a mechanical model. J Theor Biol 110: 205–215
Passmore NI, Capranica RR, Telford SR, Bishop PJ (1984) Phonotaxis in the painted reed frog (Hyperolius marmoratus). J Comp Physiol A 154: 189–197
Pinder AC, Palmer AR (1983) Mechanical properties of the frog ear: vibration measurements under free- and closed-field acoustic conditions. Proc R Soc Lond B 219: 371–396
Rheinlaender J, Klump G (1988) Behavioral aspects of sound localization. In: Fritzsch B, Ryan MJ, Wilczynski W, Hetherington TE, Walkowiak W (eds) The evolution of the amphibian auditory system. Wiley, New York, pp 297–305
Rheinlaender J, Gerhardt HC, Yager DD, Capranica RR (1979) Accuracy of phonotaxis by the green treefrog (Hyla cinerea). J Comp Physiol 133: 247–255
Rheinlaender J, Walkowiak W, Gerhardt HC (1981) Directional hearing in the green treefrog: A variable mechanism? Naturwissenschaften 67: 430–431
Ronken DA (1990) Basic properties of auditory-nerve responses from a “simple” ear: The basilar papilla of the frog. Hearing Res 47: 63–82
Ronken DA (1991) Spike discharge properties that are related to the characteristic frequency of single fibers in the frog auditory nerve. J Acoust Soc Am 90: 2428–2440
Schmitz B, White TD, Narins PM (1992) Directionality of phase locking in auditory nerve fibers of the leopard frog Rana pipiens pipiens. J Comp Physiol A 170: 589–604
Vlaming MSMG, Aertsen AMHJ, Epping WJM (1984) Directional hearing in the grass frog (Rana temporaria L.): I. Mechanical vibrations of tympanic membrane. Hearing Res 14: 191–201
White TD, Schmitz B, Narins PM (1992) Directional dependence of auditory sensitivity and frequency selectivity in the leopard frog. J Acoust Soc Am 92: 1953–1691
Wilczynski W, Capranica RR (1984) The auditory system of anuran amphibians. Prog Neurobiol 22: 1–38
Wilczynski W, Resler C, Capranica RR (1987) Tympanic and extratympanic sound transmission in the leopard frog. J Comp Physiol A 161: 659–669
Xu J, Gooler DM, Feng AS (1994) Single neurons in the frog inferior colliculus exhibit direction-dependent frequency selectivity to isointensity tone bursts. J Acoust Soc Am 95: 2160–2170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Ludwig, T.A. & Narins, P.M. Spatial and spectral dependence of the auditory periphery in the northern leopard frog. J Comp Physiol A 178, 159–172 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188159
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188159