Summary
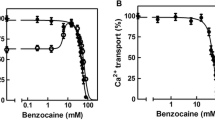
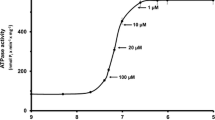
Calcium uptake of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) isolated fromCarcinus skeletal muscle was examined under control conditions and in the presence of 5 mM quinine and 10 mM caffeine. Quinine was without significant effect on SR intrinsic calcium but caffeine caused a release of about 17% of this calcium compartment. Both alkaloids depressed ATP-promoted calcium binding by the SR, caffeine inducing a greater depression of binding. In addition, both alkaloids were able to release calcium from previously loaded SR.
It is concluded that caffeine-induced release of intrinsic calcium may contribute to the rise in myoplasmic calcium associated with caffeine contracture, but caffeine action on SR labile calcium is the major basis for contracture-induction. In the case of quinine, electron microscopic evidence suggests that this drug acts on the mitochondrial calcium compartment of the muscle fibre as well as on the SR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelsson, J., Thesleff, S.: Activation of the contractile mechanism in striated muscle. Acta physiol. scand.44, 55–66 (1958)
Batra, S.: The effects of zinc and lanthanum on calcium uptake by mitochondria and fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog skeletal muscle. J. cell. Physiol.82, 245–256 (1973)
Bittar, E. E., Hift, H., Huddart, H., Tong, E. Y.: The effects of caffeine on sodium transport, membrane potential, mechanical tension and ultrastructure in barnacle muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) (in press) (1974)
Borys, H. K., Karler, R.: Effects of caffeine on the intracellular distribution of calcium in frog sartorius muscle. J. cell. Physiol.78, 387–404 (1971)
Carvalho, A. P.: Effects of potentiators of muscular contraction on binding of cations by sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.51, 427–442 (1968a)
Carvalho, A. P.: Calcium-binding properties of sarcoplasmic reticulum as influenced by ATP, caffeine, quinine and local anesthetics. J. gen. Physiol.52, 622–642 (1968b)
Chiarandini, D. J., Reuben, J. P., Brandt, P. W., Grundfest, H.: Effects of caffeine on crayfish muscle fibres. I. Activation of contraction and induction of Ca spike electrogenesis. J. gen. Physiol.55, 640–664 (1970)
Fuchs, F., Gertz, E. W., Briggs, F. N.: The effect of quinidine on calcium accumulation by isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal and cardiac muscle. J. gen. Physiol.52, 955–968 (1968)
Huddart, H.: Caffeine activation of crab skeletal muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.29, 1031–1038 (1969)
Huddart, H.: The effect of quinine on tension development, membrane potentials and excitation-contraction coupling of crab skeletal muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)216, 641–657 (1971)
Huddart, H.: Factors modifying caffeine and quinine contractures and the recovery of contractility in crab skeletal muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.43A, 369–379 (1972)
Huddart, H., Greenwood, M., Williams, A. J.: The effect of some organo-phosphorous and organochlorine compounds on calcium uptake by sarcoplasmic reticulum isolated from insect and crustacean skeletal muscle. J. comp. Physiol. (in press) (1974)
Huddart, H., Oates, K.: Localization of the intracellular site of action of caffeine on skeletal muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.36, 677–682 (1970)
Isaacson, A., Yamaji, K., Sandow, A.: Quinine contractures and Ca45 movements of frog sartorius muscles as affects by pH. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.171, 36–31 (1970)
Kloot, W. G. van der: The effects of potentiators and of anticholin-esterases on the kinetics of calcium uptake by isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum from the lobster and the rat. Comp. gen. Pharmac.1, 209–220 (1970)
Lehninger, A. L.: Mitochondria and calcium ion transport. Biochem. J.119, 129–138 (1970)
Nakamaru, Y., Schwartz, A.: The influence of hydrogen ion concentration on calcium binding and release by skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.59, 22–32 (1972)
Weber, A.: The mechanism of the action of caffeine on sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.52, 760–772 (1968)
Weber, A., Herz, R.: The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J. gen. Physiol.52, 750–759 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huddart, H., Williams, A.J. The effect of caffeine and quinine on calcium uptake by sarcoplasmic reticulum isolated from crustacean skeletal muscle in relation to the disruption of excitation-contraction coupling. J Comp Physiol B 94, 331–338 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710645
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710645